科技面面观 | Block Chain
Posted Interpretime
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了科技面面观 | Block Chain相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
资料来源:TED | Youtube | Wikipedia
整合:Yang
校对: Lu
阅读时间:5 min
学习时间:3.5 hr
Blockchain
Block Chain and
Future Economy
本期我们把目光转向“科技与金融”领域的一个热点话题 “区块链 (Block Chain) ”;
优秀的译员一定具备Broad Knowledge Base; 这些抽象的概念和技术原理看似“无用”,但是尝试接触不同领域的知识,会对我们的Cognitive Map产生非常积极的影响,Life-long Learning的意义大概也就在此。
--Near Perfection
*事实证明,对待知识应该常怀有敬畏之心,查阅、梳理相关知识的时候,我才恍然大悟,区块链背后所用的技术就是本科“数据结构”这门课所学的知识啊啊啊...不过今天我们主要来点相对轻松的内容,主要跟大家分享一些相关术语、一个Ted演讲(可以做交传练习)、一个YouTube小视频(快速了解技术原理)
Terms and Expression
Cryptography 密码学;密码系统
Decentralized 去中心化
Fiat currency 不兑现纸币
Digital currency 数字货币
Cryptocurrency 加密货币
Ledger 分类账簿
Remittance 汇款(兑)
Intermediary / middleman 中间人
Peer-to-peer networks P2P网络
Internet of Things 物联网
Fintech 金融技术
Encrypted 加密
Immutability 不可更改性
Teller 出纳员
Avatar 化身
Collateralize 作抵押
Double spend 双花
Time-stamped 时间戳
Registry 记录簿
Tamper 篡改
Escrow 第三方保管人
Recourse 赔索
Custodianship 管理人
Attestation 证词
Account level 账户等级
Visualise Transaction 可视化交易
Verification 验证
Token 代币
System security 系统安全
Node 节点
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) 安全散列算法
Raw value 原始价格
Random wallets 随机钱包
Eavesdropper 窃听者
Architecture 架构
Background knowledge
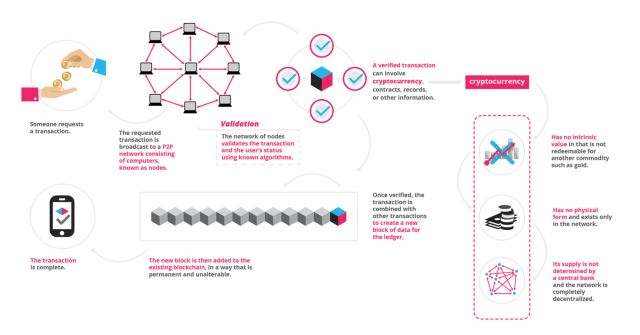
What is Blockchain?
The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.
——Don & Alex Tapscott, authors Blockchain Revolution (2016)
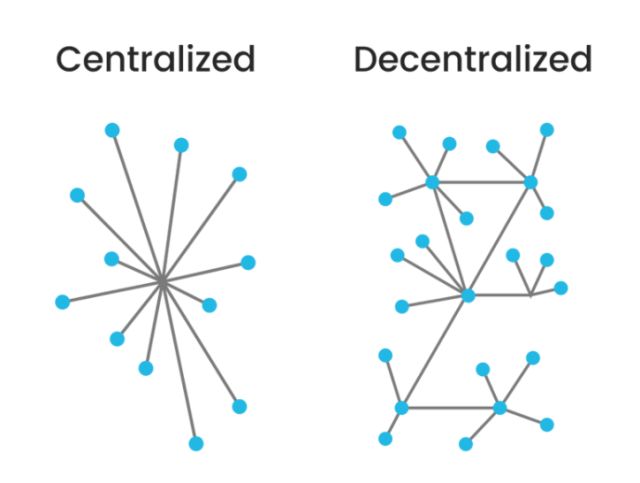
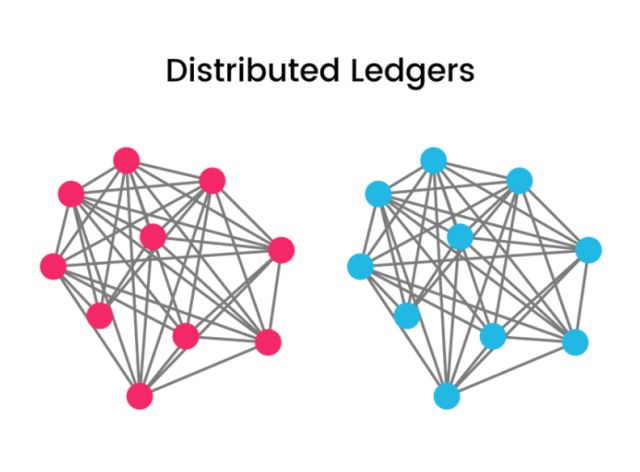
区块链起源于中本聪的比特币,作为比特币的底层技术,本质上是一个去中心化的数据库,通过去中心化和去信任的方式集体维护一个可靠数据库的技术方案。区块链技术是一种不依赖第三方、通过自身分布式节点进行网络数据的存储、验证、传递和交流的一种技术方案。从金融学的角度来考虑,区块链技术是一种分布式开放性去中心化的大型网络记账薄,任何人任何时间都可以采用相同的技术标准加入自己的信息,延伸区块链,持续满足各种需求带来的数据录入需要。
Basic technology
Cryptography——Hash function
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to data of fixed size. It is useful in cryptography. A cryptographic hash function allows one to easily verify that some input data maps to a given hash value, but if the input data is unknown, it is deliberately difficult to reconstruct it (or equivalent alternatives) by knowing the stored hash value. This is used for assuring integrity of transmitted data, and is the building block for HMACs, which provide message authentication.
Hash函数——将可变长度的数据块M作为输入,产生固定长度的Hash值h = H(M)。用于验证数据的完整性,即判断数据是否被篡改过。
Development and Evolution of Blockchain
区块链1.0——数字货币(基于密码学安全的分布式账本)
区块链2.0——数字资产与智能合约
区块链3.0——DAO、DAC(区块链自洽组织、区块链自洽公司)、区块链大社会(科学,医疗,教育etc,区块链+人工智能)
TED Study
How the blockchain will radically transform the economy
The concept put forward by Douglass North

Now, one of the first people to really explore the idea of institutions as a tool in economics to lower our uncertainties about one another and be able to do trade was the Nobel economist Douglass North. He passed away at the end of 2015, but North pioneered what's called "new institutional economics." And what he meant by institutions were really just formal rules like a constitution, and informal constraints, like bribery. These institutions are really the grease that allow our economic wheels to function, and we can see this play out over the course of human history.
Evolution of Blockchain
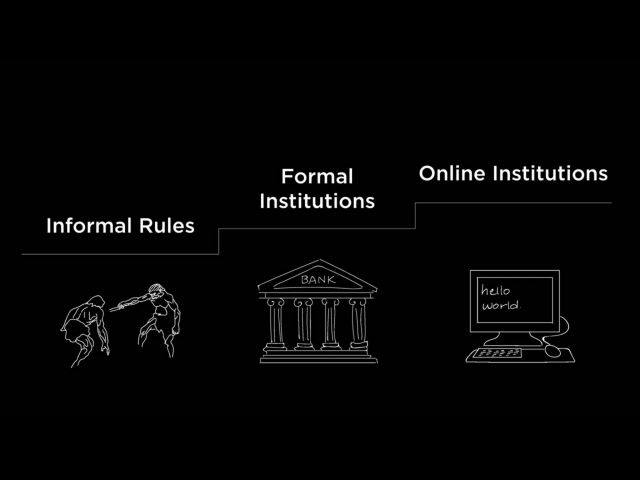
If we think back to when we were hunter-gatherer economies, we really just traded within our village structure. We had some informal constraints in place, but we enforced all of our trade with violence or social repercussions. As our societies grew more complex and our trade routes grew more distant, we built up more formal institutions, institutions like banks for currency, governments, corporations. These institutions helped us manage our trade as the uncertainty and the complexity grew, and our personal control was much lower. Eventually with the internet, we put these same institutions online. We built platform marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, Alibaba, just faster institutions that act as middlemen to facilitate human economic activity.
Definition of Blockchain
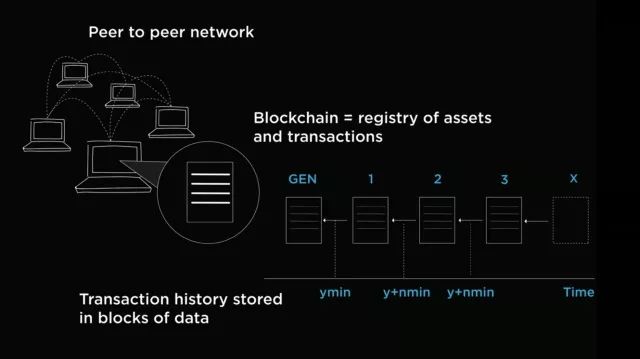
So what is the blockchain? Blockchain technology is a decentralized database that stores a registry of assets and transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It's basically a public registry of who owns what and who transacts what. The transactions are secured through cryptography, and over time, that transaction history gets locked in blocks of data that are then cryptographically linked together and secured. This creates an immutable, unforgeable record of all of the transactions across this network. This record is replicated on every computer that uses the network.
Blockchain vs Uncertainty
How blockchains lower uncertainty and how they therefore promise to transform our economic systems in radical ways. So uncertainty is kind of a big term in economics, but I want to go through three forms of it that we face in almost all of our everyday transactions, where blockchains can play a role. We face uncertainties like not knowing who we're dealing with, not having visibility into a transaction and not having recourse if things go wrong.
*TED原文链接:
https://www.ted.com/talks/bettina_warburg_how_the_blockchain_will_radically_transform_the_economy
Further Study
可以通过下面这个小视频进一步了解区块链的工作原理~
以上是关于科技面面观 | Block Chain的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章