数据结构与算法第三章:表栈和队列
Posted Coder的自我修养
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构与算法第三章:表栈和队列相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【数据结构与算法】第三章:表、栈和队列
标签(空格分隔): 【数据结构与算法】
第三章:表、栈和队列
3.1 抽象数据类型
抽象数据类型(abstract data type,ADT) ADT是数学的抽象,在ADT的定义中根本没有设计如何实现操作的集合。可以看作是模块化设计的扩充。例如,对于集合ADT,我们有并(union),交(intersection),测定大小(size),取余(complement),查找(find)等操作. 思想:这些操作的实现只在程序中编写一次,在程序中任何其他部分要在该ADT上运行其中的一种操作时可以通过调用适当的函数来进行.
3.2 表ADT
形如 $ A1 ,A2,...A_N $ 的表,我们说这个表的大小是N.
名词解释
空表:大小为0的表.(empty list)
前驱元、后继元:对于非空表以外的任何表,我们说 $ A{i+1} $ 是 $ Ai $ 的后继元,称 $ Ai $ 是 $ A{i+1} $ 的前驱元.对于 $ A1 $ 没有前驱元,对于 $ AN $ 没有后继元.
一些ADT
PrintList:打印链表.
MakeEmpty:创建一个空链表.
Find:返回关键字首次出现的位置.
Insert:从表的某个位置插入某个关键字.
Delete:从表的某个位置删除某个关键字.
FindKth:返回某个位置.
Length:返回链表长度.
3.2.1 表的数组实现
\\制作空表
List MakeEmpty(){
List PtrL;
PtrL = ( List)malloc( sizeof( struct LNode));
PtrL = -1;
return PtrL;
}
\\查找某个元素 返回下标
int Find( ElementType X, List PtrL){
int i;
while( i <= PtrL->Last && PtrL->Data[i] != X)
i++;
if( i > PtrL->Last) return -1;
else return i;
}
\\在第i个位置上插入元素
void Inser( ElementType X, int i, List PtrL){
int j;
if( PtrL->Last == MAXSIZE - 1){
printf("表满");
return;
}
if( i < 1 || i > PtrL->Last + 2){
printf("位置不合法");
return;
}
for( j = PtrL->Last; j > i; j--)
PtrL->Data[j+1] = PtrL->Data[j];
PtrL->Data[i] = X;
PtrL->Last++;
}
\\删除第i个位置的元素
void Delete( int i, List PtrL){
int j;
if( i < 1 || i > PtrL->Last + 1){
printf("位置不合法");
return;
}
for( j = i; j < PtrL->Last; j++)
PtrL->Data[j] = PtrL->Data[j+1];
PtrL->Last--;
}
3.2.2 链表
链表由一系列不必再内存中相连的结构组成。每个结构均含有表元素和指向包含该元素后继元的结构的指针.这个指针便是Next指针.
ANSI C 规定NULL为零.
表头\哑结点:一个标志结点,约定表头处于位置0处.
//ADT
List MakeEmpty( List L);
//是否是空表
int IsEmpty( List L);
//当前位置是否是末尾
int IsLast( Position P, List L);
//返回X的位置
Position Find( ElementType X, List L);
//返回X的前一个位置
Position FindPrevious( ElementType X, List L);
//删除某个位置元素
void Delete( ElementType X, List L);
//插入
void Insert( ElementType X, List L, Position P);
void DeleteList( List L);
Position Header( List L);
Position First( List L);
Position Advance( Position P);
ElementType Retriece( Position P);
//具体实现
int IsEmpty( List L){ //Return true if L is empty
return L->Next == NULL;
}
int IsLast( Position P, List L){
return P->Next == NULL;
}
Position Find( ElementType X, List L){
Position P;
P = L->Next;
while( P != NULL && P->Element != X)
P = P->Next;
return P;
}
Position FindPrevious( ElementType X, List L){
//假设存在表头
Position P;
P = L;
while( P->Next != NULL && P->Next->Element != X)
P = P->Next;
return P;
}
void Delete( ElementType X, List L){
Position P, TmpCell;
P = FindPrevious( X, L); //假设存在表头
if( !IsLast( P,L)){ //P不是最后一个位置时
TmpCell = P->Next; //考虑到P是指向X的钱一个位置
P->Next = TmpCell->Next; //若X存在,则P肯定不是最后一个位置
free( TmpCell);
}
}
void Insert( ElementType X, List L, Position P){
Position TmpCell;
TmpCell = ( Position)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
if( TmpCell == NULL)
FatalError("Out of space!");
TmpCell->Element = X;
TmpCell->Next = P->Next;
P->Next = TmpCell;
}
3.2.3 双链表
在数据结构上附加一个域,使它包含只想钱一个单元的指针. 代价:由于需要更多的指纹定位,因此增加了空间的需求,同时使得删除和插入的开销增加了一倍.

3.2.4 循环链表
最后的单元反过来直接指向第一个单元. 它可以有表头、也可以没有.当表头存在的时候,便让最后一个单元指向它. 还可以是一种双向链表.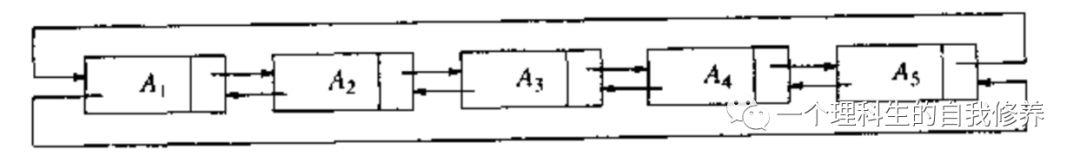
3.2.5 例题
多项式ADT 定义一种一元(具有非负次幂)多项式的抽象数据类型, $$ F(X) = \sum{i=0}^NAiX^i $$
对于大部分系数为0的多项式,可以使用一个简单数组来储存这些系数.之后进行加减乘除等操作.
//数组实现声明
typedef struct{
int CoeffArray[ NaxDegree + 1];
int HighPower;
} *Polynomial;
//初始化为0
void ZeroPolynomial( Polynomial Poly){
int i;
for( i=0; i <= MaxDegree; i++)
Poly->CoeffArray[ i] = 0;
Poly->HighPower = 0;
}
//相加
void AddPolynomial( const Polynomial Poly1, const Polynomial Poly2,
Polynomial PolySum){
int i;
ZeroPolynomial( PolySum);
PolySum->HighPower = Poly1->HighPower > Poly2->HighPower ? Poly1->HighPower : Poly2->HighPower;
for( i = PolySum->HighPower; i >= 0; i--){
PolySum->CoeffArray[i] = Poly1->CoeffArray[i] + Poly2->CoeffArray[i];
}
}
//相乘
void MultPolynomial( const Polynomial Poly1, const Polynomial Poly2,
Polynomial PolyProd){
int i, j;
ZeroPolynomial( PolyProd);
PolyProd->HighPower = Poly1->HighPower * Poly2->HighPower;
if( PolyProd->HighPower > MaxDegree)
Error("Exceeded array size");
else
for( i = 0; i < Poly1->HighPower; i++)
for( j = 0; j < Poly2->HighPower; j++)
PolySum->CoeffArray[ i+j] = Poly1->CoeffArray[i] + Poly2->CoeffArray[j];
}
2 . 使用单链表表示,多项式的每一项包含于一个单元中,同时,这些单元以次数递减的顺序排序.如下图: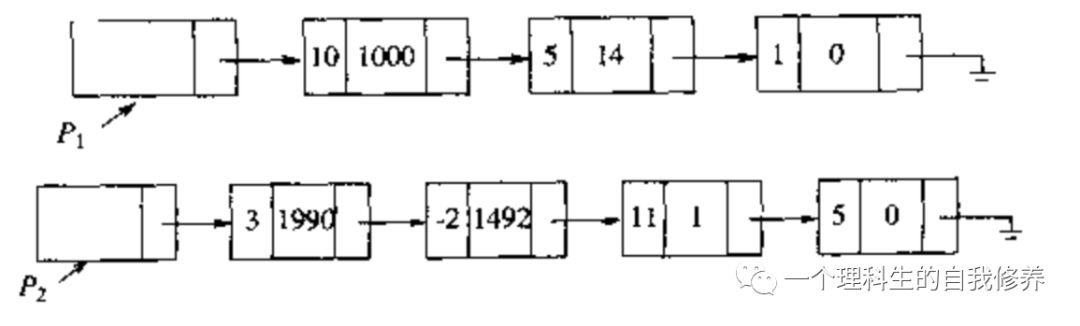
//链表实现声明
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node{
int Coefficient;
int ExPonent;
PtrToNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToNode Polynomial;
void Attach( int c, int e, Polynomial *pRear){
Polynomial P;
P = ( Polynomial)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
P->Coef = c;
P->Expon = e;
*pRear -> Next = P;
*pRear = P;
}
//相加
Polynomial PolyAdd( Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2){
Polynomial front, rear, temp;
int sum;
rear = ( Polynomial)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
front = rear; //front 指向表头
while( P1 && P2){
if( P1->Expon > P2->Expon){
Attach( P1->Coef, P1->Expon, &rear);
P1 = P1->Next;
}
else if( P1->Expon < P2->Expon){
Attach( P2->Coef, P2->Expon, &rear);
P2 = P2->Next;
}
else if( P1->Expon < P2->Expon){
sum = P1->Coef + P2->Coef;
if( sum) //sum not equals 0
Attach( sum, P1->Expon, &rear);
P2 = P2->Next;
P1 = P1->Next;
}
}
for( ; P1; P1 = P1->Next) Attach( P1->Coef, P1->Expon, &rear);
for( ; P2; P2 = P2->Next) Attach( P2->Coef, P2->Expon, &rear);
rear->Next = NULL;
temp = front;
front = front->Next;
free(temp);
return fornt;
}
//相乘
Polynomial PolyMult( Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2){
Polynomial P, Rear, t1, t2, t;
int c, e;
if( !P1 || !P2) return NULL; //存在空表时
t1 = P1; t2 = P2;
P = ( Polynomial)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
Rear = P;
while( t2){ //先用P1的第一项乘P2
Attach( t1->Coef * t2->Coef, t1->Expon + t2->Expon, &Rear);
t2 = t2->Next;
}
t1 = t1->Next;
while( t1){
t2 = P2; Rear = P;
while( t2){
c = t1->Coef * t2->Coef;
e = t1->Expon + t2->Expon;
while( Rear->Next && Rear->Next->Expon > e)
Rear = Rear->Next;
if( Rear->Next && Rear->Next->Expon == e){
if( Rear->Next->Coef + c)
Rear->Next->Coef += c;
else{
t = Rear->Next;
Rear->Next = t->Next;
free(t);
}
}
else{
t = ( Polynomial)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
t->Coef = c; t->Expon = e;
t->Next = Rear->Next;
Rear->Next = t;
Rear = Rear->Next;
}
t2 = t2->Next;
}
t1 = t1->Next;
}
t2 = P;
P = P->Next;
free( t2);
return P;
}
基数排序 基数排序有时候也成为卡式排序. 桶式排序:假定我们有 $ N $ 个整数,大小范围从 $ 1 $ 到 $ M $ (或者从 $ 0 $ 到 $ M-1 $),我们创建一个数组,名为 $ Count $ ,大小为 $ M $ ,并初始化为0,当 $ Ai $ 被读入时, $ Count[Ai] $ 增 $ 1 $ .当所有的输入被读进后,扫描数组 $ Count $,打印输出排好序的表.该算法时间复杂度为 $ O(M+N) $. 基数排序:上述方法的推广.假设我们有 10 个数字,带下范围从 0 到 999 之间,显然,如果采取桶排序的方法,“桶”便太多了. 于是,我们可以对最低的有效位优先进行排序. 举例: 输入: 64, 8, 216, 512, 27, 729, 0, 1, 343, 125. 第一趟排序:对个位数字
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 512 | 343 | 64 | 125 | 216 | 27 | 8 | 729 |
第二趟排序:对十位数字
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 512 | 125 | 343 | 64 | |||||
| 1 | 216 | 27 | |||||||
| 8 | 729 |
第二趟排序:对百位数字
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 125 | 216 | 343 | 512 | 729 | ||||
| 1 | |||||||||
| 8 | |||||||||
| 27 | |||||||||
| 64 |
3.2.6 多重表
3.2.7 链表的游标实现
3.3 栈ADT
3.3.1 栈模型
栈 被限制插入和删除只能在一个位置上进行的表,这个位置是表的末端,叫做栈顶.
基本操作 进栈 $ Push $ 出栈 $ Pop $
LIFO: Last In First Out 后进先出
3.3.2 栈的实现
3.3.2.1 单链表
在表的顶端(不可以是尾端,因为尾端无法实现出栈的操作)实现进栈 $ Push $ 和 出栈 $ Pop $.
struct Node{
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode Next;
};
int IsEmpty( Stack S); //是否是空栈
Stack CreateStack(); //创建一个栈
void DisposeStack( Stack S);
void MakeEmpty( Stack S); //变空
void Push( ElementType X, Stack S);
void Pop( Stack S);
ElementType Top( Stack S); //返回栈顶
//检测是否为空栈
int IsEmpty( Stack S){
return S->Next == NULL;
}
//创建一个空栈
Stack CreateStack(){
Stack S;
S = ( Stack)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
if( S == NULL)
FatalError(" Out of space");
S->Next = NULL;
MakeEmpty( S);
return S;
}
void MakeEmpty( Stack S){
if( S == NULL)
Error(" Must use CreateStack first");
else{
while( IsEmpty( S))
Pop( S);
}
}
//进栈
void Push( ElementType X, Stack S){
PtrToNode TmpCell;
TmpCell = ( Stack)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
if( TmpCell == NULL)
FatalError(" Out of space");
else{
TmpCell->Element = X;
TmpCell->Next = S->Next; //存在表头
S->Next = TmpCell;
}
}
//出栈
void Pop( Stack S){
PtrToNode FirstCell;
if( IsEmpty( S))
Error(" Empty stack");
else{
FirstCell = S->Next;
S->Next = S->Next->Next
free( FirstCell);
}
}
//返回栈顶元素
ElementType Top( Stack S){
if( !IsEmpty( S)) //当S不空时
return S->Next->Element;
Error(" Empty stack");
return 0; //避免警告
}
3.3.2.2 数组实现
注意:如果使用数组实现,我们需要提前声明数组大小.
struct StackRecord{
int Capacity;
int TopOfStack;
ElementType *Array;
};
int IsEmpty( Stack S);
int IsFull( Stack S);
Stack CreateStack( int MaxElements);
void DisposeStack( Stack S);
void MakeEmpty( Stack S);
void Push( ElementType X, Stack S);
ElementType Top( Stack S);
void Pop( Stack S);
ElementType TopAndPop( Stack S);
//栈的创建
int CreateStack( int MaxElements){
Stack S;
if( MaxElements < MinStackSize)
Error(" Stack size is too small");
S = ( Stack)malloc( sizeof( struct StackRecord));
if( S == NULL)
FatalError(" Out of space");
S->Array = malloc( sizeof( struct ElementType));
if( S->Array == NULL)
FatalError(" Out of space");
S->Capacity = MaxElements;
MakeEmpty(S);
return S;
}
//创建一个空栈
int MakeEmpty( Stack S){
S->TopOfStack = EmptyTOS;
}
//检测一个栈是否为空
int IsEmpty( Stack S){
return S->TopOfStack == EmptyTOS;
}
//释放栈
void DisposeStack( Stack S){
if( S != NULL){
free( S->Array);
free( S);
}
}
//返回栈顶
ElementType Top( Stack S){
if( !IsEmpty( S)) //栈非空
return S->Array[ S->TopOfStack];
Error(" Empty Stack");
return 0; //防止出现警告
}
//进栈
void Push( ElementType X, Stack S){
if( IsFull( S))
Error(" Full Stack");
else
S->Array[ ++ S->TopOfStack ] = X;
}
//出栈
void Pop( Stack S){
if( IsEmpty( S))
Error(" Empty Stack");
else
S->TopOfStack--;
}
//给出栈顶元素并弹出
ElementType TopAndPop( Stack S){
if( !IsEmpty( S))
return S->Array[ S->TopOfStack --];
Error(" Empty Stack");
return 0; //防止出现警告
}
3.3.3 应用
平衡符号
描述: 序列 "[()]" 是合法的,"[(])"是非法的.
解题思路: 创建一个空栈,读入字符直到文件尾. 如果字符是一个开放的符号,比如左括号,那么就将他推入堆栈中, 如果字符是一个封闭的括号,比如有括号,当栈是空时,就报错,否则就将栈的元素弹出.如果弹出的不是对应的开放符号,就报错.在文件尾,如果栈非空就报错.
中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式
改写成后缀表达式方法:对于一行表达式,从左到右依次读取,如果是操作数就将它输出.遇到操作符 A 就将它压入堆栈 (此时可以视 A 为栈顶元素) ,直到遇到下一个操作符 B ,如果操作符 B 比栈顶操作符 (A) 的优先级低(或者相同),则弹出 A ,反之则压入堆栈. 遇到括号时,把左括号压入堆栈中,并同时从左括号起视为一个新的堆栈.
举例: 对于中缀表达式:a + b * c + ( d * e + f) * g
| 步骤 | 堆栈 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | |
| 2 | + | a |
| 3 | + | ab |
| 4 | +* | ab |
| 5 | +* | abc |
| 6 | + | abc*+ |
| 7 | + | abc*+ |
| 8 | +( | abc*+ |
| 9 | +( | abc*+d |
| 10 | +(* | abc*+de |
| 11 | +(+ | abc+def |
| 12 | +(+ | abc+def |
| 13 | +* | abc+def+g |
| 14 | abc+def+g*+ |
递归调用: 系统将整个程序运行时所需的数据空间安排在一个栈中,每当调用一个函数时,就为它在栈顶分配一个存储区,每当从一个函数退出时,就释放这个存储区,因此当前运行的函数的数据必定储存在栈顶.
3.4 队列ADT
队列: 插入在一端进行而删除在另一端进行的一种表.
3.4.1 队列模型
基本操作: $ Enqueue $ 入队:在表的末端( $ rear $ 队尾 )插入一个元素. $ Dequeue $ 入队:删除(或返回)表的开头( $ front $ 队头 )的元素.
3.4.2 队列实现
3.4.2.1 队列的链表实现
只能在链表头部进行删除(出队)操作,尾部进行插入(入队)操作
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node{ //队列中的结点
ElementType Data;
PtrToNode Next;
};
typedef struct PtrToNode Position;
struct QNode{
Position Front, Rear;
int MaxSize;
};
typedef struct QNode *Queue;
//判断是否为空
int IsEmpty( Queue Q){
return Q->Front == NULL;
}
//出队
ElementType DeleteQ( Queue Q){
Position FrontCell;
ElementType FrontElem;
if( IsEmpty( Q)){
printf("队列空");
return ERROR;
}
else{
FrontCell = Q->Front;
if( Q->Rear == Q->Front)
Q->Rear = Q->Front = NULL;
else
Q->Front = Q->Front->Next;
FrontElem = FrontCell->Data;
return FrontElem;
}
}
//入队
void Enqueue( ElementType X, Queue Q){
Position P;
P = ( Position)malloc( sizeof( struct Node));
P->Data = X;
P->Next = NULL;
Q->Rear->Next = P;
}
3.4.2.2 队列的数组实现
typedef int Position;
struct QNode{
ElementType *Data;
Position Front, Rear;
int MaxSize;
};
typedef QNode *Queue;
//创建队列
Queue CreatQueue( int MaxSize){
Queue Q = ( Queue)malloc( sizeof( struct QNode));
Q->Data = ( ElementType *)malloc( MaxSize * sizeof( ElementTYpe));
Q->Front = Q->Rear = 0;
Q->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return Q;
}
//是否满
int IsFull( Queue Q){
return (Q->Rear + 1) % Q->MaxSize == Q->Front ;
}
//入队
int AddQ( Queue Q, ElementType X){
if( IsFull( Q)){
printf("队列满");
return ERROR;
}
else{
Q->Rear = (Q->Rear+1) % Q->MaxSize;
Q->Data[Q->Rear] = X;
return 1;
}
}
//是否空
int IsEmpty( Queue Q){
return Q->Front == Q->Rear;
}
//出队
ElementType DeleteQ( Queue Q){
if( IsEmpty( Q)){
printf("队列空");
return ERROR;
}
else{
Q->Front = (Q->Front+1) % Q->MaxSize;
return Q->Data[ Q->Front];
}
}
3.4.2 队列的应用
生活中排队购票;
公司的传呼.
以上是关于数据结构与算法第三章:表栈和队列的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章