Hystrix执行原理
Posted 程序员泥瓦匠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Hystrix执行原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前奏
Hystrix的常规使用姿势
@Test
public void test_run(){
String s = new CommandHelloWorld("Bob").execute();
System.out.println(s);
}
我们的command在new的时候发生了什么?execute()是如何执行的?execute执行失败或者超时如何fallback?
一、PREPARE 初始化
当我们new XXCommand()的时候,大部分的工作都是在 AbstractCommand完成
protected AbstractCommand(HystrixCommandGroupKey group, HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixCircuitBreaker circuitBreaker, HystrixThreadPool threadPool,
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter commandPropertiesDefaults, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter threadPoolPropertiesDefaults,
HystrixCommandMetrics metrics, TryableSemaphore fallbackSemaphore, TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore,
HystrixPropertiesStrategy propertiesStrategy, HystrixCommandExecutionHook executionHook) {
this.commandGroup = initGroupKey(group);
this.commandKey = initCommandKey(key, getClass());
this.properties = initCommandProperties(this.commandKey, propertiesStrategy, commandPropertiesDefaults);
this.threadPoolKey = initThreadPoolKey(threadPoolKey, this.commandGroup, this.properties.executionIsolationThreadPoolKeyOverride().get());
this.metrics = initMetrics(metrics, this.commandGroup, this.threadPoolKey, this.commandKey, this.properties);
this.circuitBreaker = initCircuitBreaker(this.properties.circuitBreakerEnabled().get(), circuitBreaker, this.commandGroup, this.commandKey, this.properties, this.metrics);
this.threadPool = initThreadPool(threadPool, this.threadPoolKey, threadPoolPropertiesDefaults);
//Strategies from plugins
this.eventNotifier = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getEventNotifier();
this.concurrencyStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy();
HystrixMetricsPublisherFactory.createOrRetrievePublisherForCommand(this.commandKey, this.commandGroup, this.metrics, this.circuitBreaker, this.properties);
this.executionHook = initExecutionHook(executionHook);
this.requestCache = HystrixRequestCache.getInstance(this.commandKey, this.concurrencyStrategy);
this.currentRequestLog = initRequestLog(this.properties.requestLogEnabled().get(), this.concurrencyStrategy);
/* fallback semaphore override if applicable */
this.fallbackSemaphoreOverride = fallbackSemaphore;
/* execution semaphore override if applicable */
this.executionSemaphoreOverride = executionSemaphore;
}
可以很清晰的看到,这里面在进行command配置装载、线程池配置装载及线程池的创建、指标搜集器、熔断器的初始化等等。
//HystrixCommandMetrics
ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCommandMetrics> metrics = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCommandMetrics>();
//HystrixThreadPoolDefault
final static ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixThreadPool> threadPools = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixThreadPool>();
//com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCircuitBreaker.Factory
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCircuitBreaker> circuitBreakersByCommand = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCircuitBreaker>();
除HystrixCommand每次都需要重新建立,其它基本都以commandKey维护着配置,熔断器,指标的单例而线程池则以threadkey进场存储。
我们可以了了解下Hystrix的线程池如何管理 创建线程调用 HystrixThreadPool.Factory.getInstance
static HystrixThreadPool getInstance(HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter propertiesBuilder) {
// get the key to use instead of using the object itself so that if people forget to implement equals/hashcode things will still work
String key = threadPoolKey.name();
// this should find it for all but the first time
HystrixThreadPool previouslyCached = threadPools.get(key);
if (previouslyCached != null) {
return previouslyCached;
}
// if we get here this is the first time so we need to initialize
synchronized (HystrixThreadPool.class) {
if (!threadPools.containsKey(key)) {
threadPools.put(key, new HystrixThreadPoolDefault(threadPoolKey, propertiesBuilder));
}
}
return threadPools.get(key);
}
从缓存中以threadPoolKey获取线程池,获取不到则 调用 newHystrixThreadPoolDefault新建
public HystrixThreadPoolDefault(HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter propertiesDefaults) {
this.properties = HystrixPropertiesFactory.getThreadPoolProperties(threadPoolKey, propertiesDefaults);
HystrixConcurrencyStrategy concurrencyStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy();
this.queueSize = properties.maxQueueSize().get();
this.metrics = HystrixThreadPoolMetrics.getInstance(threadPoolKey,
concurrencyStrategy.getThreadPool(threadPoolKey, properties),
properties);
this.threadPool = this.metrics.getThreadPool();
this.queue = this.threadPool.getQueue();
/* strategy: HystrixMetricsPublisherThreadPool */
HystrixMetricsPublisherFactory.createOrRetrievePublisherForThreadPool(threadPoolKey, this.metrics, this.properties);
}
注意
this.metrics = HystrixThreadPoolMetrics.getInstance(threadPoolKey,concurrencyStrategy.getThreadPool(threadPoolKey, properties),properties);
其中 concurrencyStrategy.getThreadPool, HystrixConcurrencyStrategy就是hystrix的线程创建策略者
真正的创建线程执行 HystrixConcurrencyStrategy#getThreadPool
public ThreadPoolExecutor getThreadPool(final HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties) {
.....各种配置,此处代码省略......
if (allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize) {
final int dynamicMaximumSize = threadPoolProperties.maximumSize().get();
if (dynamicCoreSize > dynamicMaximumSize) {
logger.error("Hystrix ThreadPool configuration at startup for : " + threadPoolKey.name() + " is trying to set coreSize = " +
dynamicCoreSize + " and maximumSize = " + dynamicMaximumSize + ". Maximum size will be set to " +
dynamicCoreSize + ", the coreSize value, since it must be equal to or greater than the coreSize value");
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(dynamicCoreSize, dynamicCoreSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES, workQueue, threadFactory);
} else {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(dynamicCoreSize, dynamicMaximumSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES, workQueue, threadFactory);
}
} else {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(dynamicCoreSize, dynamicCoreSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES, workQueue, threadFactory);
}
}
这里调用java JUC原生的 ThreadPoolExecutor创建线程
二、Observable 大串烧
Hystrix的执行利用RxJava,组合了很多的Observable,形成一个Observable,和传统的调用链相比更加简洁。
三、各色Observable显神通
3.1.command 状态位
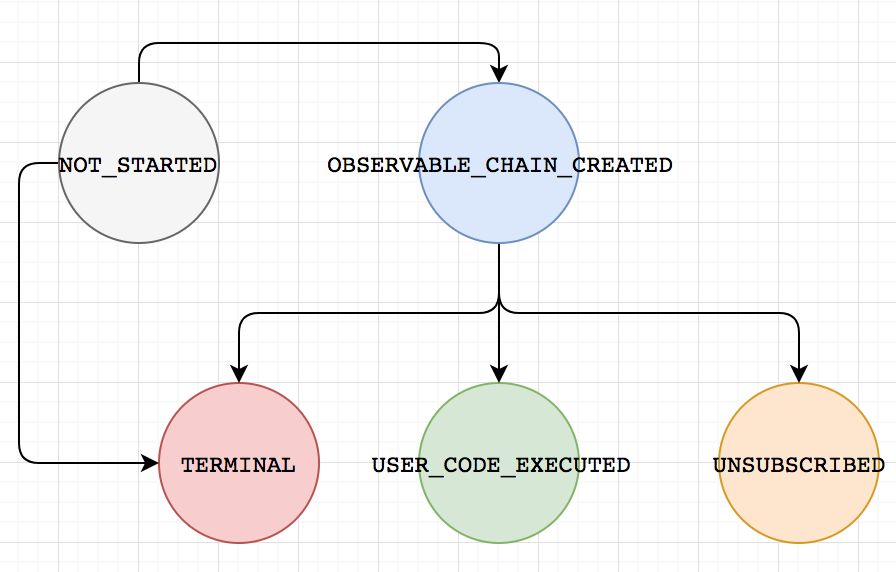
toObservable第一个observable,在下一个chain之前,会更改HystrixCommand状态位OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATEDtoObservabledoOnTerminate,探测到terminate时,会将HystrixCommand更改为TERMINALexecuteCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation在开始执行的时候会更改HystrixCommand更改为USER_CODE_EXECUTEDtoObservabledoOnUnsubscribe,探测到terminate时,会将HystrixCommand更改为UNSUBSCRIBED
3.2.executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation
分配执行线程,维护线程状态
private Observable<R> executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
if (properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get() == ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD) {
// mark that we are executing in a thread (even if we end up being rejected we still were a THREAD execution and not SEMAPHORE)
return Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call() {
.....省略干扰代码.....
if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED)) {
return Observable.error(new IllegalStateException("execution attempted while in state : " + commandState.get().name()));
}
if (isCommandTimedOut.get() == TimedOutStatus.TIMED_OUT) {
// the command timed out in the wrapping thread so we will return immediately
// and not increment any of the counters below or other such logic
return Observable.error(new RuntimeException("timed out before executing run()"));
}
if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.STARTED)) {
try {
.....省略干扰代码.....
return getUserExecutionObservable(_cmd);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
return Observable.error(ex);
}
} else {
//command has already been unsubscribed, so return immediately
return Observable.error(new RuntimeException("unsubscribed before executing run()"));
}
}
}).doOnTerminate(new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.STARTED, ThreadState.TERMINAL)) {
handleThreadEnd(_cmd);
}
if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.TERMINAL)) {
//if it was never started and received terminal, then no need to clean up (I don't think this is possible)
}
//if it was unsubscribed, then other cleanup handled it
}
}).doOnUnsubscribe(new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.STARTED, ThreadState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) {
handleThreadEnd(_cmd);
}
if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) {
//if it was never started and was cancelled, then no need to clean up
}
//if it was terminal, then other cleanup handled it
}
}).subscribeOn(threadPool.getScheduler(new Func0<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean call() {
return properties.executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnTimeout().get() && _cmd.isCommandTimedOut.get() == TimedOutStatus.TIMED_OUT;
}
}));
} else {
.....省略干扰代码.....
}
}
具体逻辑 1.判断隔离策略,如果是Semaphore 信号量则在当前线程上执行,否则进入线程分配逻辑 2.更改HystrixCommand的状态 USER_CODE_EXECUTED 3.判断HystrixCommand超时状态,如果已经超时则抛出异常 4.更改当前command的线程执行状态为 STARTED 5.调用 getUserExecutionObservable 执行具体逻辑 6. doOnTerminate 当Observale执行完毕后(HystrixCommand可能失败也可能执行成功),此时的线程状态可能有两种分别是 STARTED 和 NOT_USING_THREAD , 然后更改线程状态为 TERMINAL 7. doOnUnsubscribe 当Observable被取消订阅,更改线程状态为 TERMINAL 8. subscribeOn 指定scheduler,这里Hystrix实现了自己的scheduler,在scheduler的worker指定线程池,在配置线程之前会重新加载线程池配置(这里是Rxjava的东西,暂时大家可以粗略的认为这里就是指定线程池,然后把要执行的任务扔到这个线程池里)
@Override
public Scheduler getScheduler(Func0<Boolean> shouldInterruptThread) {
touchConfig();
return new HystrixContextScheduler(HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy(), this, shouldInterruptThread);
}
// allow us to change things via fast-properties by setting it each time
private void touchConfig() {
final int dynamicCoreSize = properties.coreSize().get();
final int configuredMaximumSize = properties.maximumSize().get();
int dynamicMaximumSize = properties.actualMaximumSize();
final boolean allowSizesToDiverge = properties.getAllowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize().get();
boolean maxTooLow = false;
if (allowSizesToDiverge && configuredMaximumSize < dynamicCoreSize) {
//if user sets maximum < core (or defaults get us there), we need to maintain invariant of core <= maximum
dynamicMaximumSize = dynamicCoreSize;
maxTooLow = true;
}
// In JDK 6, setCorePoolSize and setMaximumPoolSize will execute a lock operation. Avoid them if the pool size is not changed.
if (threadPool.getCorePoolSize() != dynamicCoreSize || (allowSizesToDiverge && threadPool.getMaximumPoolSize() != dynamicMaximumSize)) {
if (maxTooLow) {
logger.error("Hystrix ThreadPool configuration for : " + metrics.getThreadPoolKey().name() + " is trying to set coreSize = " +
dynamicCoreSize + " and maximumSize = " + configuredMaximumSize + ". Maximum size will be set to " +
dynamicMaximumSize + ", the coreSize value, since it must be equal to or greater than the coreSize value");
}
threadPool.setCorePoolSize(dynamicCoreSize);
threadPool.setMaximumPoolSize(dynamicMaximumSize);
}
threadPool.setKeepAliveTime(properties.keepAliveTimeMinutes().get(), TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
touchConfig 执行具体的线程池参数调整。
从上面的过程也能发现,该observable也是维护线程状态的地方,线程的状态变更见下图
3.3.getUserExecutionObservable
执行具体业务逻辑
private Observable<R> getUserExecutionObservable(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
Observable<R> userObservable;
try {
userObservable = getExecutionObservable();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// the run() method is a user provided implementation so can throw instead of using Observable.onError
// so we catch it here and turn it into Observable.error
userObservable = Observable.error(ex);
}
return userObservable
.lift(new ExecutionHookApplication(_cmd))
.lift(new DeprecatedOnRunHookApplication(_cmd));
}
userObservable=getExecutionObservable(); 由HystrixCommand自己实现
//HystrixCommand
final protected Observable<R> getExecutionObservable() {
return Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call() {
try {
return Observable.just(run());
} catch (Throwable ex) {
return Observable.error(ex);
}
}
}).doOnSubscribe(new Action0() {
@Override
public void call() {
// Save thread on which we get subscribed so that we can interrupt it later if needed
executionThread.set(Thread.currentThread());
}
});
}
这里看到 run()应该就明白了,就是我们自己的业务代码 CommandHelloWorld去实现的。
3.4.getFallbackOrThrowException
当executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation探测到异常时触发该Observable。getFallbackOrThrowException里具体fallback执行看 executeCommandAndObserve。
private Observable<R> executeCommandAndObserve(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
.....省略干扰代码.....
final Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>> handleFallback = new Func1<Throwable, Observable<R>>() {
.....省略干扰代码.....
};
.....省略干扰代码.....
Observable<R> execution;
if (properties.executionTimeoutEnabled().get()) {
execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd)
.lift(new HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator<R>(_cmd));
} else {
execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd);
}
return execution.doOnNext(markEmits)
.doOnCompleted(markOnCompleted)
.onErrorResumeNext(handleFallback)
.doOnEach(setRequestContext);
}
doErrorResumeNext 会触发下一个 handleFallback。
private Observable<R> getFallbackOrThrowException(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd, final HystrixEventType eventType, final FailureType failureType, final String message, final Exception originalException) {
....省略干扰代码....
if (isUnrecoverable(originalException)) {
....省略干扰代码....
} else {
....省略干扰代码....
if (properties.fallbackEnabled().get()) {
....省略干扰代码....
Observable<R> fallbackExecutionChain;
// acquire a permit
if (fallbackSemaphore.tryAcquire()) {
try {
if (isFallbackUserDefined()) {
executionHook.onFallbackStart(this);
fallbackExecutionChain = getFallbackObservable();
} else {
//same logic as above without the hook invocation
fallbackExecutionChain = getFallbackObservable();
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//If hook or user-fallback throws, then use that as the result of the fallback lookup
fallbackExecutionChain = Observable.error(ex);
}
return fallbackExecutionChain
.doOnEach(setRequestContext)
.lift(new FallbackHookApplication(_cmd))
.lift(new DeprecatedOnFallbackHookApplication(_cmd))
.doOnNext(markFallbackEmit)
.doOnCompleted(markFallbackCompleted)
.onErrorResumeNext(handleFallbackError)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
} else {
return handleFallbackRejectionByEmittingError();
}
} else {
return handleFallbackDisabledByEmittingError(originalException, failureType, message);
}
}
}
这里优先几个步骤 1.判断异常是否是能走fallback处理,不能则抛出HystrixRuntimeException 2.判断配置是否开启允许fallback,开启,则进入 getFallbackObservable(),而该方法具体有HystrixCommand实现,调用的则是用户的Command的fallback方法,如果调用方没有覆盖该方法,则会执行HystrixCommand的fallback方法,抛出未定义fallback方法的异常
protected R getFallback() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("No fallback available.");
}
@Override
final protected Observable<R> getFallbackObservable() {
return Observable.defer(new Func0<Observable<R>>() {
@Override
public Observable<R> call() {
try {
//调用方 fallback逻辑
return Observable.just(getFallback());
} catch (Throwable ex) {
return Observable.error(ex);
}
}
});
}
相关热门推荐文章:
长按二维码,扫扫关注哦
✬如果你喜欢这篇文章,欢迎分享和点赞✬
以上是关于Hystrix执行原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章