第18期:对称加密和非对称加密 | Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
Posted 曹帅读书笔记与生活随笔
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第18期:对称加密和非对称加密 | Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
读万卷书,行万里路,尝千家食,交一二友。月下,灯前,捧一本佳作,品一杯茗茶。窗外霓虹闪烁,川流不息。桌前清淡如水,万物静谧。任思绪驰骋,凭大浪滔天,我自埋头于知识的象牙塔,享受一时之欢愉。
公开密钥加密(英语:Public-key cryptography),也称为非对称加密(英语:asymmetric cryptography),是密码学的一种算法,它需要两个密钥,一个是公开密钥,另一个是私有密钥;一个用作加密,另一个则用作解密。使用其中一个密钥把明文加密后所得的密文,只能用相对应的另一个密钥才能解密得到原本的明文;甚至连最初用来加密的密钥也不能用作解密。由于加密和解密需要两个不同的密钥,故被称为非对称加密;不同于加密和解密都使用同一个密钥的对称加密。虽然两个密钥在数学上相关,但如果知道了其中一个,并不能凭此计算出另外一个;因此其中一个可以公开,称为公钥,任意向外发布;不公开的密钥为私钥,必须由用户自行严格秘密保管,绝不透过任何途径向任何人提供,也不会透露给被信任的要通信的另一方。
基于公开密钥加密的特性,它还提供数字签名的功能,使电子文件可以得到如同在纸本文件上亲笔签署的效果。
公开密钥基础建设透过信任数字证书认证机构的根证书、及其使用公开密钥加密作数字签名核发的公开密钥认证,形成信任链架构,已在TLS实现并在万维网的HTTP以HTTPS、在电子邮件的SMTP以STARTTLS引入。
另一方面,信任网络则采用去中心化的概念,取代了依赖数字证书认证机构的公钥基础设施,因为每一张电子证书在信任链中最终只由一个根证书授权信任,信任网络的公钥则可以累积多个用户的信任。PGP就是其中一个例子。
(中文介绍来源链接:https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%85%AC%E5%BC%80%E5%AF%86%E9%92%A5%E5%8A%A0%E5%AF%86)
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption – What are differences?
对称加密和非对称加密的区别
Information security has grown to be a colossal(巨大的)factor, especially with modern communication networks, leaving loopholes(漏洞)that could be leveraged(利用)to devastating effects(毁灭性的后果). This article presents a discussion on two popular encryption schemes(加密方法)that can be used to tighten communication security in Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption. In principle, the best way to commence(开始)this discussion is to start from the basics first. Thus, we look at the definitions of algorithms and key cryptographic concepts and then dive into the core part of the discussion where we present a comparison of the two techniques.
Algorithms(算法)
An algorithm is basically a procedure(程序)or a formula(公式)for solving a data snooping(窥探;窥视)problem. An encryption algorithm is a set of mathematical procedure for performing encryption on data. Through the use of such an algorithm, information is made in the cipher text(密文)and requires the use of a key to transforming the data into its original form. This brings us to the concept of cryptography(密码学)that has long been used in information security in communication systems.
Cryptography(密码学)
Cryptography is a method of using advanced mathematical principles in storing(存储)and transmitting(传输)data in a particular form so that only those whom it is intended can read and process it. Encryption(加密)is a key concept in cryptography – It is a process whereby a message is encoded(编码)in a format that cannot be read or understood by an eavesdropper(窃听者). The technique is old and was first used by Caesar to encrypt his messages using Caesar cipher(凯撒密码). A plain text from a user can be encrypted to a ciphertext, then send through a communication channel(信道)and no eavesdropper can interfere with the plain text. When it reaches the receiver end, the ciphertext is decrypted(解密)to the original plain text.
Cryptography Terms(密码学术语)
---Encryption(加密): It is the process of locking up information using cryptography. Information that has been locked this way is encrypted.
---Decryption(解密): The process of unlocking the encrypted information using cryptographic techniques.
---Secret Key(密钥): A secret like a password used to encrypt and decrypt information. There are a few different types of keys used in cryptography.
---Steganography(速记式加密): It is actually the science of hiding information from people who would snoop on(窥探)you. The difference between steganography and encryption is that the would-be snoopers(潜在的窥探者)may not be able to tell there’s any hidden information in the first place.
Symmetrical Encryption(对称加密)
This is the simplest kind of encryption that involves only one secret key(密钥)to cipher(加密)and decipher(解密)information. Symmetrical encryption is an old and best-known technique. It uses a secret key that can either be a number, a word or a string of random letters. It is a blended with the plain text of a message to change the content in a particular way. The sender(发送者)and the recipient(接收者)should know the secret key that is used to encrypt and decrypt all the messages. Blowfish, AES, RC4, DES, RC5, and RC6 are examples of symmetric encryption. The most widely used symmetric algorithm is AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256.
The main disadvantage of the symmetric key encryption is that all parties involved have to exchange the key used to encrypt the data before they can decrypt it.
Asymmetrical Encryption(非对称加密),又称Public-Key Cryptography(公开密钥加密)
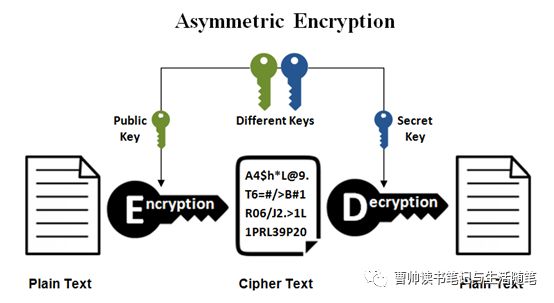
Asymmetrical encryption is also known as public key cryptography, which is a relatively new method, compared to symmetric encryption. Asymmetric encryption uses two keys to encrypt a plain text. Secret keys are exchanged over the Internet or a large network. It ensures that malicious(邪恶的)persons do not misuse the keys. It is important to note that anyone with a secret key can decrypt the message and this is why asymmetrical encryption uses two related keys to boosting security(增强安全性). A public key is made freely available to anyone who might want to send you a message. The second private key is kept a secret so that only you can know.
A message that is encrypted using a public key can only be decrypted using a private key, while also, a message encrypted using a private key can be decrypted using a public key. Security of the public key is not required because it is publicly available and can be passed over the internet. Asymmetric key has a far better power in ensuring the security of information transmitted during communication.
Asymmetric encryption is mostly used in day-to-day communication channels, especially over the Internet. Popular asymmetric key encryption algorithm includes EIGamal, RSA, DSA, Elliptic curve techniques, PKCS.
Asymmetric Encryption in Digital Certificates
To use asymmetric encryption, there must be a way of discovering public keys. One typical technique is using digital certificates(数字证书)in a client-server model of communication. A certificate is a package of information that identifies a user and a server. It contains information such as an organization’s name, the organization that issued the certificate, the users’ email address and country, and user’s public key.
When a server and a client require a secure encrypted communication, they send a query over the network to the other party, which sends back a copy of the certificate. The other party’s public key can be extracted from the certificate. A certificate can also be used to uniquely identify the holder.
SSL/TLS uses both asymmetric and symmetric encryption, quickly look at digitally signed certificates issued by trusted certificate authorities (CAs).
Source: https://www.ssl2buy.com/wiki/symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption-what-are-differences
读书笔记与生活随笔
英语王国
以上是关于第18期:对称加密和非对称加密 | Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章