Android View知识
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android View知识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 1, View是除了android四大组件外,最常用的东西2,什么是View:
View是android中所有控件的父类,比如TextView,LinearLayout等等
其中LinearLayout继承自控件组ViewGroup,当然ViewGroup也是继承自View
3,View的位置
top:左上角纵坐标
left:左上角横坐标
right:右下角横坐标
bottom:右下角纵坐标
如下图:
4,view的MotionEvent和TouchSlop
4.1MotionEvent:
ACTION_DOWN:手指接触屏幕
ACTION_MOVE:手指在屏幕上滑动
ACTION_UP:手指离开屏幕。
4.2TouchSlop
处理滑动时的过滤条件,简单来说就是,手指在屏幕上的一次操作算不算滑动。
系统默认值:ViewConfiguration.get(context).getScaledTouchSlop()
5,getX()getY()和getRawX()和getRawY()
前两者相对于父控件View 后两者相对于手机屏幕
6,VelocityTracker,GestureDetector,Scroller
6.1VelocityTracker:滑动速度,在view的ontouch事件中,查看速度
6.2 GestureDetector:手势判断,比如长按,点击,双击等,很少用,可以用 ontouch事件来代替
6.3Scroller:弹性滑动对象,实现view的位置改变等
7,原始滑动方式
7.1:ScrollerTo和Scroller By()
实现简单 但是只能滑动view里面的子元素
7.2:改变view参数
实现复杂,但是如果view有交互,这种方式比较好
7.3:动画
适用于没有交互的,或者动画复杂的view的滑动
8View的事件分发:
8.1:Activity-window-View
8.2:view中是从父到子,也就是从外到内,都不处理,返回给最顶级
8.3:ViewGroup默认不拦截任何事件,默认返回false
8.4:分发方法:dispatchTouchEvent,OnInterceptTouchEvent,OnTouchEvent
dispatchTouchEvent:分发
OnInterceptTouchEvent:拦截
OnTouchEvent:处理点击事件
Android中View的相关知识
Android中View的相关知识(6)
@(Android)
在前文Android中View的相关知识(4)和Android中View的相关知识(5)中,我们分析了在Activity中setContentView();和initWindowDecorActionBar();方法,即创建TitleView和ContentView的方法。但是这些方法中最终都牵扯了LayoutInflater加载布局的方式
今天我们就来分析分析LayoutInflater加载~
LayouInflater加载布局
我们回到Activity的setContentView();从头开始,先来看下源码的流程:
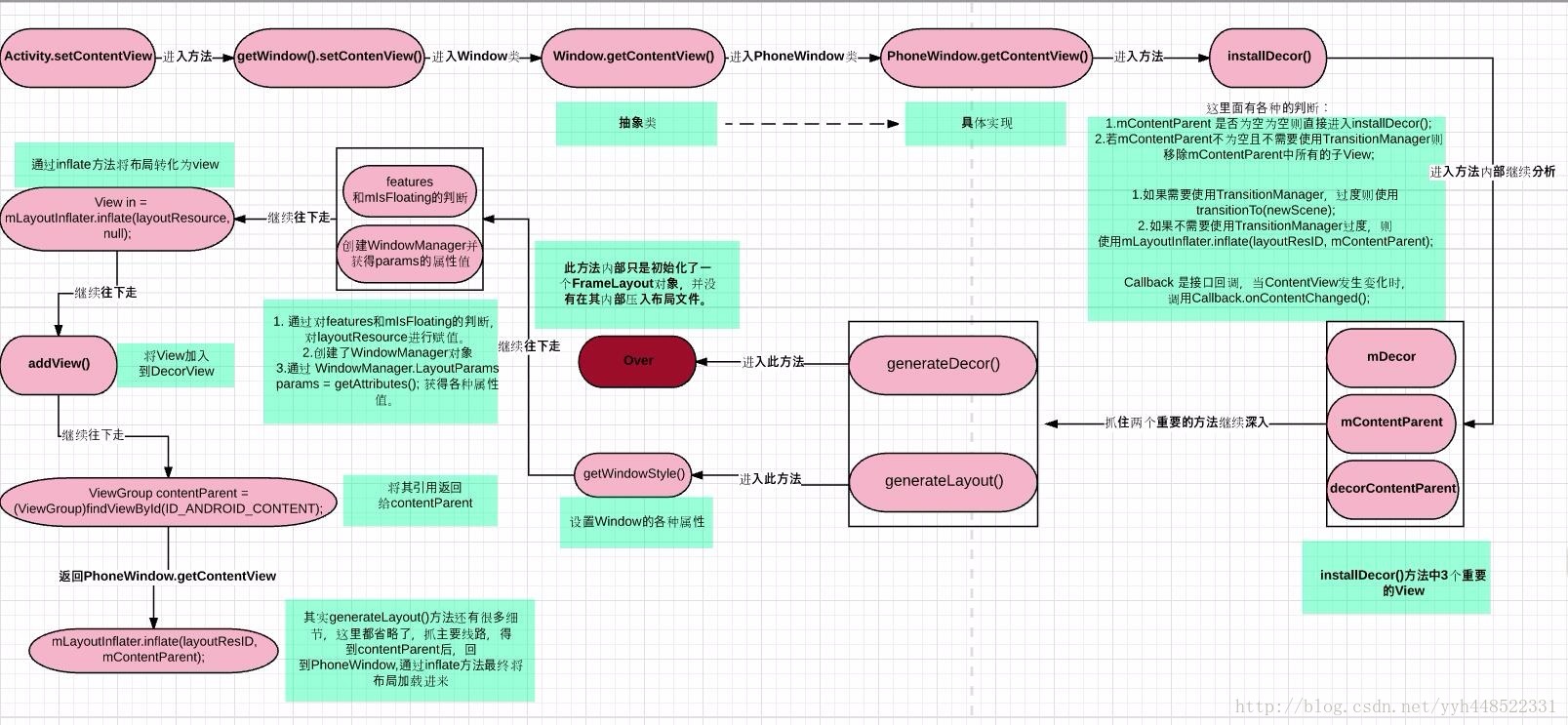
走到最后,调用了mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID,mContentParent);
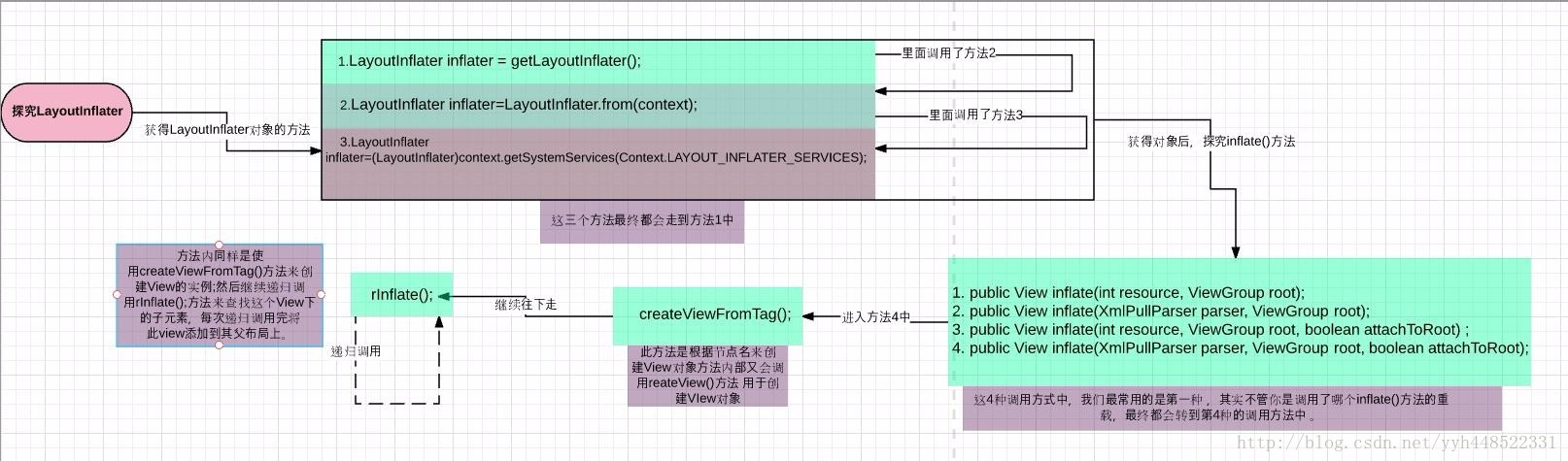
那么,我们先来看一下LayoutInflater的基本用法,首先是获取LayoutInflater的实例,这里有3中方法:
1 . 通过SystemService获得:
LayoutInflater inflater=(LayoutInflater)context.getSystemServices(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICES);2 . 从给定的context中获得
LayoutInflater inflater=LayoutInflater.from(context);3 . 在Activity中通过getLayoutInflater();获得(实际是View子类下Window的一个函数)
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
这3种获得LayoutInflater对象的方式本质上是一样的,其实后面的两种方式本质上都用到了第一种的方式:我们来看后面两种方式的源码:
//第二种方式
public static LayoutInflater from(Context context)
LayoutInflater LayoutInflater =
(LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
if (LayoutInflater == null)
throw new AssertionError("LayoutInflater not found.");
return LayoutInflater;
//第三种方式(Activity类中)
public LayoutInflater getLayoutInflater()
return getWindow().getLayoutInflater();
/*
*getWindow()-->进入Window类找到getLayoutInflater()-->Window类抽象类
*进入其实现类PhoneWindow;
*
*/
public PhoneWindow(Context context)
super(context);
mLayoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
从源码可以看到,后面的两种方法归根到底都到了
(LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
获得了这个LayoutInflater对象,我们来继续探究inflate的方法,它有4个重载方法:
1. public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root);
2. public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root);
3. public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) ;
4. public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot);
这4种调用方式中,我们最常用的是第一种,inflate方法的主要作用就是将一个xml文件转换成一个View对象,用于动态的创建布局。其实不管你是调用了哪个inflate()方法的重载,最终都会转到第4种的调用方法中,那么 我们来看第四种方式的源码:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
synchronized (mConstructorArgs)
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate");
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context)mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext;
View result = root;
try
// Look for the root node.
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT)
// Empty
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG)
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
final String name = parser.getName();
if (DEBUG)
System.out.println("**************************");
System.out.println("Creating root view: "
+ name);
System.out.println("**************************");
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name))
if (root == null || !attachToRoot)
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
rInflate(parser, root, attrs, false, false);
else
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
//起始~
final View temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, attrs, false);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null)
if (DEBUG)
System.out.println("Creating params from root: " +
root);
// Create layout params that match root, if supplied
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot)
// Set the layout params for temp if we are not
// attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
if (DEBUG)
System.out.println("-----> start inflating children");
// Inflate all children under temp
rInflate(parser, temp, attrs, true, true);
if (DEBUG)
System.out.println("-----> done inflating children");
// We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp)
// to root. Do that now.
if (root != null && attachToRoot)
root.addView(temp, params);
// Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
// top view found in xml.
if (root == null || !attachToRoot)
result = temp;
catch (XmlPullParserException e)
InflateException ex = new InflateException(e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
catch (IOException e)
InflateException ex = new InflateException(
parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": " + e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
finally
// Don't retain static reference on context.
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
mConstructorArgs[1] = null;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
return result;
从源码可以清楚的看出,LayoutInflater其实就是使用Android提供的Pull解析方式来解析布局文件的。源码里的注释很清楚,首先通过createViewFromTag();这个方法,并把节点名和参数传入,此方法的作用是根据节点名来创建View对象的,在 createViewFromTag();方法内部又会调用reateView()方法;然后使用反射的方式创建出View的实例并返回。这里不是重点知道就行,感兴趣的童鞋也可以去分析分析~
//Creates a view from a tag name using the supplied attribute set.
View createViewFromTag(View parent, String name, AttributeSet attrs, boolean inheritContext)
...
//省略其中的代码
...
//Low-level function for instantiating a view by name. This attempts to instantiate a view class of the given name found in this LayoutInflater's ClassLoader.
public final View createView(String name, String prefix, AttributeSet attrs)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InflateException
...
//省略了其中代码
...
从createViewFromTag();方法出来,只是创建了一个根布局的实例,接下来会调用rInflate();方法来循环遍历这个根布局下的子元素,直到全部遍历完:
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs,
boolean finishInflate, boolean inheritContext) throws XmlPullParserException,
IOException
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT)
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG)
continue;
final String name = parser.getName();
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name))
parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
else if (TAG_TAG.equals(name))
parseViewTag(parser, parent, attrs);
else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name))
if (parser.getDepth() == 0)
throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs, inheritContext);
else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name))
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
else
//重点地方。。。
final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, attrs, inheritContext);
final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
rInflate(parser, view, attrs, true, true);
viewGroup.addView(view, params);
if (finishInflate) parent.onFinishInflate();
可以看到,同样是使用createViewFromTag()方法来创建View的实例;然后继续递归调用rInflate();方法来查找这个View下的子元素,每次递归调用完将此view添加到其父布局上。
经过这样一层层的遍历,把整个布局文件都解析完就形成了一个完整的DOM结构,最终会把最顶层的根布局返回,至此inflate()过程全部结束。
关于LayoutInflater的流程分析算是完了,当然这里还有个小问题,关于有3个参数的inflate();使用的问题。
LayoutInflater.inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)的使用
第一个参数用于传入布局资源的ID,第二个参数是传入当前视图的父视图,通常需要父视图来正确配置组件。第三个参数告知布局生成器是否将生成的视图添加给父视图。
我们分成两种情况对这个方法进行分析:
1. root不为空的情况:
a. 如果attachToRoot为true,就直接将这个布局添加到root父布局了,并且返回的view就是父布局
b. 如果attachToRoot为false,就不会添加这个布局到root父布局,返回的view为resource指定的布局
2. root为空的情况:
相当于使用等价于:LayoutInflater.from(this).layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.button_layout, null);方法那么关键就在于这个root了,它有什么作用呢?
1. 如果root为null,attachToRoot将失去作用,设置任何值都没有意义。同时这个布局的最外层参数就没有效了
2. 如果root不为null,attachToRoot设为false,则会将布局文件最外层的所有layout属性进行设置,当该view被添加到父view当中时,这些layout属性会自动生效。
3. 如果root不为null,attachToRoot设为true,则会给加载的布局文件的指定一个父布局,即root。
其实View必须存在于一个父布局中,这样layout_width和layout_height才会有效,这也是为什么这两个属性叫作layout_width和layout_height,而不是width和height。所以:inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)的第二个参数不为空,resource的最外层布局参数才会有效,否则就无效了。
这里我们用一个例子来说明下:
activity_main.xml的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/main_layout"
tools:context="com.example.yyh.testin.MainActivity">
</RelativeLayout>再新建一个Button控件的布局,代码也很简单
<Button xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="360dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/button_layout"
android:text="Button" >
</Button>
然后是MainActivity.class
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity
private RelativeLayout mainLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mainLayout = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.main_layout);
LayoutInflater layoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
View buttonLayout = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.buttion_layout, null);
mainLayout.addView(buttonLayout);
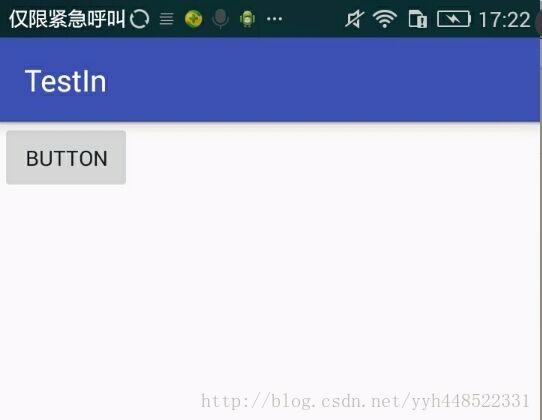
来看效果图:
我去,设置的Button的宽高完全不起作用,看起来还是warp_content的效果。不管怎么设置,这个Button的宽高就是不起作用,平时我们经常使用layout_width和layout_height来设置View的大小,并且一直都能正常工作,就好像这两个属性确实是用于设置View的大小的。而实际上它是用于设置View在布局中的大小,即View必须包含在一个布局中,他的宽高设置才有效果。所以 这里我们改变Button控件的布局:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:layout_width="360dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="Button" >
</Button>
</RelativeLayout> 改变后我们再来看效果图:
可以看到,我们将Button放到了一个RelativeLayout当中,此时,设置宽高就有效果了。
到了这里,大家肯定还有个疑惑,那平时在Activity中指定布局文件的时候,最外层的布局不是可以指定大小的么?layout_width和layout_height都是有作用的,这主要是因为,在setContentView()方法中,Android会自动在布局文件的最外层再嵌套一个FrameLayout,所以宽高的设置才有效果~。
好了,LayoutInflater加载布局我们就分析完了,在接下来的文章中,我们将继续探究VIew,分析View的绘制过程~
以上是关于Android View知识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章