.netcore consul实现服务注册与发现-集群完整版
Posted dotNET跨平台
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了.netcore consul实现服务注册与发现-集群完整版相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、Consul的集群介绍
Consul Agent有两种运行模式:Server和Client。这里的Server和Client只是Consul集群层面的区分,与搭建在Cluster之上的应用服务无关, 以Server模式运行的Consul Agent节点用于维护Consul集群的状态,官方建议每个Consul Cluster至少有3个或以上的运行在Server Mode的Agent,Client节点不限。
1、Server节点需要三台或以上机器
2、Client节点不限
二、Consul环境准备
准备了三台Linux(CentOS)虚拟机(Consul Server)二台Linux(CentOS)虚拟机(Consul Client)
Consul Server服务IP分别为:
192.168.31.175
192.168.31.176
192.168.31.177
Consul Client服务IP分别为:
192.168.31.178
192.168.31.179
其中,192.168.31.175会作为leader角色,其余两台192.168.31.176和192.168.31.177会作为follower角色。当然,实际环境中leader角色不会是一个固定的,会随着环境的变化(比如Leader宕机或失联)由算法选出新的leader。在进行下面的操作会前,请确保三台节点能够相互ping通,并能够和宿主机也ping通。另外,192.168.31.178和192.168.31.179会作为client角色,并且和其余三台虚拟机互相ping通。
三、Consul正式安装
可以参考上一篇文章的安装方法:.netcore consul实现服务注册与发现-单台节点
一定保证以上五台安装成功
1、测试Consul是否安装成功
> consul如下图表示成功:
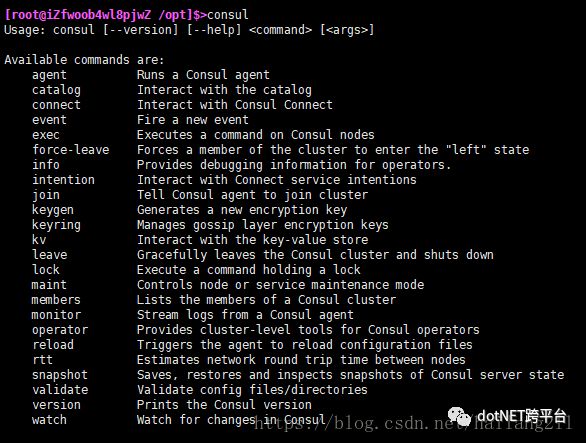
2、Consul Server服务端安装(启动与配置Consul服务)
服务端192.168.31.175执行
> consul agent -server -ui -bootstrap-expect=3 -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul-175 -client=0.0.0.0 -bind=192.168.31.175 -datacenter=dc1服务端192.168.31.176执行
> consul agent -server -ui -bootstrap-expect=3 -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul-176 -client=0.0.0.0 -bind=192.168.31.176 -datacenter=dc1 -join 192.168.31.175服务端192.168.31.177执行
> consul agent -server -ui -bootstrap-expect=3 -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul-177 -client=0.0.0.0 -bind=192.168.31.177 -datacenter=dc1 -join 192.168.31.175注:因为是集群安装,bootstrap-expect=3,以服务端的数量为准
datacenter=dc1,三台必须在一个数据中心
176和177的启动命令中,有一句 -join 192.168.31.175 => 有了这一句,就把176和177加入到了175所在的集群中。
启动之后,集群就开始了Vote(投票选Leader)的过程
命令:查看各个server的情况:
> consul members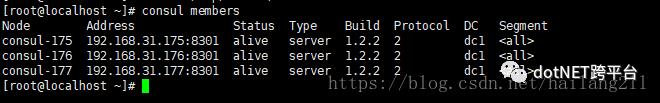
命令:查看目前全部的consul的角色状态:
> consul operator raft list-peers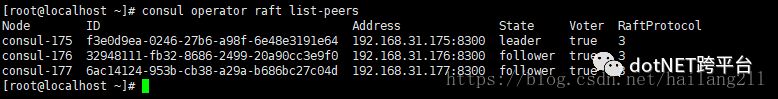
3、通过UI查看集群状态
Consul不仅提供了丰富的命令查看集群情况,还提供了一个WebUI,默认端口8500,我们可以通过访问这个URL(eg. http://192.168.31.175:8500)得到如下图所示的WebUI:
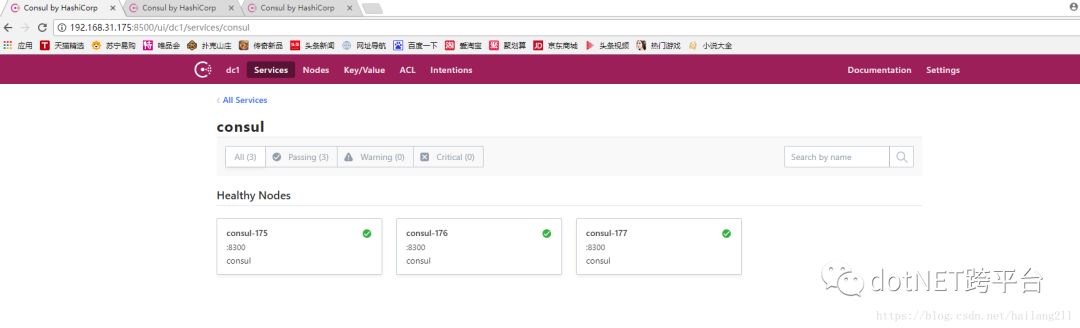
4、模拟Leader挂掉,查看Consul集群的新选举Leader
直接停止192.168.31.175的服务,或者暴力直接关机
输入命令查看服务状态
> consul members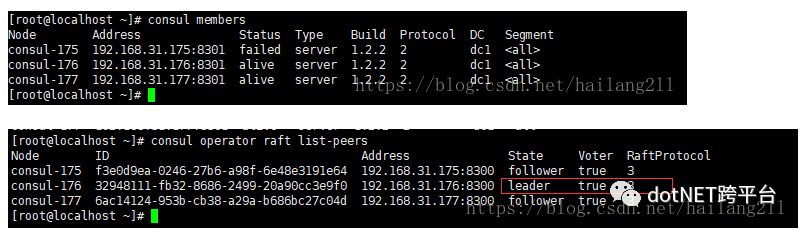
查看其余两个节点的日志或者命令可以发现,consul-176被选为了新的leader
我们也可以在次通过UI界面来查看状态:
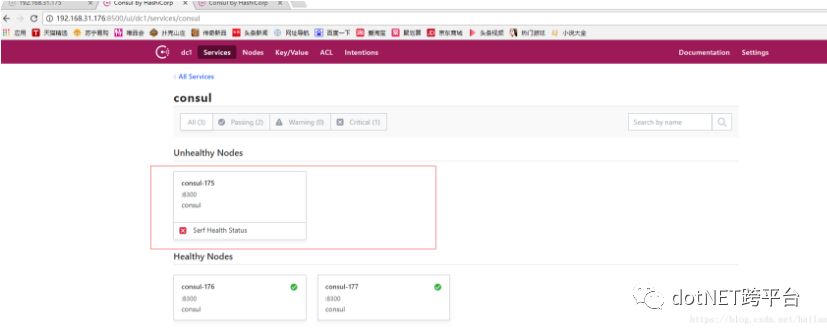
虽然这里192.168.31.175这个原leader节点挂掉了,但是只要超过一半的Server(这里是2/3还活着)还活着,集群是可以正常工作的,这也是为什么像Consul、ZooKeeper这样的分布式管理组件推荐我们使用3个或5个节点来部署的原因。
注:以上也可以将.netcore项目部署在Consul Server上,但官方建议用Consul Client来关联,分别做各自的事情,互不影响。
5、Consul Client安装
为了节约虚拟机,目前在192.168.31.178部署.netcore项目
> mkdir /data/mvc
> mkdir /data/api
> cd /data/mvc/
> dotnet new mvc
> cd /data/api/
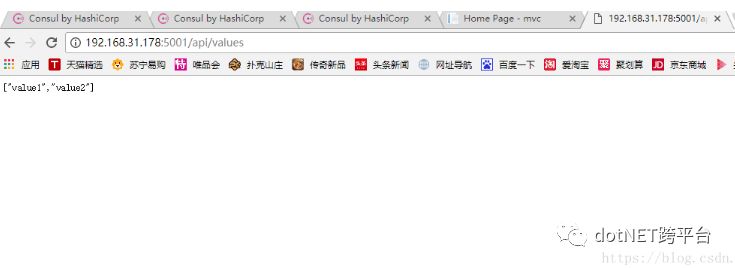
> dotnet new webapi
>dotnet run
6、将.netcore服务注册到Consul(通过配置文件来注册服务)
vi /etc/consul/services_config.json
{
"services":[
{
"id": "CLIENT_SERVICE_01",
"name" : "MVCClientService",
"tags": [
"urlprefix-/MVCClientService01"
],
"address": "192.168.31.178",
"port": 5000,
"checks": [
{
"name": "clientservice_check",
"http": "http://192.168.31.178:5000",
"interval": "10s",
"timeout": "5s"
}
]
},
{
"id": "CLIENT_SERVICE_02",
"name" : "APIClientService",
"tags": [
"urlprefix-/APIClientService02"
],
"address": "192.168.31.178",
"port": 5000,
"checks": [
{
"name": "clientservice_check",
"http": "http://192.168.31.178/api/values",
"interval": "10s",
"timeout": "5s"
}
]
}
]
}
在Consul Client 192.168.31.178运行命令:
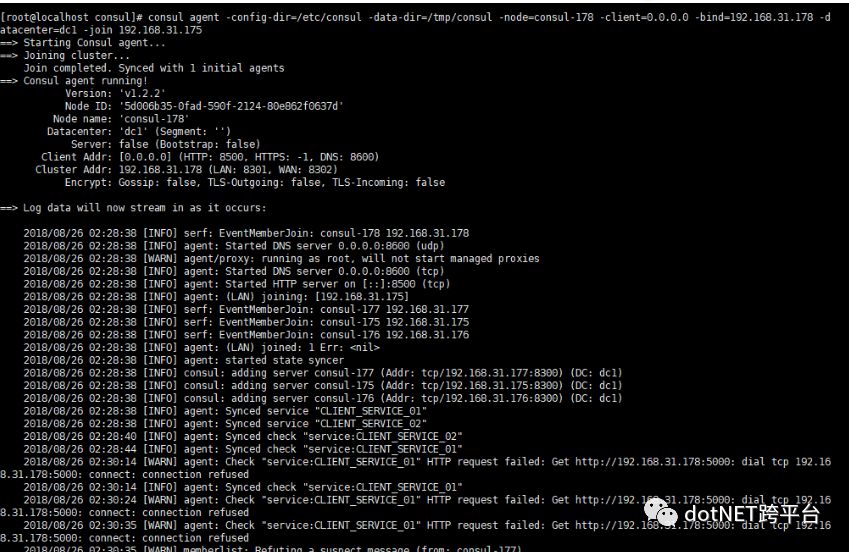
consul agent -config-dir=/etc/consul -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul-178 -client=0.0.0.0 -bind=192.168.31.178 -datacenter=dc1 -join 192.168.31.175如下图表示正常启动,并将192.168.31.178加入到服务集群192.168.31.175中
7、查看Consul集群状态
可以看到192.168.31.178加入到了集群中,表示正常,还能看到.netcore的两个服务哦,也表示正常
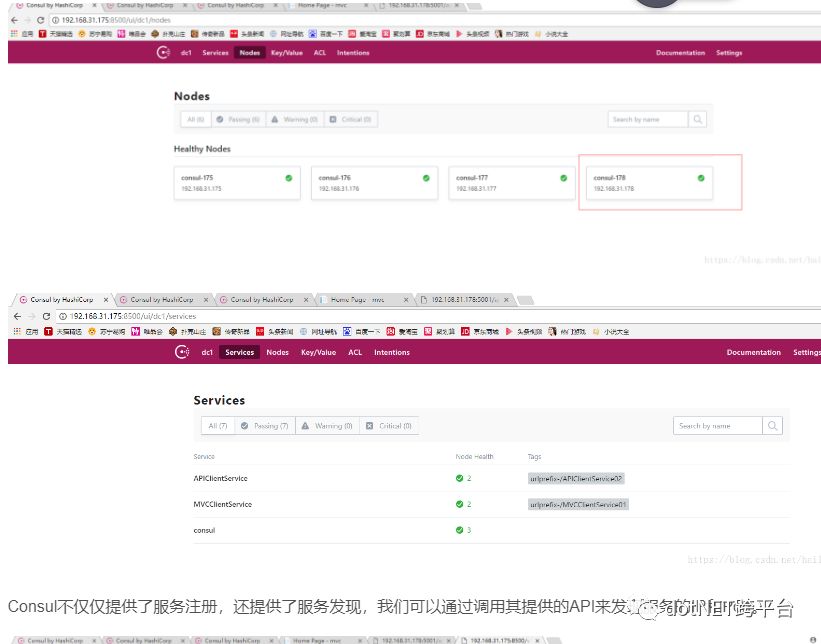
Consul不仅仅提供了服务注册,还提供了服务发现,我们可以通过调用其提供的API来发现服务的IP和Port。
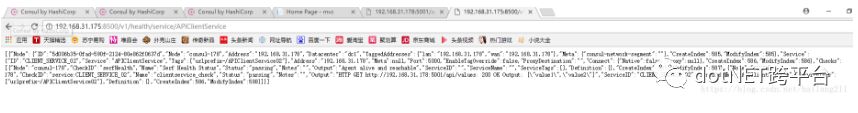
8、通过consul api 接口注册服务
创建一个ASP.NET Core WebAPI程序

创建一个HealthController用于Consul的健康检查
[Produces("application/json")]
[Route("api/Health")]
public class HealthController : Controller
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get() => Ok("ok");
}
注:Consul会通过call这个API来确认Service的健康状态。
基于IApplicationBuilder写一个扩展方法,用于调用Consul API
在nuge管理器中引入Consul包
public static class ConsulBuilderExtensions
{
// 服务注册
public static IApplicationBuilder RegisterConsul(this IApplicationBuilder app, IApplicationLifetime lifetime, HealthService healthService, ConsulService consulService)
{
var httpCheck = new AgentServiceCheck()
{
DeregisterCriticalServiceAfter = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5),//服务启动多久后注册
Interval = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10),//健康检查时间间隔,或者称为心跳间隔
Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)
};
// Register service with consul
var registration = new AgentServiceRegistration()
{
Checks = new[] { httpCheck },
ID = healthService.Name + "_" + healthService.Port,
Name = healthService.Name,
Address = healthService.IP,
Port = healthService.Port,
Tags = new[] { $"urlprefix-/{healthService.Name}" }//添加 urlprefix-/servicename 格式的 tag 标签,以便 Fabio 识别
};
consulClient.Agent.ServiceRegister(registration).Wait();//服务启动时注册,内部实现其实就是使用 Consul API 进行注册(HttpClient发起)
lifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
consulClient.Agent.ServiceDeregister(registration.ID).Wait();//服务停止时取消注册
});
return app;
}
}
在Starup类的Configure方法中,调用此扩展方法
#region register this service
ConsulService consulService = new ConsulService()
IP = Configuration["Consul:IP"],
Port = Convert.ToInt32(Configuration["Consul:Port"])
};
HealthService healthService = new HealthService()
{
IP = Configuration["Service:IP"],
Port = Convert.ToInt32(Configuration["Service:Port"]),
Name = Configuration["Service:Name"],
};
app.RegisterConsul(lifetime, healthService, consulService);
#endregion
其中用到了appSettings.json配置文件,其定义如下:
"Service": {
"Name": "DMSWebAPITest",
"IP": "localhost",
"Port": "5001"
},
"Consul": {
"IP": "localhost",
"Port": "8500"
}
其中ConsulService类定义如下:
public class ConsulService
{
public string IP { get; set; }
public int Port { get; set; }
}
其中HealthService类定义如下:
public class HealthService
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string IP { get; set; }
public int Port { get; set; }
}
确保HealthController的API能正常访问,以便做健康检查
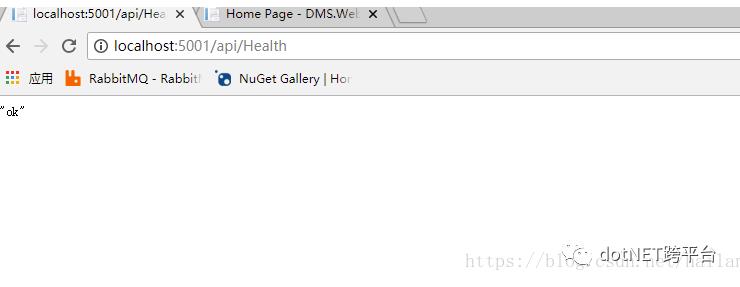
成功运行后,查看Consul集群的状态,UI界面
四、总结与后续工作
本篇主要基于一个最小化的集群搭建了一个Consul服务治理组件,并将ASP.NET Core API程序注册到了Consul(通过配置文件注册),并尝试通过Consul进行服务发现。希望整理这篇文章对大家有一些帮助,同时希望大家把.NET Core应用起来,将来能够跑在Linux和Docker上,希望大家早日实现目标。
后续我会继续尝试基于Ocelot构建API网关,到时会结合Consul进行进一步的集成。另外,还会尝试Polly进行熔断降级、Identity Server进行验证
相关文章:
以上是关于.netcore consul实现服务注册与发现-集群完整版的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章