GraphQL入门指南
Posted 51reboot运维开发
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了GraphQL入门指南相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Introduction
GraphQL is Facebook’s new query language for fetching application data in a uniform way.
GraphQL并不是一个面向图数据库的查询语言,而是一个数据抽象层,包括数据格式、数据关联、查询方式定义与实现等等一揽子的东西。GraphQL也并不是一个具体的后端编程框架,如果将REST看做适合于简单逻辑的查询标准,那么GraphQL可以做一个独立的抽象层,通过对于多个REST风格的简单的接口的排列组合提供更多复杂多变的查询方式。与REST相比,GraphQL定义了更严格、可扩展、可维护的数据查询方式。
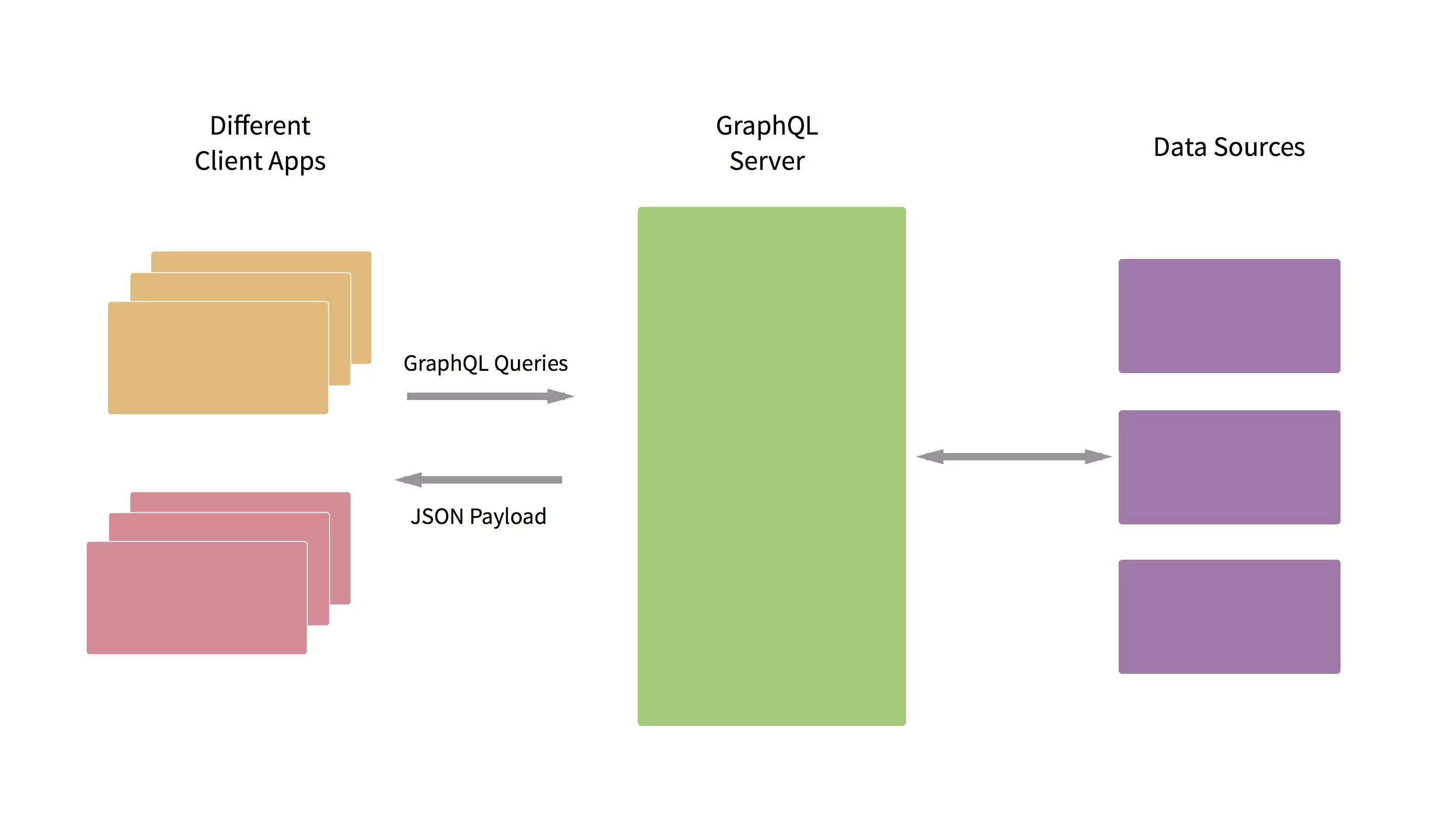
GraphQL与之前Netflix出品的Falcor,都是致力于解决相同的问题:如何有效处理日益增长不断变化的Web/Mobile端复杂的数据需求。笔者一直认为,REST原论文最大的功劳在于前后端分离与无状态请求,而REST的资源化的请求方式只适合面向简单的请求,对于具有复杂资源间关联的请求就有点无能为力。关于这一点,笔者在之前的系列中有过充分的讨论。
GraphQL is a specification.
还是需要强调一点,引入GraphQL并不意味着要像之前从Struts迁移到SpringBoot一样需要去修改你的真实的后端代码,因此GraphQL可以看做一个业务逻辑层灵活有效地辅助工具。这一点也是GraphQL与原来的REST API最大的差别,举例而言:
{
latestPost {
_id,
title,
content,
author {
name
},
comments {
content,
author {
name
}
}
}
}这是一个很典型的GraphQL查询,在查询中指明了需要返回某个Blog的评论与作者信息,一个典型的返回结果譬如:
{
"data": {
"latestPost": {
"_id": "03390abb5570ce03ae524397d215713b",
"title": "New Feature: Tracking Error Status with Kadira",
"content": "Here is a common feedback we received from our users ...",
"author": {
"name": "Pahan Sarathchandra"
},
"comments": [
{
"content": "This is a very good blog post",
"author": {
"name": "Arunoda Susiripala"
}
},
{
"content": "Keep up the good work",
"author": {
"name": "Kasun Indi"
}
}
]
}
}
}而如果采用REST API方式,要么需要前端查询多次,要么需要去添加一个新的接口,专门针对前端这种较为特殊的请求进行响应,而这样又不可避免地导致后端代码的冗余,毕竟很有可能这个特殊的请求与返回哪天就被废了。
Reference
Tutorials & Docs
GraphQL系列教程 (https://learngraphql.com/basics/introduction)
:从REST到GraphQL的思维变迁(https://blog.jacobwgillespie.com/from-rest-to-graphql-b4e95e94c26b#.klx32whu6)
Mechanism:原理介绍
:GraphQL简单的原理介绍,可以有助于理解GraphQL的设计理念与作用(https://medium.com/apollo-stack/graphql-explained-5844742f195e#.rsa2k61tx)
(https://medium.com/apollo-stack/how-do-i-graphql-2fcabfc94a01#.wzt7u46uc)
Practices & Resources
(https://medium.com/the-graphqlhub/graphql-and-authentication-b73aed34bbeb#.qgau20poo)
Comparison:框架对比
(https://medium.com/apollo-stack/graphql-vs-falcor-4f1e9cbf7504#.dngpjldea)
Collection
:一系列的关于GraphQL相关的资源的搜集(https://github.com/chentsulin/awesome-graphql)
Quick Start
Official Quick Start:官方的简单的Quick Start教程
Setup
首先创建项目文件夹:
mkdir graphql-demo
cd graphql-demo然后使用npm安装必要的依赖:
npm init -f
npm install graphql express express-graphql --saveData
作为一个简单的数据服务器,我们仅使用最简单的JSON文件作为数据源:
{
"1": {
"id": "1",
"name": "Dan"
},
"2": {
"id": "2",
"name": "Marie"
},
"3": {
"id": "3",
"name": "Jessie"
}
}Server
一个简单的GraphQL服务器需要创建Scheme以及支持的查询:
// Import the required libraries
var graphql = require('graphql');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var express = require('express');
// Import the data you created above
var data = require('./data.json');
// Define the User type with two string fields: `id` and `name`.
// The type of User is GraphQLObjectType, which has child fields
// with their own types (in this case, GraphQLString).
var userType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'User',
fields: {
id: { type: graphql.GraphQLString },
name: { type: graphql.GraphQLString },
}
});
// Define the schema with one top-level field, `user`, that
// takes an `id` argument and returns the User with that ID.
// Note that the `query` is a GraphQLObjectType, just like User.
// The `user` field, however, is a userType, which we defined above.
var schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({
query: new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
user: {
type: userType,
// `args` describes the arguments that the `user` query accepts
args: {
id: { type: graphql.GraphQLString }
},
// The resolve function describes how to "resolve" or fulfill
// the incoming query.
// In this case we use the `id` argument from above as a key
// to get the User from `data`
resolve: function (_, args) {
return data[args.id];
}
}
}
})
});
express()
.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({ schema: schema, pretty: true }))
.listen(3000);
console.log('GraphQL server running on http://localhost:3000/graphql');然后使用node命令启动服务器:
node index.js如果你直接访问会得到如下反馈:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Must provide query string."
}
]
}Queries
按照如下方式可以创建一个简单的根据ID查询用户的姓名,从中可以看出基本的GraphQL的查询的样式,就是一个JSON的Key-Value对,键值就是查询值:
{
user(id: "1") {
name
}
}返回数据是:
{
"data": {
"user": {
"name": "Dan"
}
}
}如果你希望以GET方式进行查询,可以移除所有的空格,即得到如下方式的请求:
http://localhost:3000/graphql?query={user(id:"1"){name}}Another First GraphQL Server:另一个Step By Step的介绍
Setup an HTTP Server:构建一个HTTP服务器
注意,GraphQL定义了一种通用的数据查询语言,并不一定要基于HTTP协议,不过目前绝大部分应用服务器的交互协议都是HTTP,因此这里也是基于以及 构建一个简单的GraphQL服务器。
$ mkdir graphql-intro && cd ./graphql-intro
$ npm install express --save
$ npm install babel --save
$ touch ./server.js
$ touch ./index.js而核心的服务端代码为:
// index.js
// by requiring `babel/register`, all of our successive `require`s will be Babel'd
require('babel/register');
require('./server.js');
// server.js
import express from 'express';
let app = express();
let PORT = 3000;
app.post('/graphql', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello!');
});
let server = app.listen(PORT, function () {
let host = server.address().address;
let port = server.address().port;
console.log('GraphQL listening at http://%s:%s', host, port);
});直接使用Node命令即可以启动服务器:
$ node index.js
GraphQL listening at http://0.0.0.0:3000可以用Curl进行简单的测试:
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:3000/graphql
Hello!创建一个Schema
现在我们已经创建了一个简单的HTTP Server可以进行交互,下面我们就要为该Server添加GraphQL查询的解析的支持。首先回顾下一个基本的GraphQL的查询请求如下:
query getHighScore { score }该查询意味着某个GraphQL的客户端希望获取getHighScore域的score子域的信息,Fields就是客户端要求GraphQL返回的数据说明,一个Fields也可以包含参数,譬如:
query getHighScores(limit: 10) { score }而我们的GraphQL Server首先需要知道应该如何去解析这样的请求,即需要去定义Schema。构建一个Schema的过程有点类似于构建RESTful的路由树的过程,Schema会包含Server可以返回给前端的Fields以及响应中的数据类型。GraphQL中是采取了静态数据类型,因此Client可以依赖于其发起请求时声明的数据类型。首先我们声明使用Schema所需要的依赖项:
$ npm install graphql --save
$ npm install body-parser --save
$ touch ./schema.js然后我们创建一个GraphQLSchema实例,一般来说我们会将配置放入一个单独的文件夹中:
// schema.js
import {
GraphQLObjectType,
GraphQLSchema,
GraphQLInt
} from 'graphql/lib/type';
let count = 0;
let schema = new GraphQLSchema({
query: new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'RootQueryType',
fields: {
count: {
type: GraphQLInt,
resolve: function() {
return count;
}
}
}
})
});
export default schema;该Schema的定义用通俗地语言表达即是针对查询会返回一个RootQueryType的对象,而每个RootQueryType对象会包含一个整型的count域。
Connect the Schema
在定义好了Schema之后,我们就需要将其应用到HTTP Server中:
import express from 'express';
import schema from './schema';
// new dependencies
import { graphql } from 'graphql';
import bodyParser from 'body-parser';
let app = express();
let PORT = 3000;
// parse POST body as text
app.use(bodyParser.text({ type: 'application/graphql' }));
app.post('/graphql', (req, res) => {
// execute GraphQL!
graphql(schema, req.body)
.then((result) => {
res.send(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2));
});
});
let server = app.listen(PORT, function () {
var host = server.address().address;
var port = server.address().port;
console.log('GraphQL listening at http://%s:%s', host, port);
});所有针对/graphql的查询都会在定义好的Schema下执行,这里我们默认的返回count值,还是使用Curl进行简单的调试可以得到:
$ node ./index.js // restart your server
// in another shell
$ curl -XPOST -H "Content-Type:application/graphql" -d 'query RootQueryType { count }' http://localhost:3000/graphql
{
"data": {
"count": 0
}
}Introspect the Server:获取Server定义的Schema信息
实际上,GraphQL Server也可以返回其定义好的Schema信息:
$ curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type:application/graphql' -d '{__schema { queryType { name, fields { name, description} }}}' http://localhost:3000/graphql
{
"data": {
"__schema": {
"queryType": {
"name": "RootQueryType",
"fields": [
{
"name": "count",
"description": null
}
]
}
}
}
}其使用的查询实际上就是这个样子:
{
__schema {
queryType {
name,
fields {
name,
description
}
}
}
}实际上,我们也可以为每个定义的域添加譬如description, isDeprecated, 以及 deprecationReason这样的描述信息,譬如:
let schema = new GraphQLSchema({
query: new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'RootQueryType',
fields: {
count: {
type: GraphQLInt,
// add the description
description: 'The count!',
resolve: function() {
return count;
}
}
}
})
});那么返回的新的元信息就是:
$ curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type:application/graphql' -d '{__schema { queryType { name, fields { name, description} }}}' http://localhost:3000/graphql
{
"data": {
"__schema": {
"queryType": {
"name": "RootQueryType",
"fields": [
{
"name": "count",
"description": "The count!"
}
]
}
}
}
}Add a Mutation:GraphQL中支持增删改
上文中所讲的都是基于GraphQL定义一个查询方式,而GraphQL也是支持对于数据的增删改,这在GraphQL中称为mutations。Mutations也是一个域,其主要是为了指明某个请求打来的Side Effects,因此大部分的语法还是一致的。Mutations也是需要提供一个返回值的,主要是为了返回你改变的值以供验证修改是否成功。
let schema = new GraphQLSchema({
query
mutation: new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'RootMutationType',
fields: {
updateCount: {
type: GraphQLInt,
description: 'Updates the count',
resolve: function() {
count += 1;
return count;
}
}
}
})
});对应的查询方式就是:
$ curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type:application/graphql' -d 'mutation RootMutationType { updateCount }' http://localhost:3000/graphql
{
"data": {
"updateCount": 1
}
}GraphiQL
graphiql-graphql-s-killer-app (https://medium.com/the-graphqlhub/graphiql-graphql-s-killer-app-9896242b2125#.gork8qie3)
Reboot 课程升级了:三个课程均有升级,全新开班日期已定。
“点击原文”或回复“课程”,即可获取课程表和开班时间。 欢迎咨询 QQ:279312229

以上是关于GraphQL入门指南的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章