c语言怎么用文件保存和读取 结构体数组/
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了c语言怎么用文件保存和读取 结构体数组/相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
txt
#include <stdio.h>int main()
struct test
int a;
char s[10] ;
double d ;
tr[3] , tw[3] =
1,"hello1" , 100 ,
2,"hello2" , 90,
3,"hello3", 200
; //定义一个结构体数组
FILE *fp ;
fp=fopen("struct.dat" , "wb" );
if ( fp == NULL )
return -1 ;
fwrite( (char*)tw , sizeof(struct test), 3 , fp ); //将数组写入文件
fclose(fp);
//以上完成写操作
fp=fopen("struct.dat" , "rb" );
if ( fp == NULL )
return -1 ;
fread( (char*)tr , sizeof(struct test), 3 , fp ); //从文件中读三个结构体的数据,也可以一个一个的读
fclose(fp);
//输出读到的数据
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++ )
printf("%d %s %lf\n" , tr[i].a , tr[i].s, tr[i].d );
return 0;
参考技术A 结构体数据的保存通常以二进制形式进行.
FILE *fw = fopen(filename,"wb");
写函数是fwrite(&structdata,sizeof(structdata),1,fw);
FILE *fr = fopen(filename,"rb");
读函数是fread(*structdata,sizeof(structdata),1,fr);
每次读写都是一个完整的结构体数据。本回答被提问者采纳 参考技术B 文本方式读写
#include "stdio.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 5
struct student
char ID[10];
char Name[12];
int Score;
stud[SIZE];
void read()
FILE *fp;
int i;
if((fp=fopen("score.txt","rt"))==NULL)
printf("cannot open file\n");
return;
for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++)
fscanf(fp,"%s %s %d\n",stud[i].ID,stud[i].Name,&stud[i].Score);
fclose(fp);
void save()
FILE *fp;
int i;
if((fp=fopen("score.txt","wt"))==NULL)
printf("cannot open file\n");
return;
for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++)
fprintf(fp,"%-10s%-12s%d\n",stud[i].ID,stud[i].Name,stud[i].Score);
fclose(fp);
void main()
read();
save();
追问
&stud[i].Score 为什么它要加个&
追答因为是整数(以及浮点数)
参考技术C fread/fwrite,里面是读取/写入块,一个块多少字节,你可以把一个块想象成为一个结构,数量就是数组C语言 怎么把文件中的信息储存到结构体数组中
要把这个文件中的数据保存到结构体数组中
我是这么写的
输出为什么是这个

总体写得不错,问题出在你的
fscanf和fprintf函数参数传递错误了
#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"
struct s
int id;
char name[10];
int co1;
int co2;
int co3;
int co4;
;
int main()
int i=0,count;
struct s st[10];
char fname[10],ch;
FILE *infile,*outfile;
printf("please input data file name:\\n");
scanf("%s",fname);
infile=fopen(fname,"r");
outfile=fopen("output.txt","w");
if(infile==NULL)
printf("\\nFailed to open the file");
exit(1);
fscanf(infile,"%d",&count);
while(i<count)
fscanf(infile,"%d %s %d %d %d %d\\n",&(st[i].id),st[i].name,&(st[i].co1),&(st[i].co2),&(st[i].co3),&(st[i].co4));
fprintf(outfile,"%d %s %d %d %d %d\\n",st[i].id,st[i].name,st[i].co1,st[i].co2,st[i].co3,st[i].co4);
i++;
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
首先,你的name是结构体中的字符数组,fscanf要传入的应该是存储字符的地址,所以直接是数组名name就行
第二,fprintf你要写入文件的数据,应该是真正的数据本身,不是数据的地址,所以应该将变量前的取地址符全去掉就好,
第三,注意加好换行符\\n
结果:
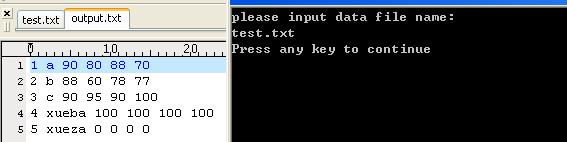
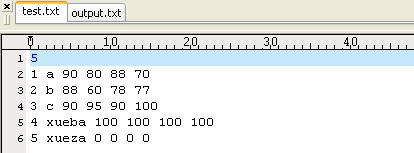
text.txt中内容就是output.txt中的内容
以上是关于c语言怎么用文件保存和读取 结构体数组/的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章