早期乳腺癌预后突变大数据分析
Posted SIBCS
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了早期乳腺癌预后突变大数据分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
编者按:PIK3CA突变常见于原发性乳腺癌,其突变不仅可以减少肿瘤细胞凋亡,而且可以促进肿瘤的浸润、提高其下游PI3K的活性,对于肿瘤细胞的生存和增殖发挥重要作用。既往若干研究评定了PIK3CA对于早期乳腺癌患者的临床意义,尤其对于预后的意义,但是由于样本量小、患者特征不一、治疗方案不一等原因,各个研究的结果互相矛盾。
2018年2月22日,美国临床肿瘤学会《临床肿瘤学杂志》在线发表国际乳腺癌协作组、比利时布鲁塞尔自由大学、澳大利亚抗癌协会、墨尔本大学、西澳大学、加文医学研究所、希腊癌症研究基金会、亚里士多德大学、海吉亚医院、希波克拉底医院、芬兰赫尔辛基大学、美国纽约纪念医院斯隆凯特林癌症中心、爱尔兰皇家外科医师学院、都柏林博蒙特医院、法国国家卫生及医疗研究院、巴黎居里研究所、里昂癌症研究中心、古斯塔夫鲁西研究所、南巴黎大学、瑞典隆德大学、林雪平大学、丹麦乳腺癌协作组、南丹麦大学、英国皇家马斯登医院、伦敦大学癌症研究院、伯明翰大学、意大利圣嘉勒医院、日本大阪大学、黎巴嫩贝鲁特美国大学、西班牙巴塞罗那自治大学、荷兰莱顿大学、加拿大圭尔夫大学、安大略癌症研究所的研究报告,通过对各个研究的患者个体数据进行汇总分析,评价其预后意义。
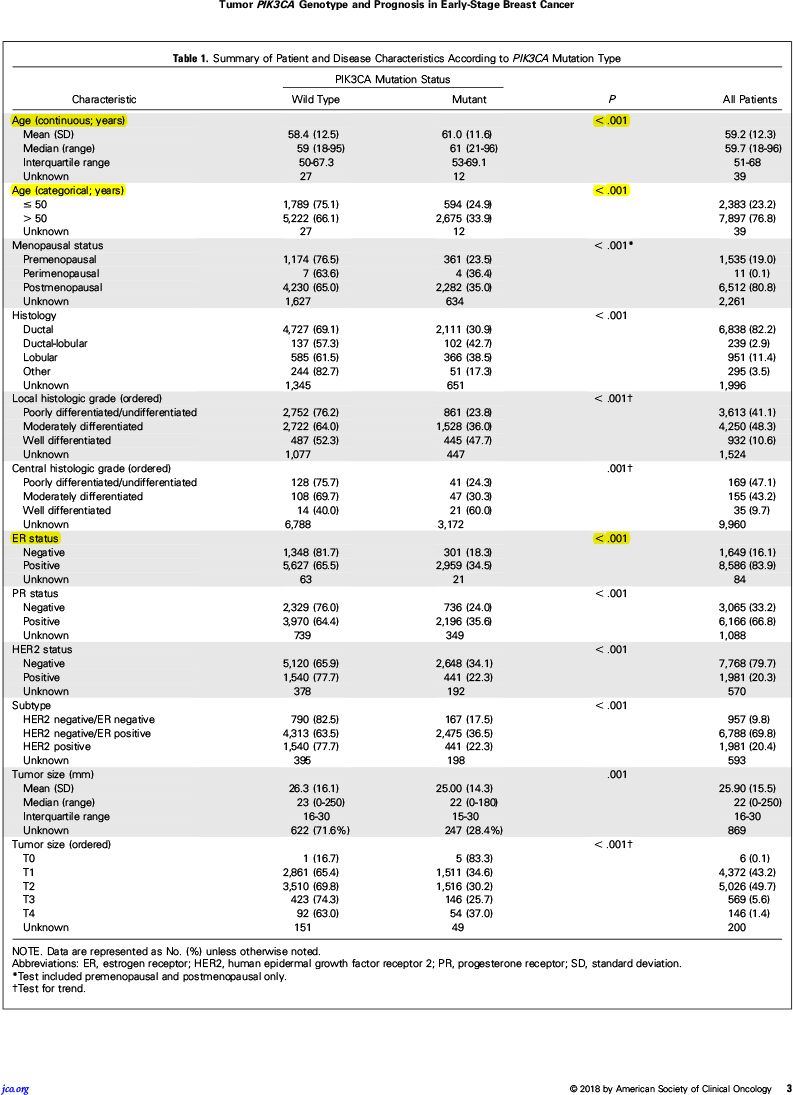
该研究通过文献检索初步选出97篇文献,通过系统回顾最终纳入19项研究共计1万319例患者数据(中位总生存随访6.9年),通过多因素比例风险回归模型,对不同的年龄、肿瘤大小、淋巴结、分级、激素受体(HR)状态、HER2状态、治疗、研究进行校正,分析PIK3CA状态与临床病理学特征之间的相关性。主要研究终点为无浸润病变生存,次要研究终点为无远处病变生存、总生存,根据整体和不同乳腺癌亚型进行分层。
结果发现:
接受化疗1787例(17%)
激素治疗4036例(39%)
两种治疗3583例(35%)
未治未知913例(9%)
其中,PIK3CA突变3281例(32%),显著多见于:
肿瘤较小(P<0.001)
分级较低(P<0.001)
HR阳性(P<0.001)
老年患者(P<0.001)
不同亚型的PIK3CA突变发生率:
HER2阴性HR阴性即三阴型:18%
HER2阳性:22%
HER2阴性HR阳性即管腔型:37%
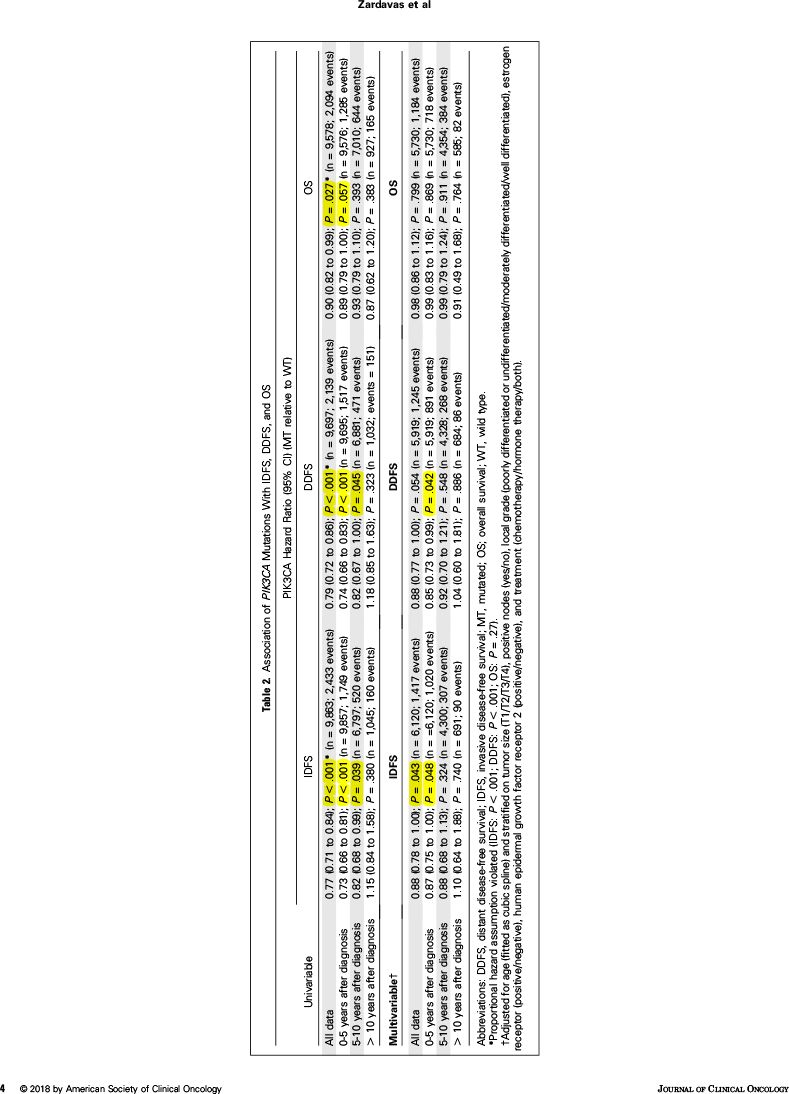
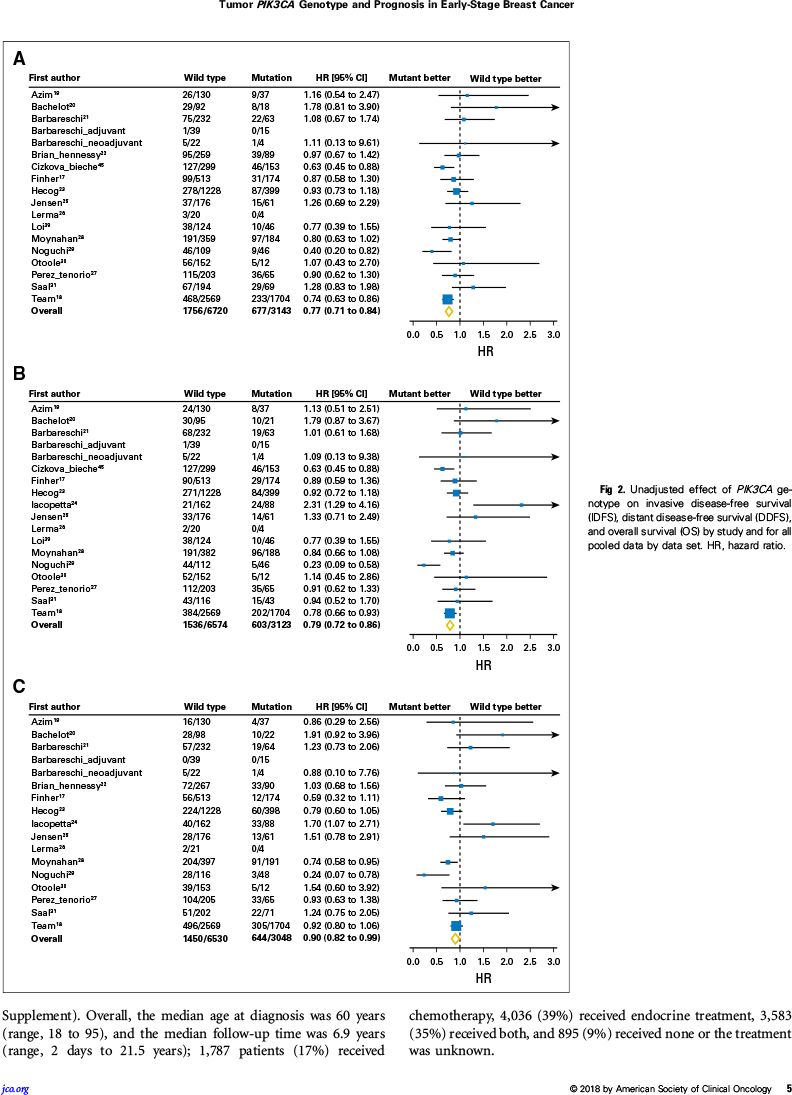
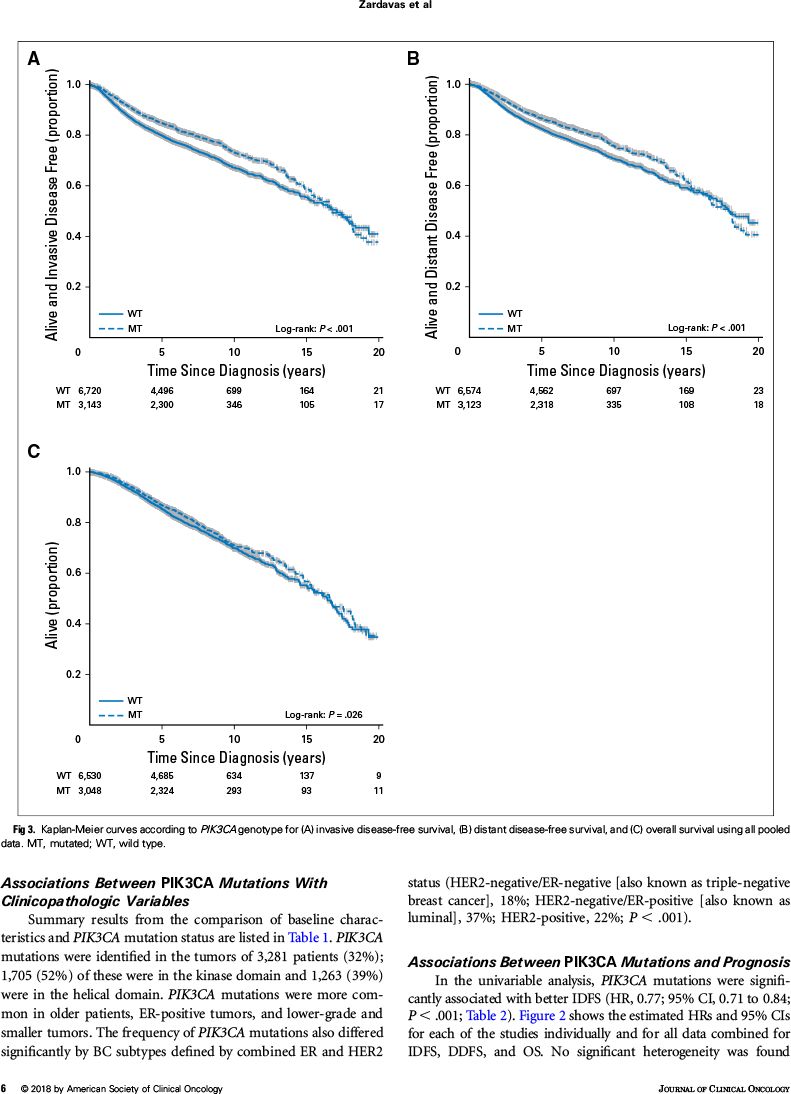
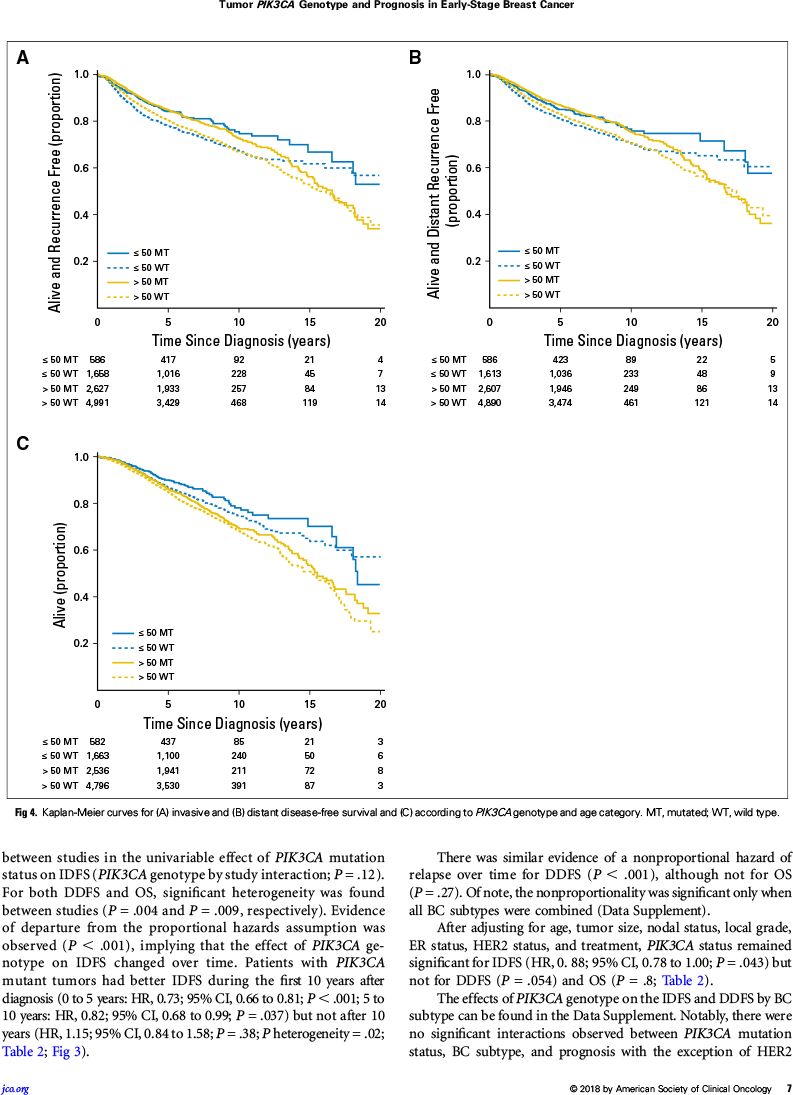
根据单因素分析,PIK3CA突变与未突变相比:
无浸润病变生存较好,尤其随访前几年
总体风险比:0.77(95%:0.71~0.84,P<0.001)
0~5年风险比:0.73(95%:0.66~0.81,P<0.001)
5~10年风险比:0.82(95%:0.68~0.99,P=0.037)
>10年风险比:1.15(95%:0.84~1.58,P=0.38)
无远处病变生存较好(P<0.001)
总生存较好(P=0.027)
根据多因素分析,PIK3CA突变与未突变相比:
无浸润病变生存较好,尤其随访前五年
总体风险比:0.88(95%:0.78~1.00,P=0.043)
0~5年风险比:0.87(95%:0.75~1.00,P=0.048)
5~10年风险比:0.88(95%:0.68~1.13,P=0.324)
>10年风险比:1.10(95%:0.64~1.88,P=0.740)
无远处病变生存相似(P=0.054)
总生存相似(P=0.799)
因此,根据该大数据汇总分析,PIK3CA突变与较好的临床结局(无浸润病变生存、无远处病变生存、总生存)显著相关,但是校正其他预后因素后,对预后的影响减少。
J Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb 22. [Epub ahead of print]
Tumor PIK3CA Genotype and Prognosis in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Patient Data.
Dimitrios Zardavas, Luc te Marvelde, Roger L. Milne, Debora Fumagalli, George Fountzilas, Vassiliki Kotoula, Evangelia Razis, George Papaxoinis, Heikki Joensuu, Mary Ellen Moynahan, Bryan T. Hennessy, Ivan Bieche, Lao H. Saal, Olle Stal, Barry Iacopetta, Jeanette Dupont Jensen, Sandra O’Toole, Elena Lopez-Knowles, Mattia Barbaraeschi, Shinzaburo Noguchi, Hatem A. AzimJr, Enrique Lerma, Thomas Bachelot, Qing Wang, Gizeh Perez-Tenorio, Cornelis J.H. can de Velde, Daniel W. Rea, Vicky Sabine, John M.S. Bartlett, Christos Sotiriou, Stefan Michiels, Sherene Loi.
Breast International Group; Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium; Cancer Council; University of Melbourne, Melbourne; University of Western Australia, Western Australia; Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Darlinghurst, Australia; Hellenic Foundation for Cancer Research/Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki; Hygeia Hospital; Hippokration Hospital, Athens, Greece; Helsinki University Hospital and University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland; Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY; Beaumont Hospital and Royal College of Surgeons, Dublin, Ireland; Curie Institut, Paris; Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Lyon, Lyon; Gustave Roussy and Inserm, Univ. Paris-Sud, Univ. Paris-Saclay, Villejuif, France; Lund University, Lund; Linkoping University, Linkoping, Sweden; University of Southern Denmark, on behalf of the Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group, Odense, Denmark; Royal Marsden NHS Trust and Institute of Cancer Research, London; University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom; Santa Chiara Hospital, Trento, Italy; Osaka University, Osaka Japan; American University of Beirut (AUB), Beirut, Lebanon; Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain; Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands; University of Guelph, Guelph; Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
PURPOSE: Phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) mutations are frequently observed in primary breast cancer. We evaluated their prognostic relevance by performing a pooled analysis of individual patient data.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Associations between PIK3CA status and clinicopathologic characteristics were tested by applying Cox regression models adjusted for age, tumor size, nodes, grade, estrogen receptor (ER) status, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status, treatment, and study. Invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) was the primary end point; distant disease-free survival (DDFS) and overall survival (OS) were also assessed, overall and by breast cancer subtypes.
RESULTS: Data from 10,319 patients from 19 studies were included (median OS follow-up, 6.9 years); 1,787 patients (17%) received chemotherapy, 4,036 (39%) received endocrine monotherapy, 3,583 (35%) received both, and 913 (9%) received none or their treatment was unknown. PIK3CA mutations occurred in 32% of patients, with significant associations with ER positivity, increasing age, lower grade, and smaller size (all P < .001). Prevalence of PIK3CA mutations was 18%, 22%, and 37% in the ER-negative/HER2-negative, HER2-positive, and ER-positive/HER2-negative subtypes, respectively. In univariable analysis, PIK3CA mutations were associated with better IDFS (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.71 to 0.84; P < .001), with evidence for a stronger effect in the first years of follow-up (0 to 5 years: HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.66 to 0.81; P < .001; 5 to 10 years: HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.68 to 0.99; P = .037); > 10 years: (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.84 to 1.58; P = .38; P heterogeneity = .02). In multivariable analysis, PIK3CA genotype remained significant for improved IDFS (P = .043), but not for the DDFS and OS end points.
CONCLUSION: In this large pooled analysis, PIK3CA mutations were significantly associated with a better IDFS, DDFS, and OS, but had a lesser prognostic effect after adjustment for other prognostic factors.
PMID: 29470143
DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.8301





以上是关于早期乳腺癌预后突变大数据分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章