可怕!RxHttp2.0重大更新!协程发请求,原来如此简单
Posted 秦子帅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了可怕!RxHttp2.0重大更新!协程发请求,原来如此简单相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

作者 | 不怕天黑 地址 | juejin.im/post/5ea04cd9f265da47c15cd752
前言
异步操作,协程已为我们提供了
async操作符处理异步问题,但用到时,每次还要包装一次,不能接受超时与重试,这种情况遇到的不多,但几乎每个开发者都会遇到,真遇到时,如果没有对应的API,也着实让人着急
请求开始/结束延迟,这种情况也不多,但遇到的人也不少,自己处理着实麻烦
在请求并行中,假设有A、B两个请求甚至更多,它们互不依赖,然而在协程中,如果A请求出现异常,那么协程就中止了,此时B也跟着中止了,这是我们不想看到的结果,如何解决?常规的做法是对每个请求都做异常处理,使得出现异常,协程不会结束。但每个请求都需要单独处理,写起来着实会让人抓破头皮,这是很大的痛点
新增一系列非常好用的操作符,如:
asysn、timeout、retry、tryAwait等等完全剔除RxJava,采用外挂方法替代,也正因如此,RxHttp做到同时支持RxJava2与RxJava3
将RxLieScope提取为单独的一个库,专门处理协程开启/关闭/异常处理,本文后续会单独介绍
gradle依赖
dependencies {
//必须
implementation 'com.ljx.rxhttp:rxhttp:2.2.0'
kapt 'com.ljx.rxhttp:rxhttp-compiler:2.2.0' //生成RxHttp类
//以下均为非必须
//管理协程生命周期,页面销毁,关闭请求
implementation 'com.ljx.rxlife:rxlife-coroutine:2.0.0'
//Converter 根据自己需求选择 RxHttp默认内置了GsonConverter
implementation 'com.ljx.rxhttp:converter-jackson:2.2.0'
implementation 'com.ljx.rxhttp:converter-fastjson:2.2.0'
implementation 'com.ljx.rxhttp:converter-protobuf:2.2.0'
implementation 'com.ljx.rxhttp:converter-simplexml:2.2.0'
}
请求三部曲
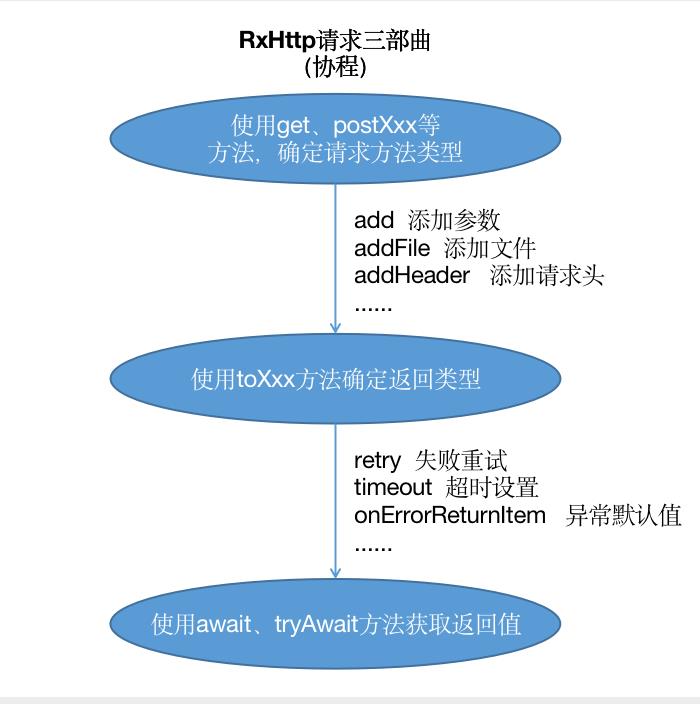
val str = RxHttp.get("/service/...") //第一步,确定请求方式,可以选择postForm、postJson等方法
.toStr() //第二步,确认返回类型,这里代表返回String类型
.await() //第二步,使用await方法拿到返回值
RxHttp操作符
/**
* 失败重试,该方法仅在使用协程时才有效
* @param times 重试次数, 默认Int.MAX_VALUE 代表不断重试
* @param period 重试周期, 默认为0, 单位: milliseconds
* @param test 重试条件, 默认为空,即无条件重试
*/
fun retry(
times: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE,
period: Long = 0,
test: ((Throwable) -> Boolean)? = null
)
retry()
方法共有3个参数,分别是重试次数、重试周期、重试条件,都有默认值,3个参数可以随意搭配,如:
retry() //无条件、不间断、一直重试
retry(2) //无条件、不间断、重试两次
retry(2, 1000) //无条件 间隔1s 重试2此
retry { it is ConnectException } //有条件、不间断、一直重试
retry(2) { it is ConnectException } //有条件、不间断、重试2次
retry(2, 1000) { it is ConnectException } //有条件、间隔1s、重试2次
retry(period = 1000) { it is ConnectException } //有条件、间断1s、一直重试
Throwable
异常对象,我们可以对异常做判断,如果需要重试,就返回true,不需要就返回false,下面看看具体代码
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.retry(2, 1000) { //重试2次,每次间隔1s
it is ConnectException //如果是网络异常就重试
}
.await()
timeout(Long)
方法,如下:
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.timeout(3000) //超时时长为3s
.await()
//同时获取两个学生信息
suspend void initData() {
val asyncStudent1 = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.async() //这里会返回Deferred<Student>
val asyncStudent2 = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.async() //这里会返回Deferred<Student>
//随后调用await方法获取对象
val student1 = asyncStudent1.await()
val student2 = asyncStudent2.await()
}
3.4、delay,startDelay延迟
delay
操作符是请求结束后,延迟一段时间返回;而
startDelay
操作符则是延迟一段时间后再发送请求,如下:
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.delay(1000) //请求回来后,延迟1s返回
.await()
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.startDelay(1000) //延迟1s后再发送请求
.await()
有些情况,我们不希望请求出现异常时,直接走异常回调,此时我们就可以通过两个操作符,给出默认的值,如下:
//根据异常给出默认值
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.timeout(100) //超时时长为100毫秒
.onErrorReturn {
//如果时超时异常,就给出默认值,否则,抛出原异常
return@onErrorReturn if (it is TimeoutCancellationException)
Student()
else
throw it
}
.await()
//只要出现异常,就返回默认值
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.timeout(100) //超时时长为100毫秒
.onErrorReturnItem(Student())
.await()
tryAwait
就派上用场了,它会在异常出现时,返回null,如下:
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.timeout(100) //超时时长为100毫秒
.tryAwait() //这里返回 Student? 对象,即有可能为空
map
操作符很好理解,RxJava即协程的Flow都有该操作符,功能都是一样,用于转换对象,如下:
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toStr()
.map { it.length } //String转Int
.tryAwait() //这里返回 Student? 对象,即有可能为空
timeout及retry
:
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.timeout(50)
.retry(2, 1000) { it is TimeoutCancellationException }
.await()
timeout
、
retry
互换下位置,就不一样了,如下:
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.retry(2, 1000) { it is TimeoutCancellationException }
.timeout(50)
.await()
timeout及retry
操作符,仅对上游代码生效。如retry操作符,下游的异常是捕获不到的,这就是为什么timeout在retry下,超时时,重试机制没有触发的原因。
timeout
和
startDelay
操作符
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.startDelay(2000)
.timeout(1000)
.await()
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.timeout(1000)
.startDelay(2000)
.await()
startDelay
延迟,它是不管的,也管不到。
协程开启/关闭/异常处理
await/tryAwait操作符获取请求返回值,它们都是suspend挂起函数,需要在另一个suspend挂起函数或者协程中才能被调用,故我们提供了RxLifeScope库来处理协程开启、关闭及异常处理,用法如下:
rxLifeScope
对象的
lanuch
方法开启协程即可,如下:
rxLifeScope.lanuch({
//协程代码块,运行在UI线程
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.await()
//可直接更新UI
}, {
//异常回调,这里可以拿到Throwable对象
})
RxLifeScope
对象,随后调用
lanuch
方法开启协程
val job = RxLifeScope().lanuch({
//协程代码块,运行在UI线程
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.await()
//可直接更新UI
}, {
//异常回调,这里可以拿到Throwable对象
})
//在合适的时机关闭协程
job.cancel()
lanuch
方法,传入协程运行回调及异常回调,我们也可以传入协程开启及结束回调,如下:
rxLifeScope.launch({
//协程代码块
val student = RxHttp.postForm("/service/...")
.toClass<Student>()
.await()
//可直接更新UI
}, {
//异常回调,这里可以拿到Throwable对象,运行在UI线程
}, {
//开始回调,可以开启等待弹窗,运行在UI线程
}, {
//结束回调,可以销毁等待弹窗,运行在UI线程
})
小结
timeout/retry
,延迟就用
delay/startDelay
,出现异常不想中断协程的运行,就用
onErrorReturn/onErrorReturnItem
或者
tryAwait
,总之,一切都是那么的优雅。
地址:
附加:
大家都知道我的微信已达上限,想微信交流的朋友可以加我的另外一个号,名额不多了,感兴趣的一起来搞事情哦:

转发至朋友圈,是绝对的真爱
以上是关于可怕!RxHttp2.0重大更新!协程发请求,原来如此简单的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章