Room 中的数据库关系
Posted 谷歌开发者
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Room 中的数据库关系相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Room 2.2
https://developer.android.google.cn/jetpack/androidx/releases/room#version_220_3
@Relation
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/android/arch/persistence/room/Relation
一对一关系
一对一关系
data class Dog(val dogId: Long,val dogOwnerId: Long,val name: String,val cuteness: Int,val barkVolume: Int,val breed: String)data class Owner( val ownerId: Long, val name: String)
data class DogAndOwner(val owner: Owner,val dog: Dog)
SELECT * FROM OwnerSELECT * FROM Dog WHERE dogOwnerId IN (ownerId1, ownerId2, …)
data class DogAndOwner(val owner: Owner,parentColumn = ,entityColumn =)val dog: Dog)
fun getDogsAndOwners(): List<DogAndOwner>
-
Dao https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/room/Dao -
@Transaction https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/room/Transaction.html
一对多关系
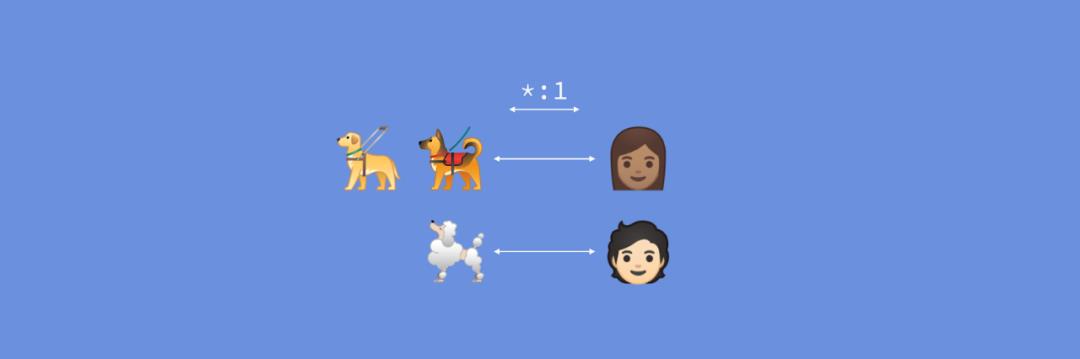
data class OwnerWithDogs(val owner: Owner,val dogs: List<Dog>)
data class OwnerWithDogs(val owner: Owner,parentColumn = ,entityColumn =)val dogs: List<Dog>)
fun getDogsAndOwners(): List<OwnerWithDogs>
多对多关系
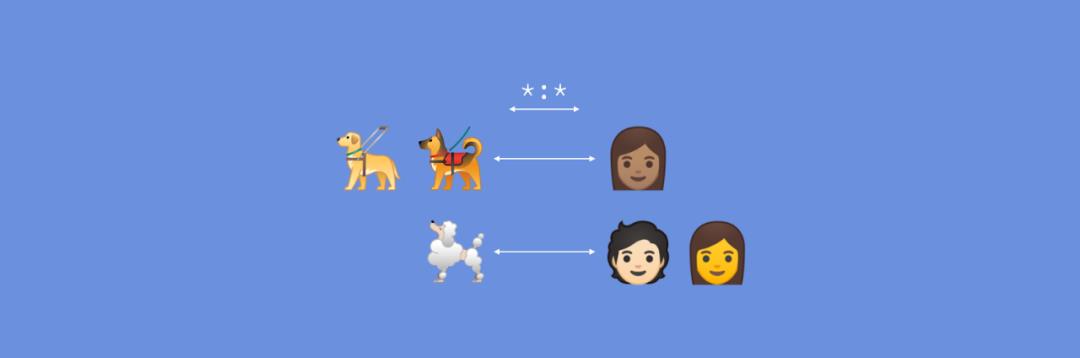
多对多关系
data class DogOwnerCrossRef(val dogId: Long,val ownerId: Long)
associative
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Associative_entity
SELECT * FROM OwnerSELECTDog.dogId AS dogId,Dog.dogOwnerId AS dogOwnerId,Dog.name AS name,_junction.ownerIdFROMDogOwnerCrossRef AS _junctionINNER JOIN Dog ON (_junction.dogId = Dog.dogId)WHERE _junction.ownerId IN (ownerId1, ownerId2, …)
data class OwnerWithDogs(val owner: Owner,parentColumn = ,entityColumn = ,associateBy = Junction(DogOwnerCrossRef::class))val dogs: List<Dog>)
Junction
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/room/Junction
在我们的 Dao 中,我们需要从 Owners 中选择并返回正确的数据类:
fun getOwnersWithDogs(): List<OwnerWithDogs>
更高阶的数据库关系用例
data class Pup(val name: String,val cuteness: Int = 11)data class OwnerWithPups(val owner: Owner,parentColumn = ,entity = Dog::class,entityColumn =)val dogs: List<Pup>)
data class OwnerWithDogs(val owner: Owner,parentColumn = ,entity = Dog::class,entityColumn = ,projection = [])val dogNames: List<String>)
-
ForeignKey https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/room/ForeignKey.html -
SQLite 中的外键 https://sqlite.org/foreignkeys.html
-
@Relation https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/room/Relation.html -
Room 2.2 的更多新功能 https://developer.android.google.cn/jetpack/androidx/releases/room#version_220_3
 点击屏末 | 阅读原文 | 进一步了解 Room
点击屏末 | 阅读原文 | 进一步了解 Room

想了解更多 Android 内容?
还有更多疑惑?欢迎点击菜单 "联系我们" 反馈您在开发过程中遇到的问题。
推荐阅读
以上是关于Room 中的数据库关系的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章