基于图论和人工神经网络的供水管网漏损检测方法(上)
Posted 给排水科学研究
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于图论和人工神经网络的供水管网漏损检测方法(上)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本期介绍一篇来自URBAN WATER JOURNAL的论文,作者是伊朗德黑兰ShahidBeheshti大学土木、水和环境工程学院的Mohammadreza Shekofteh等。这篇论文主要讨论了一种利用人工神经网络和图论对现实管网建立模型,通过输入节点数据来有效探测漏损位置的方法,与传统物理探漏方法,该模型方法更加经济高效。
供水管网漏损检测研究概况
来源于互联网
Inrecent years, various methodologies have been proposed for controlling anddetecting the leakage in WDNs. Wu and Sage (2008) used network calibration and genetic algorithm to find theamount and location of leakage in WDNs.
近年来,人们提出了各种方法来控制和检测配水管网的漏损。Wu和Sage(2008)利用网络标定和遗传算法来确定管网的泄水量和漏水位置。
Severalevolutionary algorithms(such as Particle Swarm Optimization, PSO; Ant ColonyOptimization, ACO) were applied by others (e.g. see Izquierdo et al. 2008; Lijuan, Hongwei, and Hui 2012;Ni, Jiang, and Pan 2013; Hajibandeh and Nazif 2018). Other methods such as prediction ofleakage using the Bayesian classification system, have been used to detectleakage in WDNs. Soldevila et al.(2017) proposed a method for locating a network leakage using theBayesian classification system. Intheir method, probability density functionsfor pressure residuals are calibrated for all potential leakage scenarios usinga hydraulic simulation model, considering the uncertainty of leakage size,demand, and noise of sensors.
其他人采用了几种进化算法(如粒子群优化算法;蚁群优化算法) (见Izquierdo等人. 2008; Lijuan,Hongwei, and Hui 2012;Ni, Jiang, and Pan 2013; Hajibandeh and Nazif 2018)。其他方法,如利用贝叶斯分类系统预测漏损,已经用于管网的探漏。Soldevila等人(2017)提出了一种利用贝叶斯分类系统定位网络泄漏的方法。在他们的方法中,已考虑漏水大小、需求和传感器噪声的不确定性情况下,使用一种水力仿真模型,对所有可能的漏水情况利用压力残差的概率密度函数进行校准。
Qi et al. (2014) presented an optimization approach based on a combination of thegenetic algorithm and the Bayesian classification system. which used thecalculated and measurement data in all nodes with pressure gauges to determinethe leakage (also see: Darsana and Varija 2018). Wachla, Przystalka, and Moczulski (2015) used an artificial fuzzy neural system to find leakage locationsin WDNs. The idea of their method is based on the division of the water networkinto predetermined areas, which identifies the approximate location of leakage.
Qi等人(2014)提出了一种基于遗传算法和贝叶斯分类系统相结合的优化方法,该方法使用所有带压力表节点的计算和实测数据来确定漏失量(也参见:Darsana and Varija2018)。Wachla, Przystalka和Moczulski(2015)使用了一种人工模糊神经网络来确定管网中的漏水位置。他们的方法是基于将管网划分为预定区域,以确定漏损的大致位置。
TheParticle Filter (PF) technique was employed by Anjana et al. (2015) to detect leakage in water pipelinesfor a real network in Karnataka,India. Various models based on the extended
Kalman filter have been widely used to detect leakage in pipelines(e.g.seeDelgado-Aguiñaga et al.2016;Majidi Khalilabadet al.2018).Attari and Maghrebi (2018)detected leakage in WDNs using training data and applying them to theartificial neural networks and nodes with pressure sensors.
Anjana等人(2015)在印度卡纳塔克邦的一段真实管网中使用了粒子滤波(PF)技术检测管道漏水。基于扩展的卡尔曼滤波法的各种模型已被广泛用于管网探漏(如Delgado-Aguinaga 等人. 2016;Majidi Khalilabad等人.2018)。Attari和Maghrebi(2018)利用训练数据检测管网的漏失量,并将其应用到带有压力传感器的人工神经网络和节点上。

来源于互联网
图论在供水管网漏损检测的相关应用
Agraph is a set of points and lines connected to each other.A graph is amathematical model for a discrete set whose members are interrelated in someways. The members of this collection can be cities, and the connection betweenthem is the roads and the bridges. Each graph is an ordered pair G (V, E)comprisinga set of vertices (V) and edges (E), which edges are 2-element subsets ofvertices (i.e. that each edge is associated with two vertices). In thesimulation of a WDN using the graph theory, one can consider the consumer andthe reservoir nodes as the vertices of the graph (V), and the pipes, the pumpsand the valves of the network, as the graph edges (E).One of the vital analysis of a graph is clustering. The clusteringof graphs is a crucial issue uses in many felds, such as even social networking.The main goal of the clustering is to extract parts of data that are verysimilar to each other. The use of graph theory for WDNs accelerates theanalysis of large and complex networks,and also allows for the use of theclustering algorithms in WDN.
图形是相互连接的点和线的集合。图是一个离散集的数学模型,离散集的组成单元在某些方面是相互关联的。这个集合的组成单元可以是城市,而连接城市之间的是道路和桥梁。每个图是一个有序对G (V, E),包含一组点(V)和边(E),边是点的2元素子集(即每条边都由两个点相连组成)。在基于图论建立的一个管网模型中,首先可以将用户和水源作为图形的点(V),将管网中的管道、泵和阀门作为图形的边(E)。图形分析的关键点之一是聚类。在许多领域,甚至是社会网的应用中,图形的聚类都是至关重要的问题。聚类的主要目的是提取互相相似的数据。图论在供水管网中给的应用加速了对大型复杂管网的分析,也同时使聚类算法在管网中应用成为可能。
Graphtheory has also been used in recent years to establish district metered areas(DMAs) or for detecting leakage in the networks. Arsene et al. (2012) presented a decision support system(DSS) for monitoring WDNs. Their method is based on a three-layer General FuzzyMin-Max Neural Network
(GFMMNN) and graph theory. Their training data is obtained by simulation ofleakages in a WDN for 24 hours. Their results showed that leak detection basedon the GFMMNN with considering the variation of nodal consumptions producesbetter recognition rates in comparison to the training based on patterns ofnodal heads and pipe flows state estimates. Sousa et al. (2015) located leaks in WDNs based onsteady-state modeling,supported by monitoring tank flow and pressure atstrategic nodes, and tried to build an optimization problem solving by simulatedalgorithm and graph theory. Kang et al.
近年来,图论被用于建立计量分区(DMAs)或检测管网中的漏水。Arsene等人(2012)提出了一种用于监控管网的决策支持系统(DSS)。他们的方法基于三层通用模糊最小-最大神经网络(GFMMNN)和图论,通过模拟管网24小时内的漏水量来获得训练数据。结果表明,与基于节点和管道流动状态模型的估计数据相比,基于考虑节点损耗变化的GFMMNN模型有更好的探漏识别率。Sousa等人.(2015)基于稳态建模,通过监控水箱流量和战略节点压力,定位管网中的漏水点,并尝试通过模拟算法和图论建立一个最优的探漏方法。
Rajeswaran,Narasimhan, and Narasimhan (2018)introduced a method for finding a leakage in WDNs using graph theory. In theirmethod, they limited the leakage area in the network by step-by-steppartitioning the network into small sub-sections to find the leakage using thelinked pipe flow between each section and water balance in each subsectionusing flowmeters. However, in reality, it is not easy to obtain the flowthrough the pipes between two divided parts, because it requires digging andinstalling a chamber and flowmeter which would not be economic.
Rajeswaran,Narasimhan和Narasimhan(2018)介绍了一种利用图论确定管网漏水点的方法。在他们的方法中,通过逐步将管网划分为小分段来限制漏水区域,利用每个分段之间的管道流量来发现漏水,并利用流量计来平衡每个分段的水量。但在现实中,要获得两个分段之间通过管道的流量并不容易,因为这需要开挖井室并安装流量计,并不经济。
基于图论的人工神经网络(ANN)模型
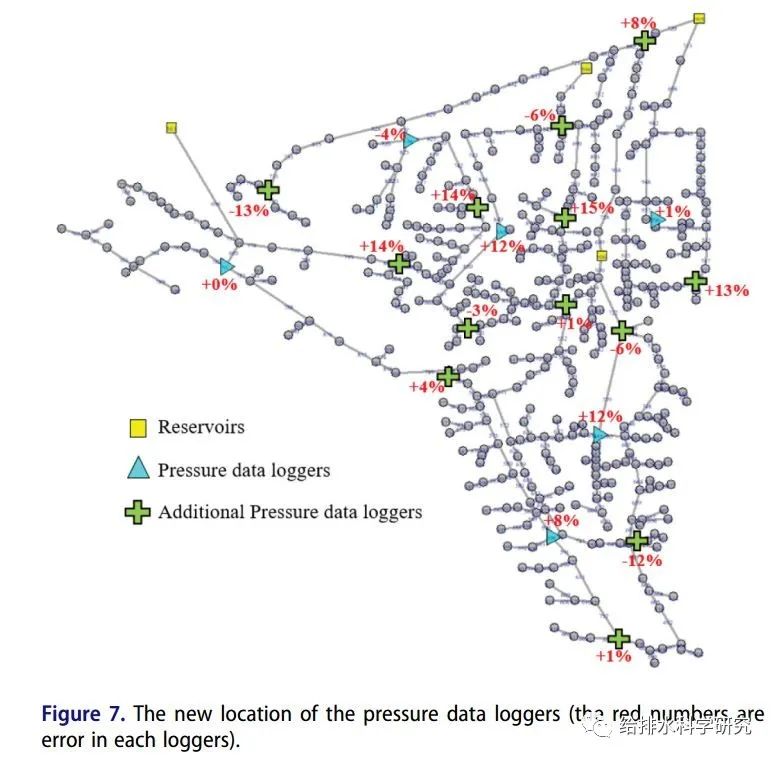
人工神经网络(ANN)是一个通过对已有数据的处理,识别出数据之间潜在关系的系统。使用ANN的目的是对一系列可能发生在现实情景下的新数据,通过生成不同的漏水场景(即改变模型中假设的漏水数量和位置,并且提供训练和验证数据)预测管网漏水的位置和数量。在每个场景中,使用压力记录仪在节点处监测压力。在神经网络的训练中,输入数据是假设的压力记录仪的压力值,目标数据是每个场景的漏水量和漏水位置。值得注意的是,假设的压力记录仪位置的压力值将通过液压求解器(本文指EPANET)获得。通过对神经网络参数的正确调整,ANN可以为每组输入数据(即压力记录仪提供的数据)提供输出(即管网中的漏水)。
一种基于图论和人工神经网络的供水管网漏损检测方法
考虑到真实的管网的规模包括许多节点和管道,在ANN训练中检查所有节点来提供所需的数据将是非常困难的。另一方面,仅对有限个节点产生随机数据似乎不足以获得具有较高泛化能力的神经网络。为了解决这个问题,在本文中,所有根据图论建立的管网的两个部分分别被划分为更小的子群,然后在子群中重复该步骤。也就是说,假设某些上级邻近节点为父节点,则在划分出的子群上继续探测漏水点,而不是在所有节点上。实际上,不是为所有节点生成ANN的训练数据,而是将它们随机重复生成到这些子群中。通过使用该技术,神经网络生成的数据量减少,网络训练更快。例如,如果一个网络有500个节点,我们将需要大量的ANN训练数据,但使用所提出的子群技术,所需数据显著减少。假设我们将10个邻近的节点视为一个父节点,那么搜索空间的规模大约从500减少到50,子群的数量取决于每个区域中的节点数量。
本文介绍了一种通过逐级分解市政配水管网从而探测漏水的方法。首先,通过图论将输配水管网分为两个部分(无漏损部分与漏损部分),然后利用压力计和人工神经网络的测定结果鉴别漏水部分的管道。该步骤重复应用于被确定漏水的部分,以此来缩小漏水的确认范围。已考虑到需水量及压力参数的不确定性情况下,该方法运用于Balerma地区配水管网的五个漏水情景中。研究结果表明,本文提出的方法能相当精确地找到配水管网中的漏水区域。
In the proposedmethod, leakage is detected in each part using the available water pressuredata loggers in the network and ANN (without using any flowmeters). Then theprocess of dividing and detecting is repeated for the selected leakage part torefne the leak location. One of the advantages of the presentapproach is thepracticality of the method for an actual WDN.
本文提出的方法中,首先每个部分的漏水区域可通过获取的压力计及人工神经网络数据探测到(不使用任何流量计),然后对所选漏水区域进行重复划分检测步骤以精确漏水位置。上述方法的优势之一是对于实际管网具有可行性。
以上是关于基于图论和人工神经网络的供水管网漏损检测方法(上)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章