基于MapReduce的并行化大矩阵乘法
Posted 追梦程序员
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于MapReduce的并行化大矩阵乘法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
并行化大矩阵乘法是较早的基于MapReduce编程模型实现的基础算法之一,最早是由Google公司为了解决PageRank中包含的大量矩阵乘法而提出的。今天我们就来一起学习一下基于MapReduce的并行化大矩阵乘法。
我们假设有两个矩阵M和N,其中M的列数等于N的行数,则记M和N的乘积P = M . N。其中Mij表示矩阵M中第i行第j列的元素,Njk表示矩阵N中第j行第K列的元素,则矩阵P中的元素可由下式求得:
即Pik为M的第i行元素和N的第k列元素对应相乘再相加。由上式我们知道最终决定Pik位置的是(i,k),我们可以把(i,k)作为Reduce输出的key,将Pik作为输出的value。为了求出Pik,我们必须知道Mij和Njk。对于Mij,我们需要知道的属性有所属矩阵为M,行号为i,列号为j,Mij本身的值大小。对于Njk,我们需要知道的属性有所属矩阵为N,行号为j,列号为k,Njk本身的值大小。Mij和Njk的属性都有Mapper类处理产生。
Map函数:对于M矩阵的每一个元素Mij,产生一系列的键值对<(i,k),(M,j,Mij)>,其中K=1、2、到N的列数。对于N矩阵中的每一个元素Njk,产生一系列的键值对<(i,k),(N,j,Njk)>,其中i=1、2、到M的行数。
Reduce函数:对于同一个键(i,k),有许多的值(M,j,Mij)、(N,j,Njk),将j值相同的Mij和Njk相乘,然后不同j值处理后的结果再相加,即可得到Pik的值。
下面我们就以一个具体的矩阵为例讲解。

我们将M矩阵存放在M.txt文件中,文件的一行为一个元素,内容格式为“元素所在行,元素所在列 元素值”。M.txt的内容如下。
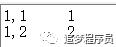
我们将N矩阵存放在N.txt中,N.txt的内容如下。

Map函数输出:经过map函数的处理,产生了一系列形如<(i,k),(M,j,Mij)>的键值对,具体如下。
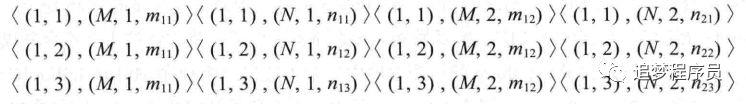
Reduce函数输出:对相同的(i,k)键,按照j值进行相乘再相加,过程如下。
所以最终得到的乘积矩阵为P = [2,5,11]。
并行化大矩阵乘法的MapReduce程序如下:
package Matrix;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
*parameters : rowM,columnM,columnN,InputPaths,OutputPath
* @author liuchen
*
*/
public class MatrixMain {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//create job = map + reduce
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//Setting global share parameters
conf.set("rowM", args[0]);
conf.set("columnM", args[1]);
conf.set("columnN", args[2]);
//create Job
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
//the entry of job
job.setJarByClass(MatrixMain.class);
//the mapper of job
job.setMapperClass(MatrixMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//the reducer of job
job.setReducerClass(MatrixReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//input and output
TextInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[3]));
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[4]));
//submit job
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
package Matrix;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
/**
* Matrix multiplication Mapper
* @author liuchen
*
*/
public class MatrixMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text , Text , Text> {
private static int columnN = 0;
private static int rowM = 0;
private Text map_key = new Text();
private Text map_value = new Text();
/**
* Before executing the map function, get the necessary parameters
*/
protected void setup(Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
columnN = Integer.parseInt(conf.get("columnN"));
rowM = Integer.parseInt(conf.get("rowM"));
}
protected void map(Object key, Text value,Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//Through filename differentiation matrix
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit();
String fileName = fileSplit.getPath().getName();
if(fileName.contains("M")){ //M Matrix
String[] arr1 = value.toString().split(",");
int i = Integer.parseInt(arr1[0]);
String[] arr2 = arr1[1].split(" ");
int j = Integer.parseInt(arr2[0]);
int Mij = Integer.parseInt(arr2[1]);
for(int k = 1;k <= columnN;k++){
map_key.set(i + "," + k);
map_value.set("M," + j + "," + Mij);
context.write(map_key, map_value);
}
}
else if (fileName.contains("N")){ //N Matrix
String[] arr1 = value.toString().split(",");
int j = Integer.parseInt(arr1[0]);
String[] arr2 = arr1[1].split(" ");
int k = Integer.parseInt(arr2[0]);
int Njk = Integer.parseInt(arr2[1]);
for(int i = 1;i<= rowM;i++){
map_key.set(i + "," + k);
map_value.set("N," + j +"," + Njk);
context.write(map_key, map_value);
}
}
}
}
package Matrix;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
public class MatrixReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
private static int columnM = 0;
protected void setup(Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
columnM = Integer.parseInt(conf.get("columnM"));
}
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int[] M = new int[columnM + 1]; //Index is 0 Empty
int[] N = new int[columnM + 1];
int sum = 0;
for(Text value : values){
String[] arr1 = value.toString().split(",");
if(arr1[0].contains("M")){
M[Integer.parseInt(arr1[1])] = Integer.parseInt(arr1[2]);
}
else if (arr1[0].contains("N")){
N[Integer.parseInt(arr1[1])] = Integer.parseInt(arr1[2]);
}
}
for(int j = 1;j<columnM + 1;j++){
sum += M[j] * N[j];
}
context.write(key, new Text(Integer.toString(sum)));
}
}
以上是关于基于MapReduce的并行化大矩阵乘法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章