3数据库管理系统mysql操作基础
Posted 蒋工谈
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了3数据库管理系统mysql操作基础相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
-datagrip连接工具使用
数据库管理系统
https://www.mysqlzh.com/
数据库类型:(了解)
关系型数据库--数据最终存储在磁盘
sql server #收费
oracle #收费
mysql mariadb #开源免费的
postgresql #免费的
非关系型数据库--
缓存数据库--数据存储在内存上
mongodb #海量的数据 ,文档型
redis #键值型
搜索引擎--
elasticsearch #分词搜索殷勤
安装运行:(了解)
service mysqld status
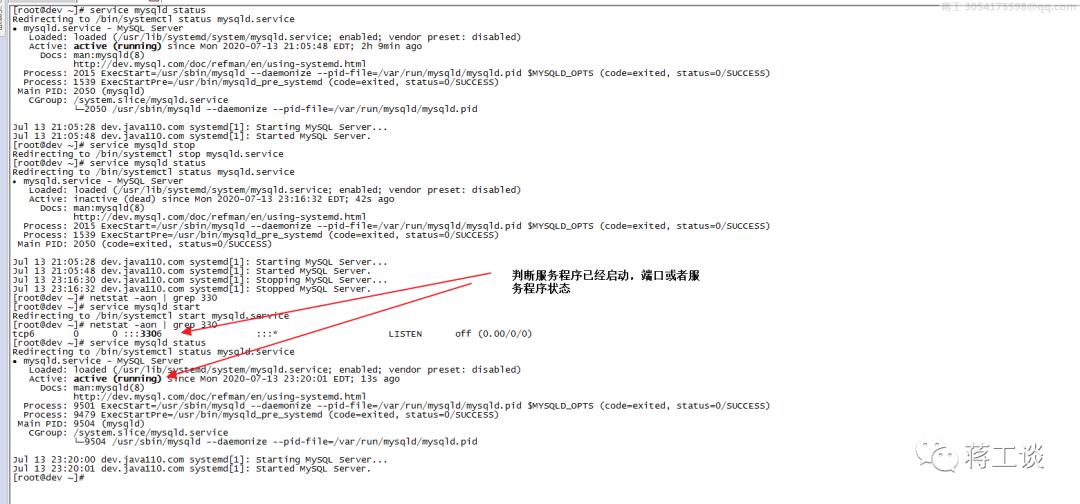
连接:(熟练)
datagrip安装

mysql启动
service mysqld start #启动mysqld服务
service mysqld status #查看mysqld服务运行状态
netstat -aon | grep 3306 #查看mysqld运行端口
服务防火墙添加3306
firewall-cmd --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent
service firewalld restart
datagrip连接 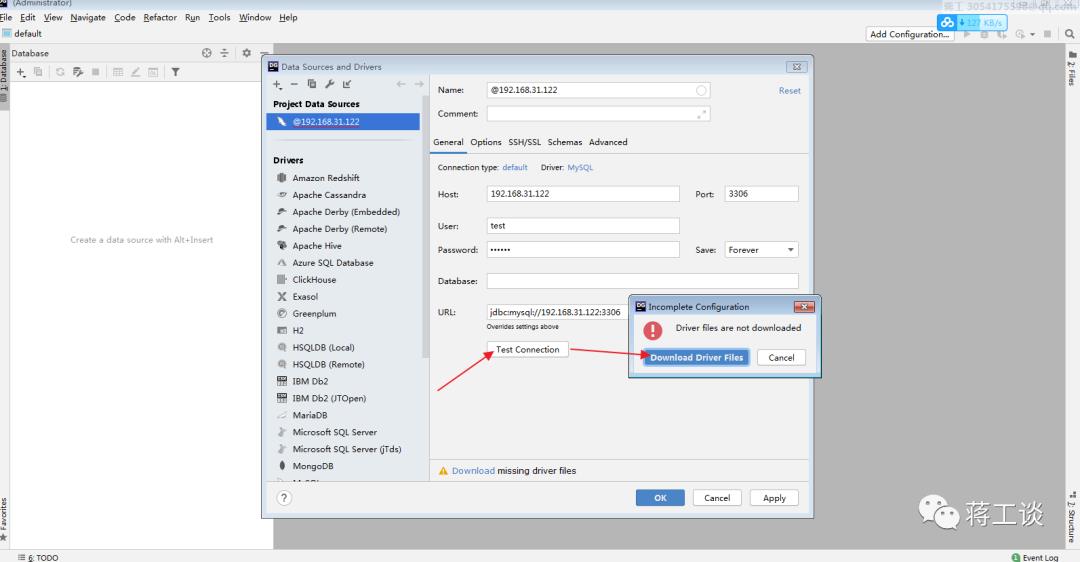
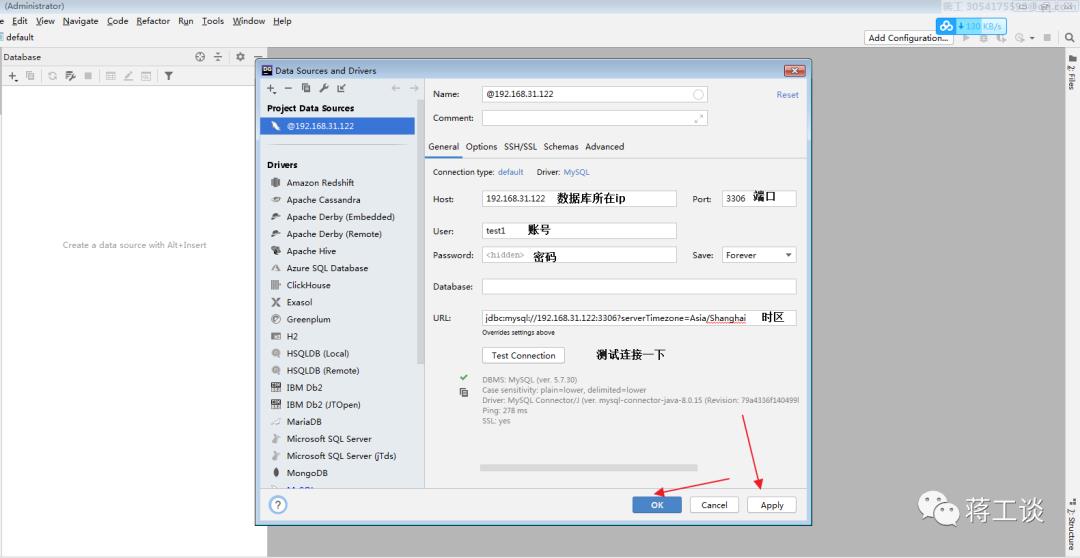
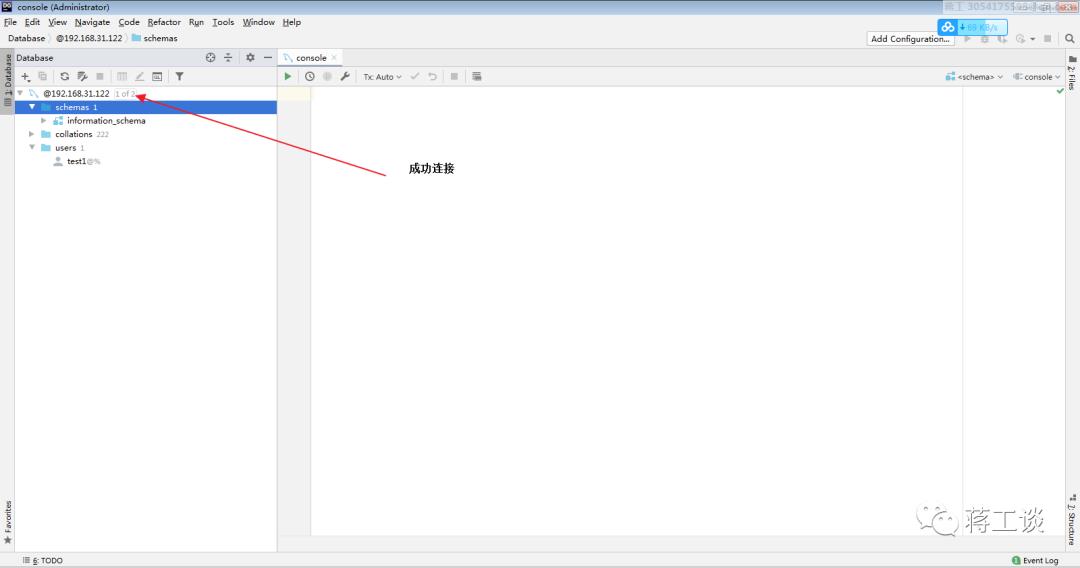
datagrip使用过程(熟练)
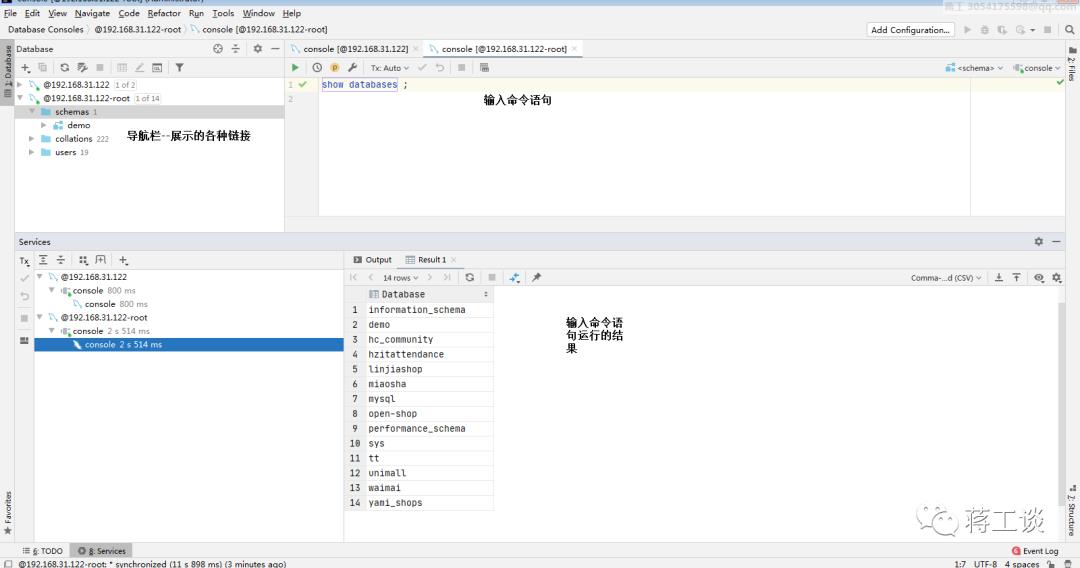
MYSQL数据库sql语法(熟悉)
类别
ddl 操作库结构表结构的---create 、drop、alter...(熟悉)
dcl 操作权限、事务控制 ---- grant、commit、roll back、save point....(了解)
dml 操作数据的增删改----insert 、 delete、update(熟练)
固定字符串char 与 可变字符串varchar的区别::固定字符串分配的实际空间是固定的,可变字符串是由实际的字符数确定,比如,声明了char(8),那么如果你写入不足8个字符,也会实际分配8个字符的实际空间,声明的是varchar(8),写入不足8个字符,分配空间依据实际字符数确定
dql 操作数据查-----select(精通)
DDL语句(创表熟悉,其它了解)
#数据库 |
|
CREATE DATABASE `数据库名` CHARACTER SET `utf8`; |
创建库 |
DROP DATABASE `数据库名`; |
删除库 |
SHOW DATABASES; |
查库 |
use `数据库名2` |
切换数据库 |
#数据表 |
|
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 , 列名 数据类型); |
创表 |
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 not null); |
设置非空属性后,必须手工插入数据 |
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 uniqe key); |
唯一键,列中的数据不能重复 |
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 , uniqe key( 列名)); |
|
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 not null uniqe key); |
非空且唯一 |
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 primary key); |
主键(主码)非空且唯一 |
CREATE TABLE `表名`( 列名 数据类型 DEFAULT 1); |
设置默认值 |
# 设置备注 create table demo08( d1 int not null default 1 COMMENT '编号', d2 int primary key comment '年龄' ) COMMENT = '这是演示comment的表'; |
备注说明下 |
# 设置字符集 create table demo12( d1 int not null default 1 COMMENT '编号', d2 int primary key comment '年龄' ) engine = 'myisam' COMMENT = '这是演示comment的表' charset = 'utf8'; |
设置字符集 |
# 复合主键 create table demo13( i1 int, i2 int, primary key (i1,i2) ); |
复合主键 |
# 外键 ,表demo15的列i2里的数据参照表demo16中的列d2 create table demo15( i1 int, i2 int, foreign key (i2) references demo16(d2) ); create table demo16( d1 int, d2 int primary key ); |
外键 |
DESC 表名; DESCRIBE 表名; |
查看表结构 |
ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY 列名 数据类型; |
修改表结构总的列,更换数据类型、约束 |
ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY 列名 数据类型 , MODIFY 列名 数据类型; |
|
ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP 列名; |
删除列 |
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD 列名 数据类型; |
增加列 |
# 改表名 ALTER TABLE demo18 rename to demo181; |
|
DML语句(熟练)
# 变量 set @x=1; -- 定义一个变量@x,初始值为1 select @x; -- 查询变量@x的值 select @y; -- 查询变量@y的值,默认为空null set @u:=2; -- 原版的赋值运算符 |
|
# 运算符 select 1=2; -- 预期 0 select 1=1; -- 预期 1 select 1!=1; -- 预期 0 select 1 <>1; -- 预期0 select not 1=1; -- 预期0 select 1=1 and 2=1; -- 预期0 select 1=1 or 2=1; -- 预期1 |
|
# dml -- 修改update set UPDATE demo181 SET d2=4 ; -- 变更列里所有数据 UPDATE demo181 set d2=6 , d1=4; -- 变更列d2中的数据都为6,变更列d1的数据都为4 UPDATE demo181 SET d1=3 WHERE d2=2; -- 过滤出列d2的数据为2的所有行,变更前面的行对应的列d1的数据为3 |
改表数据 |
# dml -- 删除 delete 或 truncate truncate table demo181; -- 清空 delete from demo181; -- 清空表数据 delete from demo181 where d1=1; -- 删除列d1=1的数据行 |
删除表数据 |
insert into stu_info values (1011,'郭靖','男','1',1353424221,'北京市海淀区','2542525@qq.com',123456789012345678), (1011,'李文才','男','1',1353444221,'北京市海淀区','2542525@qq.com',123456789012345678), (1011,'李梅','男','1',1353422221,'北京市海淀区','2542525@qq.com',123456789012345678) ; |
插入3条数据 |
# 关闭自动提交 set autocommit = 0; insert into account values (6,'林九',5000.00); delete from account where id = 4; # 事务提交 update account set money = -1 where id = 4; commit ; # 事务回滚 rollback ; |
事务 锁::表锁、行锁、记录锁、临界锁 |
DQL语句(精通)
# dql::查询所有列 SELECT * FROM student; SELECT Student.* FROM student; # dql:: 查询指定列 SELECT StudentNo,LoginPwd,Phone from student; select Student.StudentNo,Student.LoginPwd,Student.Phone from student; # dql:: 起别名 select StudentNo as 学生号,LoginPwd as 登录密码,Phone 手机号 from student; select StudentNo,LoginPwd,phone from student as 学生表; select StudentNo,LoginPwd,phone from student 学生表; # dql::select运算 select StudentNo+1, 1+1,version() from student; # dql:: select后边分支 # 新增1列,判断studentno的数据如果是1002就插入1003,否则就插入1001 select *, case when StudentNo=1002 then 1003 else 1001 end as 新增列 from student; #dql::select distinct #去重 select distinct * from goods; select all * from goods; #dql::where过滤 select all * from goods where goods_id >3; select * from goods where goods_id >=10 and goods_id <=20; select * from goods where goods_id between 10 and 20; -- 等价于上述语句闭区间 select * from goods where goods_id < 10 or goods_id >20; select * from goods where not goods_id between 10 and 20; select * from goods where goods_id = 2 or goods_id =4 or goods_id =6; select * from goods where goods_id in (2,4,6);-- 等价于上边的多个or= # is null is not null select null; select 0=null; select ''=null; -- 预期 null select null=null; -- 预期 null select null is null;-- 预期 1 select 0 is null; -- 预期 0 select '' is null; -- 预期 0 select not 0 is null; -- 预期 1 select 0 is not null; -- 预期 1 # where过滤 -模糊过滤 like,_表示任意的一个字符,%表示任意长度的任意字符 select * from goods where goods_name like '%诺基亚%';-- 包含诺基亚的 select * from goods where goods_name like '诺基亚___';-- 诺基亚开头,后边有3个字符长度 # dql::排序order by select * from goods order by goods_id;-- 依据列goods_id升序排列, select * from goods order by goods_id asc;-- 依据列goods_id升序排列, select * from goods order by goods_id desc;-- 依据列goods_id升序排列, select * from goods where goods_name like '%诺基亚%' order by goods_id;-- 过滤后排序 |
|
# 分组函数 SELECT VERSION(); SELECT CURRENT_DATE(); SELECT CURRENT_TIME(); SELECT COUNT(1999); SELECT goods_sn, COUNT(goods_sn) FROM goods; -- 查询结果表中的数据行条数 SELECT SUM(goods_id) FROM goods; -- 查询结果表中的某列的数据总和 SELECT SUM(goods_id+1) FROM goods; SELECT MAX(market_price) FROM goods;-- 查询结果表中市场价格最高的 set @@sql_mode ='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION'; show variables like '%sql_mode%'; # 需求::统计·不同栏目的商品数量 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =0;-- 0号栏目商品数量 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =1;-- 1号栏目商品数量 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =2;-- 2号栏目商品数量 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =3;-- 3号栏目商品数量 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =4;-- 4号栏目商品数量 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =5;-- 5号栏目商品数量 # dql::联合查询union 、union all (SELECT cat_id, COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =0) union all (SELECT cat_id,COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =1) union all (SELECT cat_id,COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =2) union all (SELECT cat_id, COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =3) union all (SELECT cat_id, COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =4) union all (SELECT cat_id, COUNT(*) FROM goods WHERE cat_id =5);-- 5号栏目商品数量 # dql:: 分组查询group by select cat_id,count(*) from goods group by cat_id; SELECT cat_id,count(*) FROM goods WHERE 1=1 GROUP BY cat_id HAVING count(*)>10; -- 分组后统计大于10的行 # dql:: 分页查询limit SELECT * FROM goods limit 10; SELECT * FROM goods LIMIT 0,10; SELECT * FROM goods LIMIT 1,10; # dql:: SELECT * FROM goods WHERE 1=1 GROUP BY cat_id HAVING COUNT(*)>1 ORDER BY cat_id LIMIT 10; |
分组联合 |
-- 笛卡尔积,不同表间数据行条数组合 SELECT student.studentno,result.StudentNo FROM student,result ; # 再次过滤后,等值内连接 SELECT s.studentno,r.StudentNo FROM student s,result r where s.StudentNo = r.StudentNo; SELECT s.StudentNo ,r.StudentNo from student s inner join result r on s.StudentNo=r.StudentNo; # 需求::郭靖分数 SELECT result.StudentNo,StudentName,StudentResult FROM demo.Student INNER JOIN result ON result.StudentNo=Student.StudentNo WHERE StudentName='郭靖'; select StudentNo from demo.Student where StudentName = '郭靖'; # dql::嵌套查询 select StudentNo,StudentResult from result where StudentNo = (select StudentNo from demo.Student where StudentName = '郭靖'); select StudentNo,StudentResult from result where StudentNo in (select StudentNo from demo.Student where StudentName = '郭靖'); select StudentNo,StudentResult from result where exists (select * from demo.Student s where s.StudentName = '郭靖' and s.StudentNo = result.StudentNo); |
连接查询 嵌套查询 |
#索引 CREATE TABLE index01( id1 int primary key , -- 主键,主键索引, id2 int unique key, -- 唯一键,唯一索引 id3 int , key k1 (id3)-- 普通键,常规索引 ); #查看表中声明的索引 show index from index01; CREATE TABLE index02( id int ); #修改表添加常规索引 ALTER TABLE index02 ADD INDEX key2(id); #索引执行计划--explain explain (select StudentNo,StudentResult from result where exists (select * from demo.Student s where s.StudentName = '郭靖' and s.StudentNo = result.StudentNo)); |
索引(了解) |
多子句执行顺序
连接查询关系图解 |
|
|||||||
A表 |
B表 |
|||||||
a1 |
a2 |
b1 |
b2 |
b3 |
||||
1 |
a2 |
1 |
1 |
b3 |
||||
2 |
a2 |
2 |
2 |
b09o |
||||
3 |
a2 |
|||||||
inner join内连接A.a1 = B.b2 |
||||||||
A表 |
B表 |
|||||||
a1 |
a2 |
b1 |
b2 |
b3 |
||||
1 |
a2 |
1 |
1 |
b3 |
||||
2 |
a2 |
2 |
2 |
b09o |
||||
left outter join左外连接 A.a1 = B.b2 |
||||||||
A表 |
B表 |
|||||||
a1 |
a2 |
b1 |
b2 |
b3 |
||||
1 |
a2 |
1 |
1 |
b3 |
||||
2 |
a2 |
2 |
2 |
b09o |
||||
3 |
a2 |
|||||||
right outter join右外连接 A.a1 = B.b2 |
||||||||
A表 |
B表 |
|||||||
a1 |
a2 |
b1 |
b2 |
b3 |
||||
1 |
a2 |
1 |
1 |
b3 |
||||
2 |
a2 |
2 |
2 |
b09o |
||||
以上是关于3数据库管理系统mysql操作基础的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章