统计|用R语言做Bootstrapping
Posted 52Psychology
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了统计|用R语言做Bootstrapping相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Bootstrapping
Nonparametric Bootstrapping
The boot package provides extensive facilities for bootstrapping and related resampling methods. You can bootstrap a single statistic (e.g. a median), or a vector (e.g., regression weights). This section will get you started with basic nonparametric bootstrapping.
The main bootstrapping function is boot( ) and has the following format:
bootobject <- boot(data= , statistic= , R=, ...) where
| parameter | description |
| data | A vector, matrix, or data frame |
| statistic | A function that produces the k statistics to be bootstrapped (k=1 if bootstrapping a single statistic). The function should include an indices parameter that the boot() function can use to select cases for each replication (see examples below). |
| R | Number of bootstrap replicates |
| ... | Additional parameters to be passed to the function that produces the statistic of interest |
boot( ) calls the statistic function R times. Each time, it generates a set of random indices, with replacement, from the integers 1:nrow(data). These indices are used within the statistic function to select a sample. The statistics are calculated on the sample and the results are accumulated in the bootobject. The bootobject structure includes
| element | description |
| t0 | The observed values of k statistics applied to the orginal data. |
| t | An R x k matrix where each row is a bootstrap replicate of the k statistics. |
You can access these as bootobject$t0 and bootobject$t.
Once you generate the bootstrap samples, print(bootobject) and plot(bootobject) can be used to examine the results. If the results look reasonable, you can use boot.ci( )function to obtain confidence intervals for the statistic(s).
The format is
boot.ci(bootobject, conf=, type= ) where
| parameter | description |
| bootobject | The object returned by the boot function |
| conf | The desired confidence interval (default: conf=0.95) |
| type | The type of confidence interval returned. Possible values are "norm", "basic", "stud", "perc", "bca" and "all" (default: type="all") |
Bootstrapping a Single Statistic (k=1)
The following example generates the bootstrapped 95% confidence interval for R-squared in the linear regression of miles per gallon (mpg) on car weight (wt) and displacement (disp). The data source is mtcars. The bootstrapped confidence interval is based on 1000 replications.
# Bootstrap 95% CI for R-Squared
library(boot)
# function to obtain R-Squared from the data
rsq <- function(formula, data, indices) {
d <- data[indices,] # allows boot to select sample
fit <- lm(formula, data=d)
return(summary(fit)$r.square)
}
# bootstrapping with 1000 replications
results <- boot(data=mtcars, statistic=rsq,
R=1000, formula=mpg~wt+disp)
# view results
results
plot(results)
# get 95% confidence interval
boot.ci(results, type="bca")
Bootstrapping several Statistics (k>1)
In example above, the function rsq returned a number and boot.ci returned a single confidence interval. The statistics function you provide can also return a vector. In the next example we get the 95% CI for the three model regression coefficients (intercept, car weight, displacement). In this case we add an index parameter to plot( ) and boot.ci( ) to indicate which column in bootobject$t is to analyzed.
# Bootstrap 95% CI for regression coefficients
library(boot)
# function to obtain regression weights
bs <- function(formula, data, indices) {
d <- data[indices,] # allows boot to select sample
fit <- lm(formula, data=d)
return(coef(fit))
}
# bootstrapping with 1000 replications
results <- boot(data=mtcars, statistic=bs,
R=1000, formula=mpg~wt+disp)
# view results
results
plot(results, index=1) # intercept
plot(results, index=2) # wt
plot(results, index=3) # disp
# get 95% confidence intervals
boot.ci(results, type="bca", index=1) # intercept
boot.ci(results, type="bca", index=2) # wt
boot.ci(results, type="bca", index=3) # disp
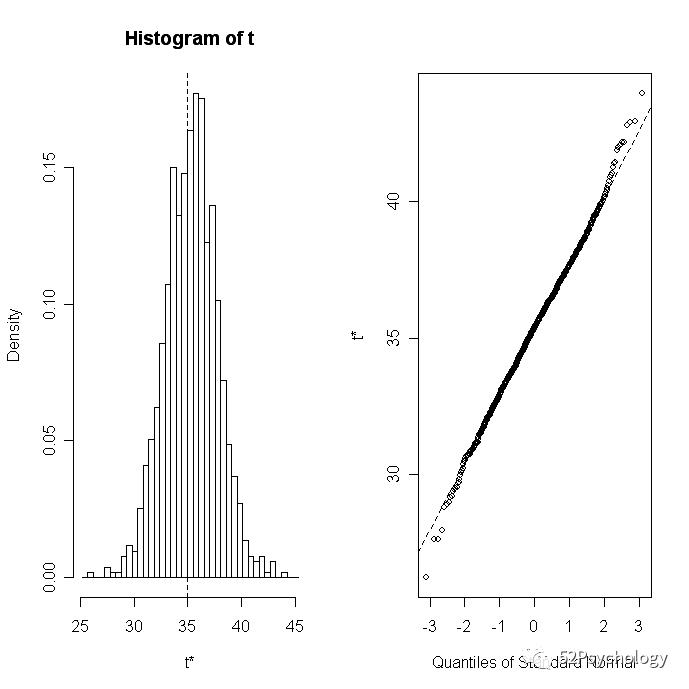
Going Further
The boot( ) function can generate both nonparametric and parametric resampling. For the nonparametric bootstrap, resampling methods include ordinary, balanced, antithetic and permutation. For the nonparametric bootstrap, stratified resampling is supported. Importance resampling weights can also be specified.
The boot.ci( ) function takes a bootobject and generates 5 different types of two-sided nonparametric confidence intervals. These include the first order normal approximation, the basic bootstrap interval, the studentized bootstrap interval, the bootstrap percentile interval, and the adjusted bootstrap percentile (BCa) interval.
Look at help(boot), help(boot.ci), and help(plot.boot) for more details.
编辑:石星琦
wechat ID:xingqi_star
以上是关于统计|用R语言做Bootstrapping的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
R语言boot包中的boot函数格式以及参数说明boot.ci函数格式以及参数说明使用boot包进行自助法Bootstrapping分析的步骤计算统计量或者统计向量的置信区间
R语言置换检验(permutation tests响应变量是否独立于组两个数值变量是独立的吗两个分类变量是独立的吗)置换检验的基本步骤R语言自助法Bootstrapping计算置信区间
R语言使用caret包中的createResample函数进行机器学习数据集采样数据集有放回的采样(bootstrapping)