掌门1对1微服务体系Solar第2弹:阿里巴巴Sentinel落地实践
Posted 掌门技术
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了掌门1对1微服务体系Solar第2弹:阿里巴巴Sentinel落地实践相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
前言
Sentinel 简介
Sentinel 深度集成 Apollo
Solar SDK 环境初始化
Sentinel Dashboard 持久化改造
Sentinel 集成 Skywalking
抽象 Sentinel ProcessorSlot 埋点输出
整合 OpenTracing & Skywalking
实现 Sentinel InitFunc SPI 扩展
Sentinel 集成 InfluxDB & Grafana
监控数据持久化到 InfluxDB
Grafana 界面展现监控数据
Sentinel Limit-App 熔断扩展
基础指标的熔断
灰度蓝绿发布指标的熔断
业务自定义指标的熔断
组合指标的熔断
Sentinel 网关流控实践
API 分组管理
网关流控规则
Sentinel 集群限流实践
作者介绍
附录信息
前言
掌门1对1精耕在线教育领域,近几年业务得到了快速发展,但同时也遭遇了“成长的烦恼”。随着微服务数量不断增加,流量进一步暴增,硬件资源有点不堪重负,那么,如何实现更好的限流熔断降级等流量防护措施,这个课题就摆在了掌门人的面前。由于 Spring Cloud 体系已经演进到第二代,第一代的 Hystrix 限流熔断降级组件已经不大适合现在的业务逻辑和规模,同时它目前被 Spring Cloud 官方置于维护模式,将不再向前发展。
如何选择一个更好的限流熔断降级组件?经过对 Alibaba Sentinel、Resilience4j、Hystrix 等开源组件做了深入的调研和比较,最终选定 Alibaba Sentinel 做微服务体系 Solar 中的限流熔断降级必选组件。
Sentinel 简介
❂阿里巴巴中间件部门开发的新一代以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性的分布式系统的流量防卫兵。它承接了阿里巴巴近10年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
它具有非常丰富的开源生态:
它和 Hystrix 相比,有如下差异:
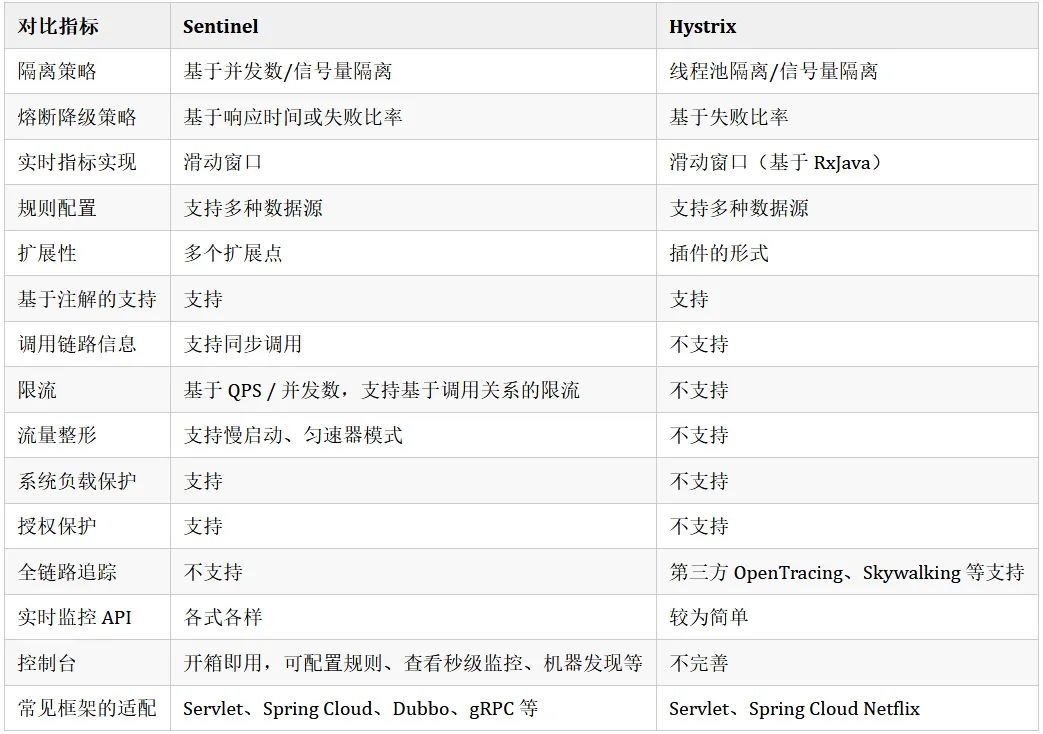
摘自官网 Sentinel Roadmap[1]
Sentinel 深度集成 Apollo
Sentinel 官方在 sentinel-datasource-apollo 模块中已经对 Apollo 做了一些扩展,主要实现了 Sentinel 规则的读取和订阅逻辑。这些并不够,我们需要对 Apollo 进行更深层次的集成。
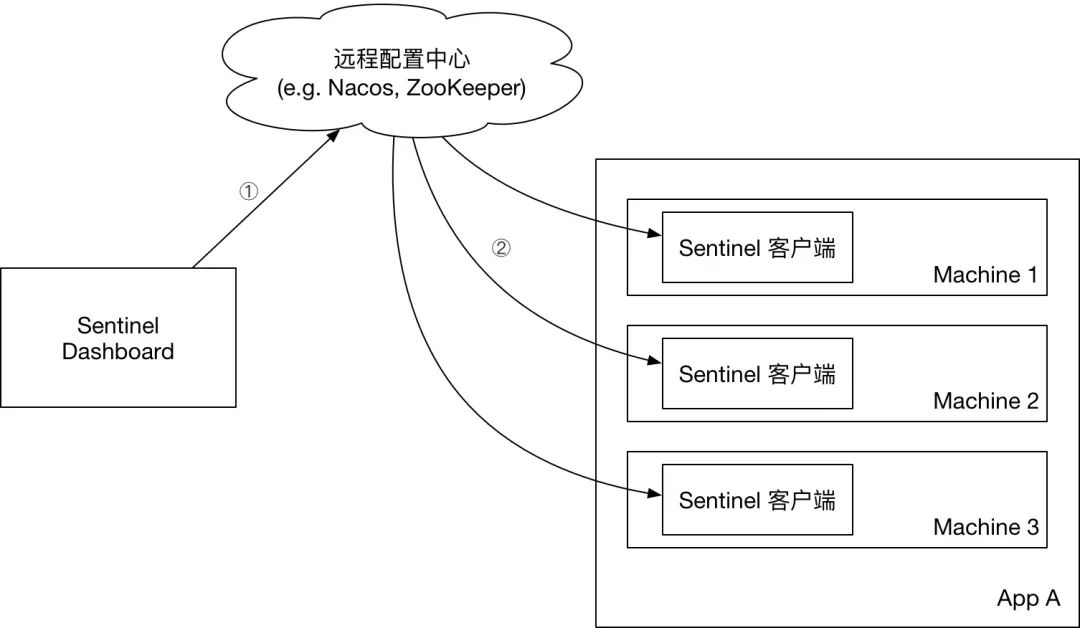
摘自官网 在生产环境中使用 Sentinel[2]
Solar SDK 环境初始化
定制 EnvironmentPostProcessor 类,实现如下:
-
Sentinel Dashboard的项目名称从ApolloAppId的维度进行展示 -
根据环境 env值读取相应的配置文件,并访问对应环境的Sentinel Dashboard域名Sentinel Dashboard在生产环境部署若干台ECS实例,阿里云SLB做负载均衡,实现对集群的水平扩展
public class SentinelClientEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor {
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
private static final String DEFAULT_CLASSPATH_LOCATION = "classpath:/META-INF/app.properties";
private static final String DEFAULT_LOCATION = "/META-INF/app.properties";
private static final String DEFAULT_LOG_LOCATION = "/opt/logs/";
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
try {
Resource appResource = resourceLoader.getResource(DEFAULT_CLASSPATH_LOCATION);
if (!appResource.exists()) {
appResource = resourceLoader.getResource(DEFAULT_LOCATION);
}
Properties appProperties = new Properties();
appProperties.load(new InputStreamReader(appResource.getInputStream()));
String appId = appProperties.getProperty("app.id");
System.setProperty("project.name", appId);
System.setProperty("csp.sentinel.log.dir", DEFAULT_LOG_LOCATION + appId);
Properties properties = new Properties();
String path = isOSWindows() ? "C:/opt/settings/server.properties" : "/opt/settings/server.properties";
File file = new File(path);
if (file.exists() && file.canRead()) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
if (fis != null) {
try {
properties.load(new InputStreamReader(fis, Charset.defaultCharset()));
} finally {
fis.close();
}
}
}
String idc = properties.getProperty("idc");
String location;
String env = System.getProperty("env");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(idc)) {
if (!isBlank(env)) {
env = env.trim().toLowerCase();
} else {
env = System.getenv("ENV");
if (!isBlank(env)) {
env = env.trim().toLowerCase();
} else {
env = properties.getProperty("env");
if (!isBlank(env)) {
env = env.trim();
} else {
env = Env.FAT.getEnv();
}
}
}
location = "classpath:/META-INF/sentinel-" + env + ".properties";
} else {
location = "classpath:/META-INF/sentinel-" + idc + ".properties";
}
Resource serverResource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
properties.load(new InputStreamReader(serverResource.getInputStream()));
for (String key : properties.stringPropertyNames()) {
System.setProperty(key, properties.getProperty(key));
}
System.setProperty(CommonConstant.SENTINEL_VERSION_NAME, CommonConstant.SENTINEL_VERSION_VALUE);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
private boolean isBlank(String str) {
return Strings.nullToEmpty(str).trim().isEmpty();
}
private boolean isOSWindows() {
String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");
return !isBlank(osName) && osName.startsWith("Windows");
}
}
把 SentinelClientEnvironmentPostProcessor 类放置
esourcesMETA-INFspring.factories 文件中,内容为
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=
com.zhangmen.solar.component.sentinel.common.context.SentinelClientEnvironmentPostProcessor
在
esourcesMETA-INF 目录下,定制环境配置文件,文件名格式为 sentinel-{环境号}.properties 。下文以 dev 环境和 flow 流控配置(其它规则配置,请自行参考 Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel 的相关资料)为样例。
sentinel-dev.properties
spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.dashboard=127.0.0.1:8080
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds.apollo.namespaceName=application
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds.apollo.flowRulesKey=sentinel.flowRules
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.ds.apollo.ruleType=flow
...
Sentinel Dashboard 持久化改造
原生的 Sentinel Dashboard 在创建完规则后,规则内容保存在服务的内存中,当服务重启后所有的规则内容都会消失。因此,在生产部署时需要考虑配置持久化,并且使用 Apollo 动态规则的感知能力。
① 向外暴露 Sentinel 规则的 Restful 接口
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/v2/flow")
public class FlowControllerV2 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("apolloFlowRuleProvider")
private DynamicRuleProvider<List<FlowRuleEntity>> ruleProvider;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("apolloFlowRulePublisher")
private DynamicRulePublisher<List<FlowRuleEntity>> rulePublisher;
....
}
② 实现 Sentinel Apollo 规则提供
@Component("apolloFlowRuleProvider")
public class ApolloFlowRuleProvider extends BaseApolloRuleProvider<FlowRuleEntity> {
@Override
public List<FlowRuleEntity> getRules(String appName) throws Exception {
List<FlowRuleEntity> flowRuleEntityList = super.getRules(appName);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(flowRuleEntityList)) {
List<FlowRuleEntity> flowRuleEntities = JSONArray.parseArray(flowRuleEntityList.toString(), FlowRuleEntity.class);
long id = 1;
for (FlowRuleEntity entity : flowRuleEntities) {
entity.setId(id++);
entity.getClusterConfig().setFlowId(entity.getId());
}
return flowRuleEntities;
} else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
protected String getDataId() {
return ApolloConfigUtil.getFlowDataId();
}
}
③ 实现 Sentinel Apollo 规则订阅
@Component("apolloFlowRulePublisher")
public class ApolloFlowRulePublisher extends BaseApolloRulePublisher<List<FlowRuleEntity>> {
@Override
public void publish(String app, String operator, List<FlowRuleEntity> rules) throws Exception {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(rules)) {
for (int i = 0; i < rules.size(); i++) {
rules.get(i).setId((long) (i + 1));
rules.get(i).setApp(null);
rules.get(i).setGmtModified(null);
rules.get(i).setGmtCreate(null);
rules.get(i).setIp(null);
rules.get(i).setPort(null);
rules.get(i).getClusterConfig().setFlowId((long) (i + 1));
}
} else {
rules = null;
}
super.publish(app, operator, rules);
}
@Override
protected String getDataId() {
return ApolloConfigUtil.getFlowDataId();
}
}
上述代码实现了对 Apollo 配置读写操作。熟悉 Apollo 的同学应该知道,这些操作需要基于 Apollo OpenApi 来操作;动态感知能力的逻辑已经由 sentinel-datasource-apollo 模块实现。
Sentinel 集成 Skywalking
❂
业务系统要求对限流熔断降级实现全链路实时埋点,并希望在 Skywalking 界面上提供限流熔断降级埋点的多维度统计。由于 Skywalking 实现了 OpenTracing 标准化协议,那么以 OpenTracing 为桥梁,通过 Solar SDK 输出 Sentinel 埋点到 Skywalking Server 不失为一个好的技术选择。下面简单扼要介绍一下基于 Sentinel InitFunc 的 SPI 机制实现埋点输出:
Sentinel 将 ProcessorSlot 作为 SPI 接口进行扩展(1.7.2 版本以前 SlotChainBuilder 作为 SPI ),使得 Slot Chain 具备了扩展的能力。您可以自行加入自定义的 slot 并编排 slot 间的顺序,从而可以给 Sentinel 添加自定义的功能。
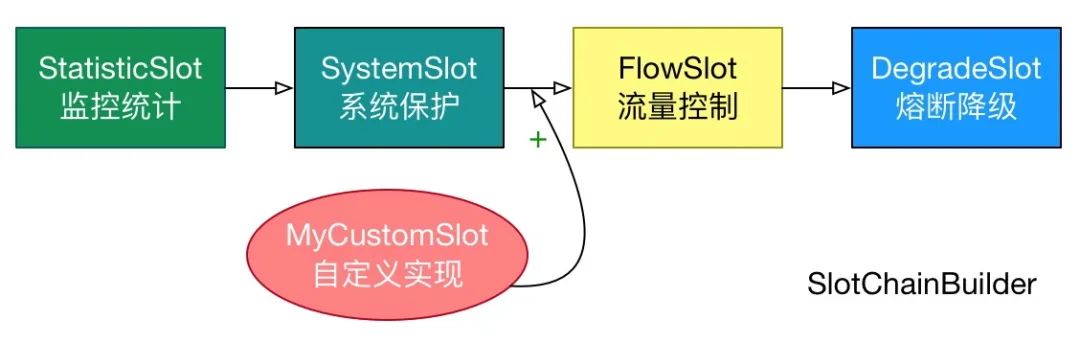
摘自官网 Sentinel 工作主流程[3]
抽象 Sentinel ProcessorSlot 埋点输出
Sentinel 的 ProcessorSlotEntryCallback 提供 onPass 和 onBlocked 两个方法,毕竟限流熔断降级并不是常规的功能,不会发生在大流量上面,所以 onPass 上我们不做任何处理,否则正常的调用去实现拦截,将为产生大量的埋点数据,会让 Skywalking Server 承受很大的性能压力,所以 onBlocked 将是我们关注的重点,它除了输出 Sentinel 本身的上下文参数之外,也会输出微服务 Solar 指标参数,主要包括:
-
埋点 Span名称,这里为SENTINEL,在Skywalking全链路监控界面中,用户可以非常容易的找到这个埋点 -
服务所在的 组名,指服务的逻辑分组 -
服务类型,包括服务和网关(网关也是一种特殊的服务), Sentinel埋点可以支持在服务和网关上的输出 -
服务的 APPID,它为Apollo组件的范畴概念 -
服务名,它对应为 spring.application.name的配置值 -
服务实例所在的 IP地址和Port端口 -
服务版本号 -
服务所在的区域 -
服务所在的子环境
接下去是 Sentinel 层面的参数,请自行参考 Sentinel 官方文档和源码,了解其含义,这里不做具体讲解。
public abstract class SentinelTracerProcessorSlotEntryCallback<S> implements ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> {
@Override
public void onPass(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode param, int count, Object... args) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void onBlocked(BlockException e, Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode param, int count, Object... args) {
S span = buildSpan();
PluginAdapter pluginAdapter = PluginContextAware.getStaticApplicationContext().getBean(PluginAdapter.class);
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.SPAN_TAG_PLUGIN_NAME, context.getName());
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_GROUP, pluginAdapter.getGroup());
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_TYPE, pluginAdapter.getServiceType());
String serviceAppId = pluginAdapter.getServiceAppId();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceAppId)) {
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_APP_ID, serviceAppId);
}
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_ID, pluginAdapter.getServiceId());
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_ADDRESS, pluginAdapter.getHost() + ":" + pluginAdapter.getPort());
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_VERSION, pluginAdapter.getVersion());
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_REGION, pluginAdapter.getRegion());
outputSpan(span, DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_ENVIRONMENT, pluginAdapter.getEnvironment());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.ORIGIN, context.getOrigin());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.ASYNC, String.valueOf(context.isAsync()));
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.RESOURCE_NAME, resourceWrapper.getName());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.RESOURCE_SHOW_NAME, resourceWrapper.getShowName());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.RESOURCE_TYPE, String.valueOf(resourceWrapper.getResourceType()));
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.ENTRY_TYPE, resourceWrapper.getEntryType().toString());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.RULE_LIMIT_APP, e.getRuleLimitApp());
if (tracerSentinelRuleOutputEnabled) {
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.RULE, e.getRule().toString());
}
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.CAUSE, e.getClass().getName());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.BLOCK_EXCEPTION, e.getMessage());
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.COUNT, String.valueOf(count));
if (tracerSentinelArgsOutputEnabled) {
outputSpan(span, SentinelStrategyConstant.ARGS, JSON.toJSONString(args));
}
finishSpan(span);
}
protected abstract S buildSpan();
protected abstract void outputSpan(S span, String key, String value);
protected abstract void finishSpan(S span);
}
整合 OpenTracing & Skywalking
实现 SentinelTracerProcessorSlotEntryCallback 的三个核心方法:
-
buildSpan- 创建Skywalking的埋点Span对象 -
outputSpan- 输出相关埋点数据的键值对到Skywalking的埋点Span对象中 -
finishSpan- 提交Skywalking的埋点Span对象到SkywalkingServer
public class SentinelSkywalkingTracerProcessorSlotEntryCallback extends SentinelTracerProcessorSlotEntryCallback<Span> {
private Tracer tracer = new SkywalkingTracer();
@Override
protected Span buildSpan() {
return tracer.buildSpan(SentinelStrategyConstant.SPAN_NAME).startManual();
}
@Override
protected void outputSpan(Span span, String key, String value) {
span.setTag(key, value);
}
@Override
protected void finishSpan(Span span) {
span.finish();
}
}
实现 Sentinel InitFunc SPI 扩展
实现 SPI 的扩展切入类
public class SentinelSkywalkingTracerInitFunc implements InitFunc {
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.addEntryCallback(SentinelSkywalkingTracerProcessorSlotEntryCallback.class.getName(), new SentinelSkywalkingTracerProcessorSlotEntryCallback());
}
}
把 SPI 的扩展切入类放置
esourcesMETA-INFservicescom.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc 文件中,内容为
com.nepxion.discovery.plugin.strategy.sentinel.skywalking.monitor.SentinelSkywalkingTracerInitFunc
摘自 Nepxion Discovery 开源社区[4]
❂对于 Sentinel 跟 Opentracing, Skywalking, Jaeger 的集成可参考 https://github.com/Nepxion/Discovery 中的 discovery-plugin-strategy-sentinel-starter-opentracing, discovery-plugin-strategy-sentinel-starter-skywalking 等模块。
最终在 Skywalking 全链路界面上输出如下:
全链路调用链中,我们可以看到 solar-service-a 服务的链路上输出了 SENTINEL 埋点,表示 solar-service-a 上发生了 Sentinel 限流熔断降级事件之一。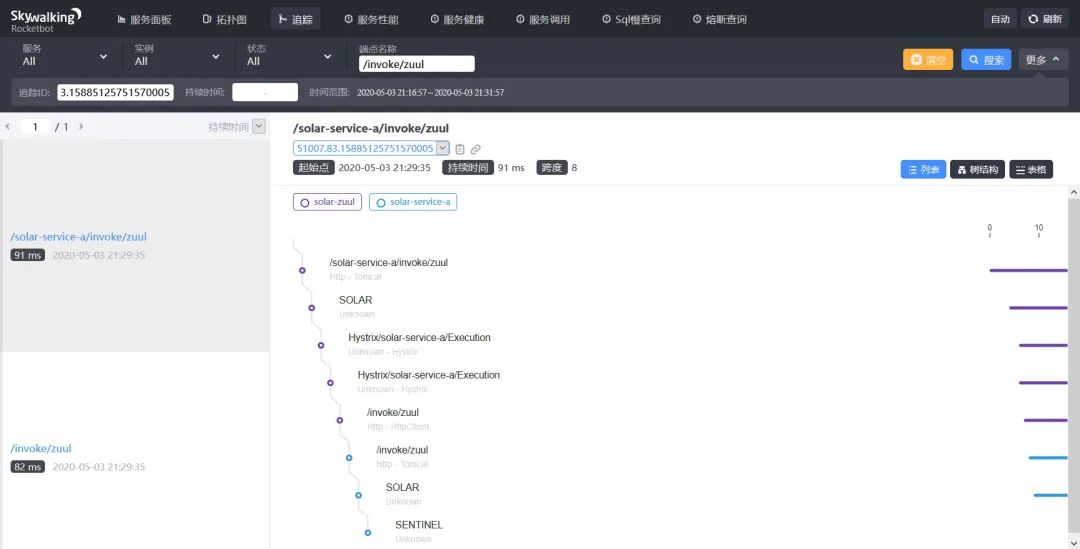
点击 SENTINEL 埋点,在呼出的内容看板上,我们可以看到 solar-service-a 服务发生了限流事件,上面显示限流的规则和异常信息以及微服务 Solar 指标等一系列参数。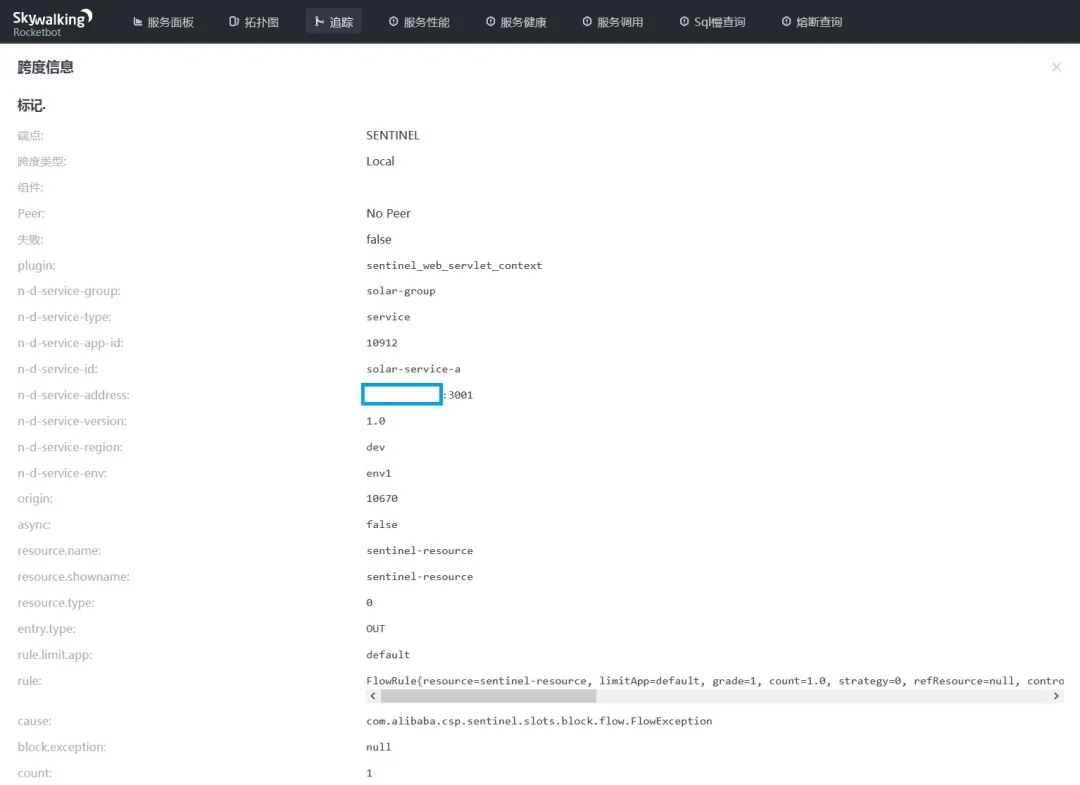
我们可以点击界面上边的【熔断查询】进行 Sentinel 相关数据的分析和统计
Sentinel 集成 InfluxDB & Grafana
监控数据持久化到 InfluxDB
① Sentinel MetricFetcher 拉取数据
实现 Dashboard 服务端拉取 Sentinel 客户端(即 Solar 微服务)的监控数据
@Component
public class MetricFetcher {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("influxDBMetricRepository")
private MetricsRepository<MetricEntity> metricStore;
...
}
② InfluxDB 实例初始化
@Configuration
public class InfluxDBAutoConfiguration {
@Value("${spring.influx.url}")
private String influxDBUrl;
@Value("${spring.influx.user}")
private String userName;
@Value("${spring.influx.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.influx.database}")
private String database;
@Bean
public InfluxDB influxDB() {
InfluxDB influxDB = null;
try {
influxDB = InfluxDBFactory.connect(influxDBUrl, userName, password);
influxDB.setDatabase(database).enableBatch(100, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
influxDB.setLogLevel(InfluxDB.LogLevel.NONE);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error(e.getMessage());
}
return influxDB;
}
}
③ Sentinel 数据写入到 InfluxDB
@Component("influxDBMetricRepository")
public class InfluxDBMetricRepository implements MetricsRepository<MetricEntity> {
@Autowired
private InfluxDB influxDB;
@Override
public void save(MetricEntity metric) {
try {
Point point = createPoint(metric);
influxDB.write(point);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public void saveAll(Iterable<MetricEntity> metrics) {
if (metrics == null) {
return;
}
try {
BatchPoints batchPoints = BatchPoints.builder().build();
metrics.forEach(metric -> {
Point point = createPoint(metric);
batchPoints.point(point);
});
influxDB.write(batchPoints);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Grafana 界面展现监控数据
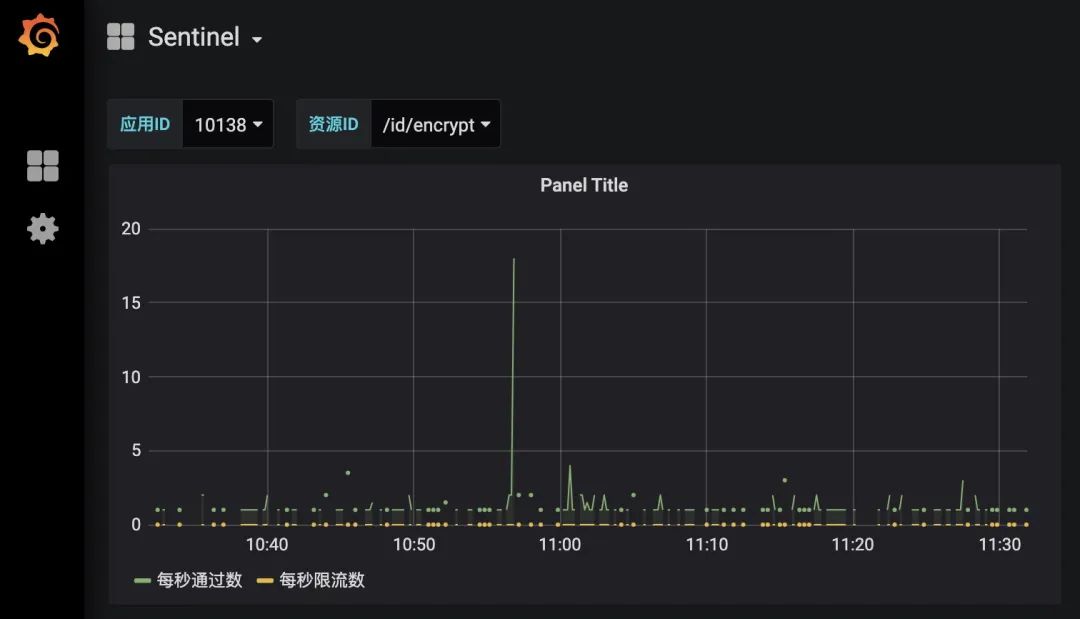
Sentinel Limit-App 熔断扩展
❂根据上一篇《掌门1对1微服务体系Solar第1弹:全链路灰度蓝绿发布智能化实践》讲到,掌门1对1已经实现通过灰度蓝绿发布方式,实现对流量的精确制导和调拨,但为了进一步实施更安全的流量保障,引入了基础指标和灰度蓝绿发布指标的熔断,同时也支持业务自定义指标和组合指标的熔断。
通过对 Sentinel Limit-App机制的扩展并定制授权规则,实现微服务 Solar 的熔断扩展。对于授权规则中涉及到的参数,简要做如下说明:
-
resource为@SentinelResource注解的value,也可以是调用的URL路径值 -
limitApp如果有多个,可以通过,分隔。特别注意,下文为了描述简单,只以单个为例 -
strategy为0表示白名单,符合条件就放行流量;strategy为1表示黑名单,符合条件就限制流量。特别注意,下文为了描述简单,只以白名单为例
基础指标的熔断
通过 Http Header 自动携带下游服务的基础指标进行全链路传递的方式,对下游调用实施基础指标的熔断。支持如下指标:
① 服务名
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 服务名不满足条件,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-id
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 A 服务名
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "a-service-id",
"strategy": 0
}
]
② 服务的 APPID
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 服务的 APPID 不满足条件,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-app-id
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 A 服务的APPID
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "a-service-app-id",
"strategy": 0
}
]
③ 服务实例所在的 IP 地址和 Port 端口
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-address
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 A 服务实例所在的IP地址和Port端口
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "a-ip:a-port",
"strategy": 0
}
]
灰度蓝绿发布指标的熔断
通过 Http Header 自动携带下游服务的灰度蓝绿发布指标进行全链路传递的方式,对下游调用实施灰度蓝绿发布指标的熔断。支持如下指标:
① 服务所在的组名
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 服务的组名和 B 服务的组名不一致,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-group
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 B 服务的组名
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "b-group",
"strategy": 0
}
]
② 服务版本号
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 服务的版本号和 B 服务的版本号不一致,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-version
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 B 服务的版本号
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "b-version",
"strategy": 0
}
]
③ 服务所在的区域
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 服务的区域值和 B 服务的区域值不一致,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-region
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 B 服务的区域值
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "b-region",
"strategy": 0
}
]
④ 服务所在的子环境
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 服务的子环境值和 B 服务的子环境值不一致,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。
-
B 服务增加配置项
spring.application.strategy.service.sentinel.request.origin.key=n-d-service-env
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为 B 服务的子环境值
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "b-env",
"strategy": 0
}
]
业务自定义指标的熔断
通过 Http Header 携带下游服务的业务自定义指标进行全链路传递的方式,对下游调用实施自定义指标的熔断。
当 A 服务发送请求到 B 服务,所携带的 A 的自定义指标不满足条件,该请求就会被 B 服务熔断。例如:A 服务把 userName 通过 Http Header 传递给 B 服务,而 B 服务只接受 userName 为 zhangsan 的请求,那么我们可以通过如下方式来解决:
-
B 服务通过适配类实现 SentinelOrigin值的解析
public class MyServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter extends AbstractServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getHeader("userName");
}
}
-
B 服务的配置类里通过 @Bean方式进行适配类创建
@Bean
public ServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter ServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter() {
return new MyServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter();
}
-
B 服务增加授权规则, limitApp为zhangsan
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "zhangsan",
"strategy": 0
}
]
假如该方式仍未能满足业务场景,业务系统希望根据 userName 获取 userType,根据用户类型做统一熔断,例如,用户类型为 AUTH_USER 的请求才能放行,其它都熔断,那么我们可以把上面的例子修改如下:
-
B 服务的适配类更改如下:
public class MyServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter extends AbstractServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
String userName = request.getHeader("userName");
String userType = getUserTypeByName(userName);
return userType;
}
}
-
B 服务的授权规则更改如下:
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "AUTH_USER",
"strategy": 0
}
]
组合指标的熔断
通过 Http Header 携带下游服务的业务自定义指标、基础指标或者灰度蓝绿发布指标进行全链路传递的方式,对下游调用实施组合指标的熔断,例如,根据传入的微服务版本号 + 用户名,组合在一起进行熔断。下面示例表示为下游服务版本为 1.0 且 userName 为 zhangsan,同时满足这两个条件下,所有服务的请求允许被放行,否则被熔断。
-
B 服务的适配类更改如下:
public class MyServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter extends AbstractServiceSentinelRequestOriginAdapter {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest request) {
String version = request.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_VERSION);
String userName = request.getHeader("userName");
return version + "&" + userName;
}
}
-
B 服务的授权规则更改如下:
[
{
"resource": "sentinel-resource",
"limitApp": "1.0&zhangsan",
"strategy": 0
}
]
Sentinel 网关流控实践
阐述网关流控实践的时候,我们使用精确匹配的方式对某个服务的请求做限流控制为例;对网关代理的 solar-service-a 服务的接口 /inspector/inspect 做限流控制为例。
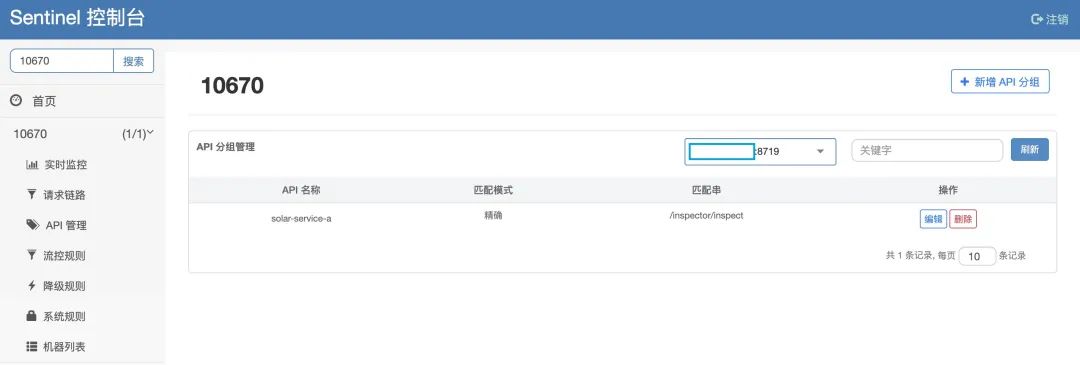
API 分组管理
API 管理页面里添加 solar-service-a, 并精确匹配串 /inspector/inspect
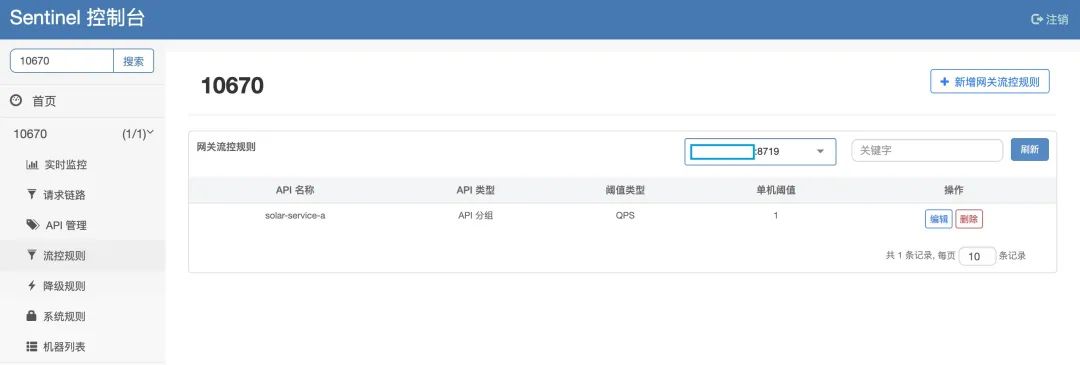
网关流控规则
在流控规则界面里配置相关的规则
最终在 Skywalking 全链路界面上输出如下(跟 Solar 服务侧 Sentinel 埋点相似,不一一阐述了):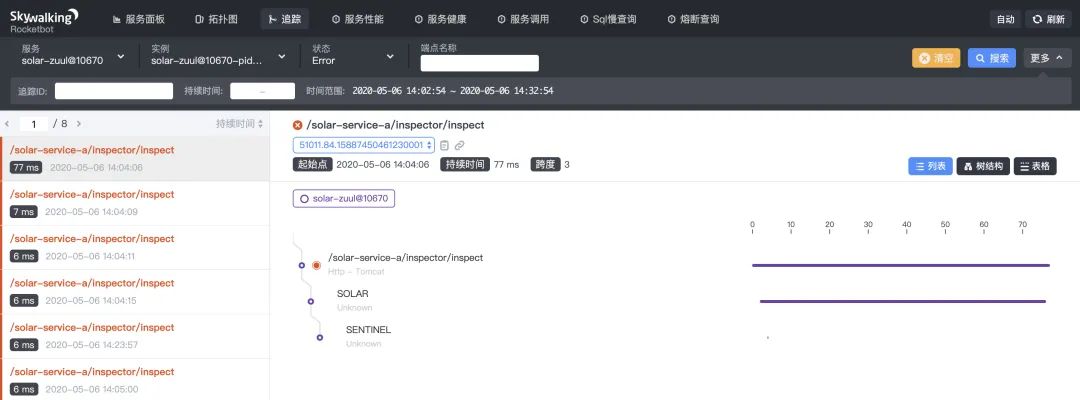
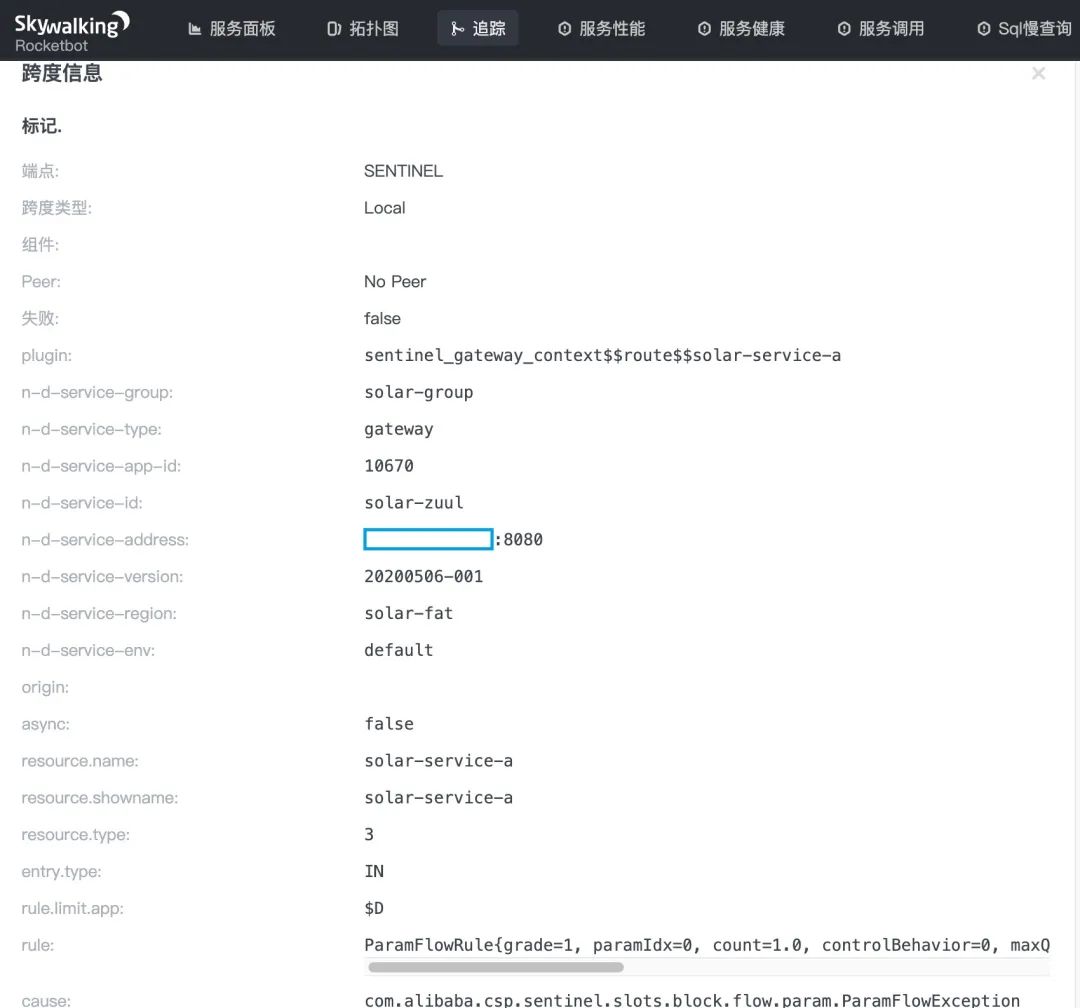
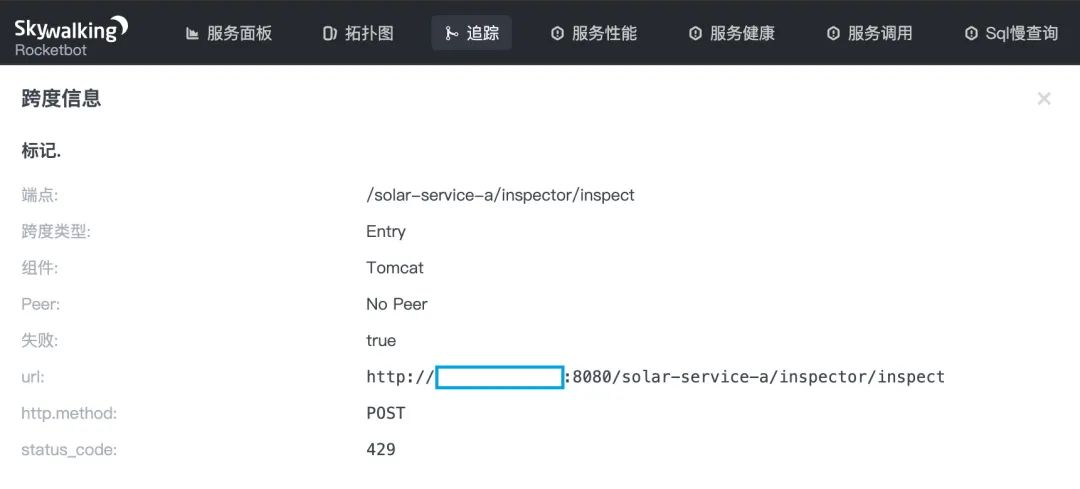
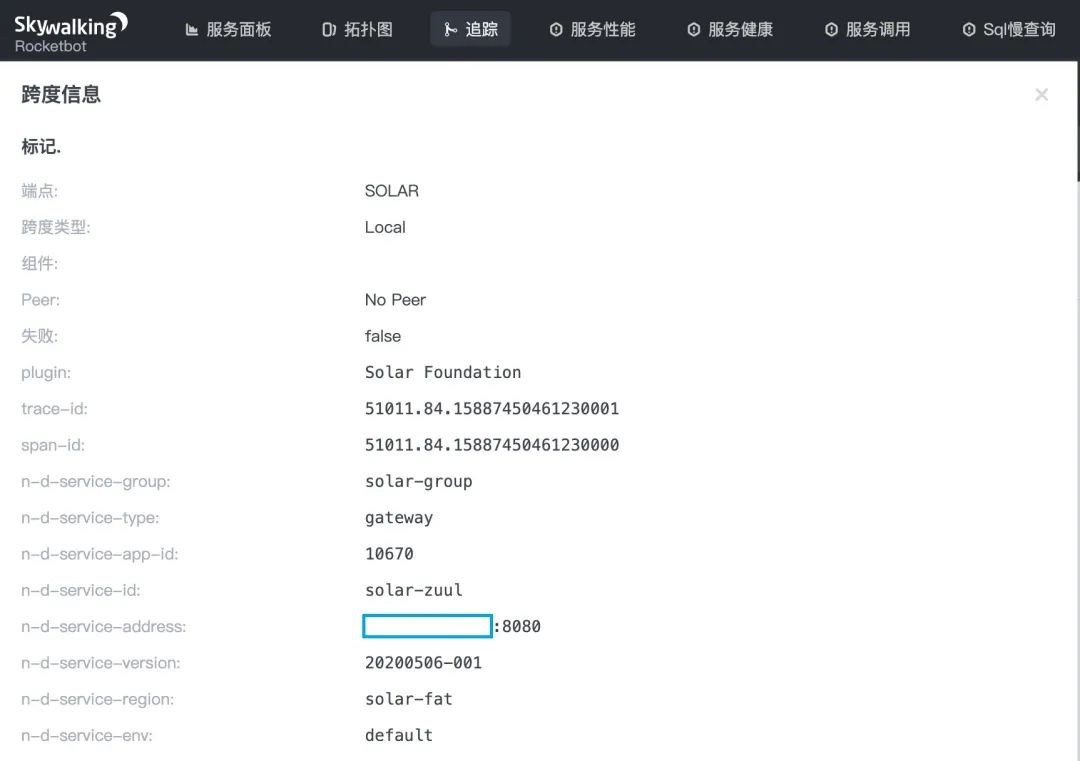
Sentinel 集群限流实践
我们采用 Sentinel 官方提供的嵌入式 Token Server 解决方案,即服务集群中选择一个节点做为 Token Server ,同时该节点也作为 Token Client 响应外部的请求的服务器。具体实现方式通过 Sentinel 实现预留的 SPI InitFunc 接口,可以参考官方 sentinel-demo 模块下面的 sentinel-demo-cluster-embedded 。
public class SentinelApolloTokenClusterInitFunc implements InitFunc {
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
// Register client dynamic rule data source.
initDynamicFlowRuleProperty();
initDynamicParamRuleProperty();
// Register token client related data source.
// Token client common config:
ClusterClientConfigInitializer.doInit();
// Token client assign config (e.g. target token server) retrieved from assign map:
ClusterClientAssignConfigInitializer.doInit();
// Register token server related data source.
// Register dynamic rule data source supplier for token server:
ClusterRuleSupplierInitializer.doInit();
// Token server transport config extracted from assign map:
ServerTransportConfigInitializer.doInit();
// Init cluster state property for extracting mode from cluster map data source.
ClusterStateInitializer.doInit();
// ServerFlowConfig 配置
ServerFlowConfigInitializer.doInit();
}
}
把 SPI 的扩展切入类放置
esourcesMETA-INFservicescom.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc 文件中,内容为
com.zhangmen.solar.sentinel.SentinelApolloTokenClusterInitFunc
作者介绍
任浩军,掌门基础架构部研发经理。曾就职于平安银行、万达、惠普,曾负责平安银行平台架构部 PaaS 平台基础服务框架研发。10 多年开源经历,Github ID:@HaojunRen,Nepxion 开源社区创始人,Nacos Group Member,Spring Cloud Alibaba & Nacos & Sentinel & OpenTracing Committer。
张彬彬,掌门基础架构部架构师。主要负责公司微服务架构以及开源项目的开发和实践,开源项目爱好者,多年互联网开发经验。
非常感谢阿里巴巴 Sentinel 项目负责人宿何在落地过程中的支持和帮助。
附录信息
欢迎大佬们加入掌门教育大家庭,一起畅谈技术,分享交流。在招职位有 Java 开发工程师/架构师、 ios 开发工程师/架构师、 android 开发工程师、Web 前端开发工程师/架构师、运维开发工程师( K8s , Docker )、测试工程师。投递信箱:zeying.shi@zhangmen.com 施老师。
参考资料
Sentinel Roadmap: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/Roadmap
[2]在生产环境中使用 Sentinel: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%9C%A8%E7%94%9F%E4%BA%A7%E7%8E%AF%E5%A2%83%E4%B8%AD%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8-Sentinel
[3]Sentinel 工作主流程: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/Sentinel%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C%E4%B8%BB%E6%B5%81%E7%A8%8B
[4]Nepxion Discovery 开源社区: https://github.com/Nepxion/Discovery
以上是关于掌门1对1微服务体系Solar第2弹:阿里巴巴Sentinel落地实践的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
阿里新一代微服务解决方案:Spring Cloud Alibaba