开发者说丨动态规划及其在Apollo项目Planning模块的应用
Posted Apollo开发者社区
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了开发者说丨动态规划及其在Apollo项目Planning模块的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
动态规划的英文为:Dynamic Programming,这里的“Programming”并非指编写程序代码,而是指一种表格计算法(A tabular method),即基于表格查询的方法计算得到最优结果,因此中文将其翻译成“动态规划”不甚严谨。关于动态规划算法的原理,MIT出版的专著:“Introduction to Algorithms Third Edition (Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, Clifford Stein)”(中文版《算法导论》)讲解得不错,本文的算法原理及示例均摘自该书。
本文由社区荣誉布道师——贺志国撰写,对动态规划及其在Apollo项目Planning模块的应用进行了详细讲解,希望这篇文章能给感兴趣的开发者带来更多帮助。
以下,ENJOY

动态规划与分治法(The Divide-and-Conquer Method)有些类似,也是将问题分解为多个子问题,并且基于子问题的结果获得最终解。二者的区别是,分治法将初始问题划分为多个不关联(Disjoint)的子问题(Subproblem)(即子问题相互之间互不依赖),递归地解决子问题,然后将子问题的解合并得到初始问题的解。与之相反,动态规划法分解得到的子问题是相互重叠的(Overlap),即子问题依赖于子子问题(Subsubproblem),子子问题又进一步依赖于下一级的子子问题,这样不断循环直至抵达不需分解的初始条件。在求解过程中,为了避免重复计算子子问题从而提高算法效率,需要将一系列子子问题的解保存到一张表中(table,C++编程一般使用std::array、std::vector或std::list实现),这也就是动态规划又被称为查表计算法的原因。
动态规划一般应用于最优化问题(Optimization Problems)。这类问题一般存在多个解,每个解都具有一个度量值,我们期望得到具有度量值最优(即取最大或最小值)的解。该最优解一般称为最优化问题的一个解。注意,这个解并非唯一,因为最优化问题可能存在多个最优解。
构建一个动态规划算法的一般步骤如下:
1、刻画出一个最优解的结构特征(即使用数学表达式来表述一个最优解);
2、迭代定义一个最优解的度量值;
3、计算每个最优解的度量值,通常采用自下而上的方式;
4、根据计算得到的信息构建出原问题的一个最优解。步骤1-3是使用动态规划求解问题的基础形式。如果我们只需获得最优解的度量值而非最优解本身,则可以忽略步骤4。

Apollo项目Planning模块的EMPlanner中使用动态规划生成代价(Cost)最小的多项式路径(DP路径,见Apollo项目中的DPRoadGraph类)和速度(DP速度,见Apollo项目中的DpStGraph类),DP路径算法和DP速度算法的示意性描述如下图所示(来自百度Apollo项目公开课PPT):
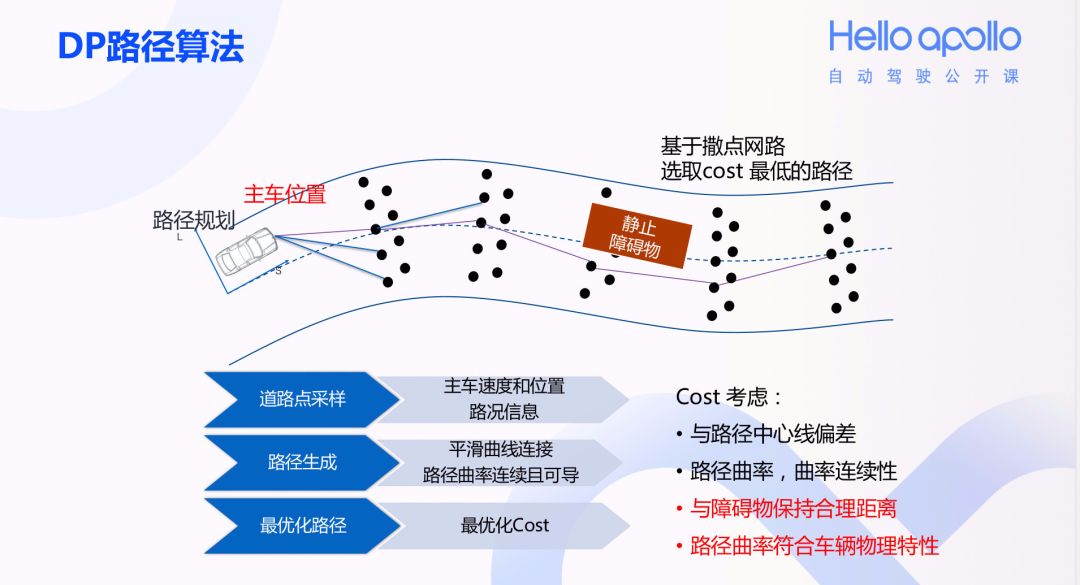
▲图1. DP路径算法
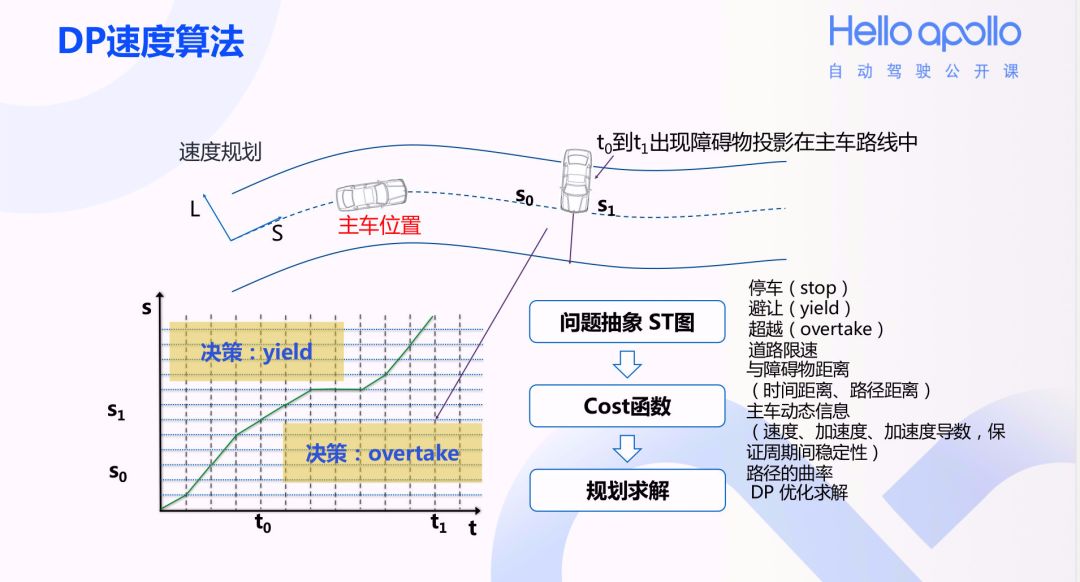
▲图2. DP速度算法
DP路径算法的基本思路是,基于给定的一条中心路径(称为参考线,ReferenceLine)和车道边界条件,每隔一定间隔的纵向距离(称为不同级(Level)上的s值)对道路截面进行均匀采样(与中心点的横向偏移值称为为l值),这样会得到图中黑点所示的采样点(这些采样点称为航点,Waypoint)数组。基于一定的规则,可以给出各航点迁移的代价值(Cost)。航点迁移不一定需要逐级进行,可以从第一级跳到第三级甚至终点,只要迁移代价值最小化即可,这显然满足动态规划的求解思路。
DP速度算法的基本思路是,在DP路径算法生成一条可行驶的路径后,从起点开始,考虑避开路径中的所有障碍物,并且让加减速最为平顺,以最优的速度曲线(即t-s平面中的绿色曲线)安全抵达终点,这也可以使用动态规划的思路求解。
航点数组生成
1// 采样获得路径航点
2bool DPRoadGraph::SamplePathWaypoints(
3 const common::TrajectoryPoint &init_point,
4 std::vector<std::vector
> *
const points) {
5 CHECK_NOTNULL(points);
6
7
// 最小采样距离
8
const
double kMinSampleDistance =
40.0;
9
// 总长度 = min(初始点 + max(初始速度 × 8, 最小采样距离), 参考线长度)
10
const
double total_length =
std::fmin(
11 init_sl_point_.s() +
std::fmax(init_point.v() *
8.0, kMinSampleDistance),
12 reference_line_.Length());
13
14
// 采样前视时长
15
constexpr
double kSamplePointLookForwardTime =
4.0;We can just use `sl = common::util::MakeSLPoint(s, l);` .
16
// 采样步长 = 初始速度 × 采样前视时长,要求:
17
// step_length_min(默认值:8) <= 采样步长 <= step_length_max(默认值:15)
18
const
double level_distance =
19 common::math::Clamp(init_point.v() * kSamplePointLookForwardTime,
20 config_.step_length_min(), config_.step_length_max());
21
// 累计轨迹弧长
22
double accumulated_s = init_sl_point_.s();
23
// 上次轨迹弧长
24
double prev_s = accumulated_s;
25
// 累计轨迹弧长小于总长度时,将累计轨迹弧长每次加上采样步长,进行循环采样
26
for (
std::
size_t i =
0; accumulated_s < total_length; ++i) {
27 accumulated_s += level_distance;
28
if (accumulated_s + level_distance /
2.0 > total_length) {
29 accumulated_s = total_length;
30 }
31
// 本次轨迹弧长:取累计轨迹弧长与总长度之间的最小值
32
const
double s =
std::fmin(accumulated_s, total_length);
33
// 最小允许采样步长
34
constexpr
double kMinAllowedSampleStep =
1.0;
35
// 若本次轨迹弧长与上次轨迹弧长间的差值小于最小允许采样步长,跳过本次采样
36
if (
std::
fabs(s - prev_s) < kMinAllowedSampleStep) {
37
continue;
38 }
39 prev_s = s;
40
41
// 左车道宽
42
double left_width =
0.0;
43
// 右车道宽
44
double right_width =
0.0;
45 reference_line_.GetLaneWidth(s, &left_width, &right_width);
46
47
// 边界缓冲
48
constexpr
double kBoundaryBuff =
0.20;
49
const
auto &vehicle_config =
50 common::VehicleConfigHelper::instance()->GetConfig();
51
const
double half_adc_width = vehicle_config.vehicle_param().width() /
2.0;
52
// 右侧允许宽度 = 右车道宽 - 半车宽 - 边界缓冲
53
const
double eff_right_width = right_width - half_adc_width - kBoundaryBuff;
54
// 左侧允许宽度 = 左车道宽 - 半车宽 - 边界缓冲
55
const
double eff_left_width = left_width - half_adc_width - kBoundaryBuff;
56
// 每步采样点数
57
const
size_t num_sample_per_level =
58 FLAGS_use_navigation_mode ? config_.navigator_sample_num_each_level()
59 : config_.sample_points_num_each_level();
60
// 默认横向采样间隔
61
double kDefaultUnitL =
1.2 / (num_sample_per_level -
1);
62
if (reference_line_info_.IsChangeLanePath() && !IsSafeForLaneChange()) {
63 kDefaultUnitL =
1.0;
64 }
65
// 横向采样距离
66
const
double sample_l_range = kDefaultUnitL * (num_sample_per_level -
1);
67
// 右采样边界(车辆右侧为负值)
68
double sample_right_boundary = -eff_right_width;
69
// 左采样边界(车辆左侧为正值)
70
double sample_left_boundary = eff_left_width;
71
// 参考线正在改变车道时
72
if (reference_line_info_.IsChangeLanePath()) {
73
// 右采样边界取右采样边界与初始点横向偏移之间的最小值
74 sample_right_boundary =
std::fmin(-eff_right_width, init_sl_point_.l());
75
// 左采样边界取左采样边界与初始点横向偏移之间的最大值
76 sample_left_boundary =
std::fmax(eff_left_width, init_sl_point_.l());
77
78
// 若初始点横向偏移 > 左侧允许宽度,则将右侧采样边界设置为右侧采样边界与(初始点横向偏移
79
// - 横向采样距离)之间的最大值
80
if (init_sl_point_.l() > eff_left_width) {
81 sample_right_boundary =
std::fmax(sample_right_boundary,
82 init_sl_point_.l() - sample_l_range);
83 }
84
// 若初始点横向偏移 < 右侧允许宽度,则将左侧采样边界设置为左侧采样边界与(初始点横向偏移
85
// + 横向采样距离)之间的最小值
86
if (init_sl_point_.l() < eff_right_width) {
87 sample_left_boundary =
std::fmin(sample_left_boundary,
88 init_sl_point_.l() + sample_l_range);
89 }
90 }
91
92
// 横向采样距离数组
93
std::
vector<
double> sample_l;
94
// 参考线正在改变车道且改变车道不安全时,将当前参考线到其他参考线的偏移值存储到横向采样距离数组
95
if (reference_line_info_.IsChangeLanePath() && !IsSafeForLaneChange()) {
96 sample_l.push_back(reference_line_info_.OffsetToOtherReferenceLine());
97 }
else {
98
// 其他情形,从右采样边界到左采样边界,按照每步采样点数进行均匀采样,并将结果存储到横向采样距离数组
99 common::util::uniform_slice(sample_right_boundary, sample_left_boundary,
100 num_sample_per_level -
1, &sample_l);
101
if (HasSidepass()) {
102
// currently only left nudge is supported. Need road hard boundary for
103
// both sides
104 sample_l.clear();
105
switch (sidepass_.type()) {
106
case ObjectSidePass::LEFT: {
107
// 左侧绕行:将(左侧允许宽度 + 左侧绕行距离)存储到横向采样距离数组
108 sample_l.push_back(eff_left_width + config_.sidepass_distance());
109
break;
110 }
111
case ObjectSidePass::RIGHT: {
112
// 右侧绕行:将-(右侧允许宽度 + 右侧绕行距离)存储到横向采样距离数组
113 sample_l.push_back(-eff_right_width - config_.sidepass_distance());
114
break;
115 }
116
default:
117
break;
118 }
119 }
120 }
121
// 本次采样点数组
122
std::
vector
level_points;
123 planning_internal::SampleLayerDebug sample_layer_debug;
124
for (
size_t j =
0; j < sample_l.size(); ++j) {
125
// 横向偏移值
126
const
double l = sample_l[j];
127
constexpr
double kResonateDistance =
1e-3;
128 common::SLPoint sl;
129
// 若为奇数采样点或者(总长度 - 累计轨迹弧长)几乎为0即已抵达采样终点,
130
// 则直接将当前采样点坐标设置为(s, l)
131
if (j %
2 ==
0 ||
132 total_length - accumulated_s <
2.0 * kResonateDistance) {
133 sl = common::util::MakeSLPoint(s, l);
134 }
else {
135
// 其他情形,将当前采样点坐标设置为(min(总长度,s+误差),l)
136 sl = common::util::MakeSLPoint(
137
std::fmin(total_length, s + kResonateDistance), l);
138 }
139 sample_layer_debug.add_sl_point()->CopyFrom(sl);
140
// 将当前采样点坐标存储到本次采样点数组
141 level_points.push_back(
std::move(sl));
142 }
143
// 若参考线未改变车道且不绕行,则将横向偏移值为0的采样点(即沿参考线方向的采样点)也加入本次采样点数组
144
if (!reference_line_info_.IsChangeLanePath() && !HasSidepass()) {
145
auto sl_zero = common::util::MakeSLPoint(s,
0.0);
146 sample_layer_debug.add_sl_point()->CopyFrom(sl_zero);
147 level_points.push_back(sl_zero);
148 }
149
150
if (!level_points.empty()) {
151 planning_debug_->mutable_planning_data()
152 ->mutable_dp_poly_graph()
153 ->add_sample_layer()
154 ->CopyFrom(sample_layer_debug);
155
// 将本次的所有采样点存储到总采样点数组
156 points->emplace_back(level_points);
157 }
158 }
159
return
true;
160}
<左右滑动以查看完整代码>
基于航点数组,使用动态规划算法求解代价值最小的路径。
1bool DPRoadGraph::GenerateMinCostPath(
2 const std::vector<const PathObstacle *> &obstacles,
3 std::vector
*min_cost_path) {
4 CHECK(min_cost_path != nullptr);
5
6
// 基于当前参考线及初始点,生成候选路径采样点数组
7
// 路径航点(path_waypoints)里面的每个vecotr存储相同s值(轨迹累计弧长)下的多个采样点
8 std::vector<std::vector
9
if (!SamplePathWaypoints(init_point_, &path_waypoints) ||
10 path_waypoints.size() <
1) {
11 AERROR <<
"Fail to sample path waypoints! reference_line_length = "
12 << reference_line_.Length();
13
return
false;
14 }
15
// 将初始点加入到路径航点数组的最前面
16 path_waypoints.insert(path_waypoints.begin(),
17 std::vector
{init_sl_point_});
18
if (path_waypoints.size() <
2) {
19 AERROR <<
"Too few path_waypoints.";
20
return
false;
21 }
22
23
// 输出路径航点调试信息
24
for (uint32_t i =
0; i < path_waypoints.size(); ++i) {
25
const auto &level_waypoints = path_waypoints.at(i);
26
for (uint32_t j =
0; j < level_waypoints.size(); ++j) {
27 ADEBUG <<
"level[" << i <<
"], "
28 << level_waypoints.at(j).ShortDebugString();
29 }
30 }
31
32
// 读取车辆配置信息
33
const auto &vehicle_config =
34 common::VehicleConfigHelper::instance()->GetConfig();
35
36
// 轨迹代价
37 TrajectoryCost trajectory_cost(
38 config_, reference_line_, reference_line_info_.IsChangeLanePath(),
39 obstacles, vehicle_config.vehicle_param(), speed_data_, init_sl_point_);
40
41
// 最小代价值路图节表点链表
42 std::list<std::list
</std::vector
> graph_nodes;
43 graph_nodes.emplace_back();
44 graph_nodes.back().emplace_back(init_sl_point_, nullptr, ComparableCost());
45 auto &front = graph_nodes.front().front();
46 size_t total_level = path_waypoints.size();
47 // 采用自下而上的动态规划算法,迭代更新最小代价值
48 // graph_nodes存储的就是各级(level)路径航点(path_waypoints)所包含的最小代价航点
49 // graph_nodes.back()(即最后一条航点链表)就是我们所需的最小代价航点链表
50 for (std::size_t level = 1; level < path_waypoints.size(); ++level) {
51 const auto &prev_dp_nodes = graph_nodes.back();
52 const auto &level_points = path_waypoints[level];
53
54 graph_nodes.emplace_back();
55
56 for (size_t i = 0; i < level_points.size(); ++i) {
57 const auto &cur_point = level_points[i];
58
59 graph_nodes.back().emplace_back(cur_point, nullptr);
60 auto &cur_node = graph_nodes.back().back();
61 // 采用多线程并行计算最小代价值航点
62 if (FLAGS_enable_multi_thread_in_dp_poly_path) {
63 PlanningThreadPool::instance()->Push(std::bind(
64 &DPRoadGraph::UpdateNode, this, std::ref(prev_dp_nodes), level,
65 total_level, &trajectory_cost, &(front), &(cur_node)));
66
67 } else {
68 // 采用单线程计算最小代价值航点
69 UpdateNode(prev_dp_nodes, level, total_level, &trajectory_cost, &front,
70 &cur_node);
71 }
72 }
73 // 多线程模式下的同步
74 if (FLAGS_enable_multi_thread_in_dp_poly_path) {
75 PlanningThreadPool::instance()->Synchronize();
76 }
77 }
78
79 // graph_nodes.back()(即最后一条航点链表)就是我们所需的最小代价航点链表
80 // find best path
81 DPRoadGraphNode fake_head;
82 for (const auto &cur_dp_node : graph_nodes.back()) {
83 fake_head.UpdateCost(&cur_dp_node, cur_dp_node.min_cost_curve,
84 cur_dp_node.min_cost);
85 }
86
87 // 从终点顺藤摸瓜向起点逐个找出最小代价值航点,并将其加入min_cost_path
88 const auto *min_cost_node = &fake_head;
89 while (min_cost_node->min_cost_prev_node) {
90 min_cost_node = min_cost_node->min_cost_prev_node;
91 min_cost_path->push_back(*min_cost_node);
92 }
93 if (min_cost_node != &graph_nodes.front().front()) {
94 return false;
95 }
96
97 // 将航点顺序调整为起点到终点
98 std::reverse(min_cost_path->begin(), min_cost_path->end());
99
100 for (const auto &node : *min_cost_path) {
101 ADEBUG << "min_cost_path: " << node.sl_point.ShortDebugString();
102 planning_debug_->mutable_planning_data()
103 ->mutable_dp_poly_graph()
104 ->add_min_cost_point()
105 ->CopyFrom(node.sl_point);
106 }
107 return true;
108}
109
110// 在当前level下,获得一条代价值最小的航点链表
111void DPRoadGraph::UpdateNode(const std::list
&prev_nodes,
112
const uint32_t level,
const uint32_t total_level,
113 TrajectoryCost *trajectory_cost,
114 DPRoadGraphNode *front,
115 DPRoadGraphNode *cur_node) {
116 DCHECK_NOTNULL(trajectory_cost);
117 DCHECK_NOTNULL(front);
118 DCHECK_NOTNULL(cur_node);
119
for (
const auto &prev_dp_node : prev_nodes) {
120
const auto &prev_sl_point = prev_dp_node.sl_point;
121
const auto &cur_point = cur_node->sl_point;
122 double init_dl =
0.0;
123 double init_ddl =
0.0;
124
if (level ==
1) {
125 init_dl = init_frenet_frame_point_.dl();
126 init_ddl = init_frenet_frame_point_.ddl();
127 }
128
// 生成当前点到前一level所有航点的的曲线
129 QuinticPolynomialCurve1d curve(prev_sl_point.l(), init_dl, init_ddl,
130 cur_point.l(),
0.0,
0.0,
131 cur_point.s() - prev_sl_point.s());
132
133
if (!IsValidCurve(curve)) {
134
continue;
135 }
136
const auto cost =
137 trajectory_cost->Calculate(curve, prev_sl_point.s(), cur_point.s(),
138 level, total_level) +
139 prev_dp_node.min_cost;
140
// 根据代价最小的原则,在前一level所有航点中找到与当前点连接代价最小的航点,
141
// 将结果存储于prev_dp_node中
142 cur_node->UpdateCost(&prev_dp_node, curve, cost);
143
144
// 尝试将当前点直接连接到初始点,看其代价是否比当前点到前一level航点的最小代价还小,
145
// 若小于则将最小代价航点更新。这种情况一般只会存在于改变车道的情形。
146
// try to connect the current point with the first point directly
147
// only do this at lane change
148
if (level >=
2) {
149 init_dl = init_frenet_frame_point_.dl();
150 init_ddl = init_frenet_frame_point_.ddl();
151 QuinticPolynomialCurve1d curve(init_sl_point_.l(), init_dl, init_ddl,
152 cur_point.l(),
0.0,
0.0,
153 cur_point.s() - init_sl_point_.s());
154
if (!IsValidCurve(curve)) {
155
continue;
156 }
157
const auto cost = trajectory_cost->Calculate(
158 curve, init_sl_point_.s(), cur_point.s(), level, total_level);
159 cur_node->UpdateCost(front, curve, cost);
160 }
161 }
162}
<左右滑动以查看完整代码>
1// 从st图中寻找代价值最小的速度曲线
2// s:行驶距离,纵坐标;
3// t:行驶时间,横坐标
4// SpeedData* const speed_data表示speed_data本身(即指针自身)不能被修改,
5// 但speed_data指向的内容可被修改,该函数就是通过它返回最优速度数据的。
6Status DpStGraph::Search(SpeedData* const speed_data) {
7 constexpr double kBounadryEpsilon = 1e-2;
8 // 对边界条件进行初步筛选
9 for (const auto& boundary : st_graph_data_.st_boundaries()) {
10 // 若边界类型为禁停区,直接跳过
11 if (boundary->boundary_type() == StBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
12 continue;
13 }
14 // 若边界位于(0.0, 0.0)(即起始位置)或者边界的min_t和min_s比边界最小分辨率
15 // kBounadryEpsilon还小,则将速度点的s值设为0.0,t值均匀采样递增。
16 if (boundary->IsPointInBoundary({0.0, 0.0}) ||
17 (std::fabs(boundary->min_t()) < kBounadryEpsilon &&
18 std::fabs(boundary->min_s()) < kBounadryEpsilon)) {
19 std::vector
speed_profile;
20
double t =
0.0;
21
for (
int i =
0; i < dp_st_speed_config_.
matrix_dimension_t();
22 ++i, t += unit_t_) {
23 SpeedPoint speed_point;
24 speed_point.set_s(
0.0);
25 speed_point.
set_t(t);
26 speed_profile.emplace_back(speed_point);
27 }
28 speed_data->set_speed_vector(speed_profile);
29
return Status::OK();
30 }
31 }
32
33
// 若st图数据的边界条件为空,意味着前方没有障碍物,匀速前进即可。
34
// speed_profile[i] = (0.0 + i * unit_s_, 0.0 + i * unit_t_);
35
if (st_graph_data_.st_boundaries().empty()) {
36 ADEBUG <<
"No path obstacles, dp_st_graph output default speed profile.";
37
std::
vector
speed_profile;
38
double s =
0.0;
39
double t =
0.0;
40
for (
int i =
0; i < dp_st_speed_config_.
matrix_dimension_t() &&
41 i < dp_st_speed_config_.matrix_dimension_s();
42 ++i, t += unit_t_, s += unit_s_) {
43 SpeedPoint speed_point;
44 speed_point.set_s(s);
45 speed_point.
set_t(t);
46 speed_profile.emplace_back(speed_point);
47 }
48 speed_data->set_speed_vector(speed_profile);
49
return Status::OK();
50 }
51
52
// 初始化代价表cost_table_
53
if (!InitCostTable().ok()) {
54
const
std::
string msg =
"Initialize cost table failed.";
55 AERROR << msg;
56
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
57 }
58
// 计算代价表cost_table_中所有节点的总代价
59
if (!CalculateTotalCost().ok()) {
60
const
std::
string msg =
"Calculate total cost failed.";
61 AERROR << msg;
62
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
63 }
64
// 通过计算得到的代价表cost_table_中所有节点的总代价,获取速度数据
65
if (!RetrieveSpeedProfile(speed_data).ok()) {
66
const
std::
string msg =
"Retrieve best speed profile failed.";
67 AERROR << msg;
68
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
69 }
70
return Status::OK();
71}
72
73
// 初始化代价表
74Status DpStGraph::InitCostTable() {
75
// 从配置文件读取s和t的维数
76
uint32_t dim_s = dp_st_speed_config_.matrix_dimension_s();
77
uint32_t
dim_t = dp_st_speed_config_.
matrix_dimension_t();
78
// 维数检查,要求大于2
79 DCHECK_GT(dim_s,
2);
80 DCHECK_GT(
dim_t,
2);
81
// 生成代价表cost_table_,列为dim_t,行为dim_s,所有节点均初始化为:StGraphpoint()
82 cost_table_ =
std::
vector<
std::
vector
>(
83
dim_t,
std::
vector
(dim_s, StGraphPoint()));
84
85
// cost_table_[i][j] = STPoint(0.0 + j * unit_s_, 0.0 + i * unit_t_);
86
double
curr_t =
0.0;
87
for (
uint32_t i =
0; i < cost_table_.size(); ++i,
curr_t += unit_t_) {
88
auto& cost_table_i = cost_table_[i];
89
double curr_s =
0.0;
90
for (
uint32_t j =
0; j < cost_table_i.size(); ++j, curr_s += unit_s_) {
91 cost_table_i[j].Init(i, j, STPoint(curr_s,
curr_t));
92 }
93 }
94
return Status::OK();
95}
96
97
// 计算总代价
98Status DpStGraph::CalculateTotalCost() {
99
// col and row are for STGraph
100
// t corresponding to col,横坐标
101
// s corresponding to row,纵坐标
102
uint32_t next_highest_row =
0;
103
uint32_t next_lowest_row =
0;
104
105
// 对于第一、二,直至最后一个时间采样值,循环计算不同距离采样值上的代价
106
// 注意:每个时间采样值上的距离采样值数目是不相同的。例如:
107
// 第一个时间采样值为起点,在该点上只能有一个距离采样值:0,否则
108
// 代价表cost_table_就不正确。正常情况下,第二个时间采样值上的距离采样值数目
109
// 会大于1,不然就是匀速前进,玩不下去了^_^
110
for (
size_t c =
0; c < cost_table_.size(); ++c) {
111
// 最高行,即最大加速度情形下所允许的最大距离采样值
112
uint32_t highest_row =
0;
113
// 最低行,即最大减速度情形下所允许的最小距离采样值
114
uint32_t lowest_row = cost_table_.back().size() -
1;
115
116
// 对于时间采样值c上的不同距离采样值r: next_lowest_row<=4<=next_highest_row
117
// 计算抵达节点(c, r)的最小总代价
118
for (
uint32_t r = next_lowest_row; r <= next_highest_row; ++r) {
119
if (FLAGS_enable_multi_thread_in_dp_st_graph) {
120
// 采用线程池方式计算(c, r)的最小总代价
121 PlanningThreadPool::instance()->Push(
122
std::bind(&DpStGraph::CalculateCostAt,
this, c, r));
123 }
else {
124
// 采用单线程方式计算(c, r)的最小总代价
125 CalculateCostAt(c, r);
126 }
127 }
128
// 线程池方式间的同步
129
if (FLAGS_enable_multi_thread_in_dp_st_graph) {
130 PlanningThreadPool::instance()->Synchronize();
131 }
132
133
// 给定时间采样值c的情形下,
134
// 更新最高行(即最大采样距离值)和最低行(即最小采样距离值)
135
for (
uint32_t r = next_lowest_row; r <= next_highest_row; ++r) {
136
const
auto& cost_cr = cost_table_[c][r];
137
if (cost_cr.total_cost() <
std::numeric_limits<
double>::infinity()) {
138
uint32_t h_r =
0;
139
uint32_t l_r =
0;
140
// 获取当前节点的最高行和最低行
141 GetRowRange(cost_cr, &h_r, &l_r);
142 highest_row =
std::max(highest_row, h_r);
143 lowest_row =
std::min(lowest_row, l_r);
144 }
145 }
146
// 更新下一次循环的最高行(即最大采样距离)和
147
// 最低行(即最小采样距离)
148 next_highest_row = highest_row;
149 next_lowest_row =
std::max(next_lowest_row, lowest_row);
150 }
151
152
return Status::OK();
153}
154
155
// 基于当前ST图上的点point,获取下一个允许的
156
// 最高行(即最大采样距离)和最低行(即最小采样距离)
157
void DpStGraph::GetRowRange(
const StGraphPoint& point,
158
uint32_t* next_highest_row,
159
uint32_t* next_lowest_row) {
160
double v0 =
0.0;
161
if (!point.pre_point()) {
162
// 起始点速度
163 v0 = init_point_.v();
164 }
else {
165
// 其他点速度
166 v0 = (point.index_s() - point.pre_point()->index_s()) * unit_s_ / unit_t_;
167 }
168
169
// cost_table_中最后一个时间采样值所包含的距离采样值数目
170
const
size_t max_s_size = cost_table_.back().size() -
1;
171
172
const
double speed_coeff = unit_t_ * unit_t_;
173
// 最大加速度情形下所允许的最大距离
174
const
double delta_s_upper_bound =
175 v0 * unit_t_ + vehicle_param_.max_acceleration() * speed_coeff;
176 *next_highest_row =
177 point.index_s() +
static_cast<
uint32_t>(delta_s_upper_bound / unit_s_);
178
if (*next_highest_row >= max_s_size) {
179 *next_highest_row = max_s_size;
180 }
181
// 最大减速度情形下所允许的最小距离
182
const
double delta_s_lower_bound =
std::fmax(
183
0.0, v0 * unit_t_ + vehicle_param_.max_deceleration() * speed_coeff);
184 *next_lowest_row +=
static_cast<
int32_t>(delta_s_lower_bound / unit_s_);
185
if (*next_lowest_row > max_s_size) {
186 *next_lowest_row = max_s_size;
187 }
188}
189
190
// 使用动态规划算法计算(c, r)点的总代价
191
// c: 时间坐标,即横坐标
192
// r: 距离坐标,即纵坐标
193
void DpStGraph::CalculateCostAt(
const
uint32_t c,
const
uint32_t r) {
194
auto& cost_cr = cost_table_[c][r];
195
// 设置当前点的障碍物代价
196 cost_cr.SetObstacleCost(dp_st_cost_.GetObstacleCost(cost_cr));
197
// 当前点的障碍物代价无穷大,直接返回
198
if (cost_cr.obstacle_cost() >
std::numeric_limits<
double>::max()) {
199
return;
200 }
201
// 初始代价
202
const
auto& cost_init = cost_table_[
0][
0];
203
// 第一个时间采样值为c(即时间t)== 0,因此r(即距离)必须为0,表示是起点,代价值自然设置为0.0。
204
if (c ==
0) {
205 DCHECK_EQ(r,
0) <<
"Incorrect. Row should be 0 with col = 0. row: " << r;
206 cost_cr.SetTotalCost(
0.0);
207
return;
208 }
209
210
// 获取速度限制条件
211
double speed_limit =
212 st_graph_data_.speed_limit().GetSpeedLimitByS(unit_s_ * r);
213
// 第二个时间采样值
214
if (c ==
1) {
215
// 加速度或减速度超出范围,返回
216
const
double acc = (r * unit_s_ / unit_t_ - init_point_.v()) / unit_t_;
217
if (acc < dp_st_speed_config_.max_deceleration() ||
218 acc > dp_st_speed_config_.max_acceleration()) {
219
return;
220 }
221
222
// 当前点与初始点有重叠,返回
223
if (CheckOverlapOnDpStGraph(st_graph_data_.st_boundaries(), cost_cr,
224 cost_init)) {
225
return;
226 }
227
// 设置当前点的代价值
228 cost_cr.SetTotalCost(cost_cr.obstacle_cost() + cost_init.total_cost() +
229 CalculateEdgeCostForSecondCol(r, speed_limit));
230
// 设置其前序节点为起点
231 cost_cr.SetPrePoint(cost_init);
232
return;
233 }
234
235
constexpr
double kSpeedRangeBuffer =
0.20;
236
// 允许的最大距离采样差值
237
const
uint32_t max_s_diff =
238
static_cast<
uint32_t>(FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit *
239 (
1 + kSpeedRangeBuffer) * unit_t_ / unit_s_);
240
// 最小距离采样值
241
const
uint32_t r_low = (max_s_diff < r ? r - max_s_diff :
0);
242
// 上一个时间采样值下不同采样距离的代价数组
243
const
auto& pre_col = cost_table_[c -
1];
244
245
// 第三个时间采样值
246
if (c ==
2) {
247
for (
uint32_t r_pre = r_low; r_pre <= r; ++r_pre) {
248
// 从距离采样值r_pre到r所需的加速度
249
const
double acc =
250 (r * unit_s_ -
2 * r_pre * unit_s_) / (unit_t_ * unit_t_);
251
// 若加速度越界,则忽略该距离采样值
252
if (acc < dp_st_speed_config_.max_deceleration() ||
253 acc > dp_st_speed_config_.max_acceleration()) {
254
continue;
255 }
256
// 与前一时间采样值上的节点有重合,忽略该距离采样值
257
if (CheckOverlapOnDpStGraph(st_graph_data_.st_boundaries(), cost_cr,
258 pre_col[r_pre])) {
259
continue;
260 }
261
// 计算当前节点(c, r)的代价值
262
const
double cost = cost_cr.obstacle_cost() +
263 pre_col[r_pre].total_cost() +
264 CalculateEdgeCostForThirdCol(r, r_pre, speed_limit);
265
// 若新代价值比节点(c, r)的原有代价值更小,则更新当前节点(c, r)的总代价值
266
if (cost < cost_cr.total_cost()) {
267 cost_cr.SetTotalCost(cost);
268 cost_cr.SetPrePoint(pre_col[r_pre]);
269 }
270 }
271
return;
272 }
273
274
// 其他时间采样值
275
for (
uint32_t r_pre = r_low; r_pre <= r; ++r_pre) {
276
277
// 若节点(c - 1, r_pre)上的总代价无穷大或前一次时间采样c - 1上没有前序节点,忽略该节点
278
if (
std::isinf(pre_col[r_pre].total_cost()) ||
279 pre_col[r_pre].pre_point() ==
nullptr) {
280
continue;
281 }
282
// 从r_pre抵达r所需的加速度
283
const
double curr_a = (cost_cr.index_s() * unit_s_ +
284 pre_col[r_pre].pre_point()->index_s() * unit_s_ -
285
2 * pre_col[r_pre].index_s() * unit_s_) /
286 (unit_t_ * unit_t_);
287
// 若加速度越界,忽略该距离采样值
288
if (curr_a > vehicle_param_.max_acceleration() ||
289 curr_a < vehicle_param_.max_deceleration()) {
290
continue;
291 }
292
// 与前一时间采样值上的节点有重合,忽略该距离采样值
293
if (CheckOverlapOnDpStGraph(st_graph_data_.st_boundaries(), cost_cr,
294 pre_col[r_pre])) {
295
continue;
296 }
297
298
// 上上次距离采样值
299
uint32_t r_prepre = pre_col[r_pre].pre_point()->index_s();
300
// ST图上的上上个点
301
const StGraphPoint& prepre_graph_point = cost_table_[c -
2][r_prepre];
302
// 若上上个节点总代价无穷大,忽略之。
303
if (
std::isinf(prepre_graph_point.total_cost())) {
304
continue;
305 }
306
// 若上上个节点没有前序节点,忽略之。
307
if (!prepre_graph_point.pre_point()) {
308
continue;
309 }
310
// 上上上个节点
311
const STPoint& triple_pre_point = prepre_graph_point.pre_point()->point();
312
// 上上个节点
313
const STPoint& prepre_point = prepre_graph_point.point();
314
// 上个节点
315
const STPoint& pre_point = pre_col[r_pre].point();
316
// 当前节点
317
const STPoint& curr_point = cost_cr.point();
318
// 计算从上上上个节点、上上个节点、上个节点与当前节点之间的最小连接代价
319
double cost = cost_cr.obstacle_cost() + pre_col[r_pre].total_cost() +
320 CalculateEdgeCost(triple_pre_point, prepre_point, pre_point,
321 curr_point, speed_limit);
322
323
// 若新代价值比节点(c, r)的原有代价值更小,则更新当前节点(c, r)的总代价值
324
if (cost < cost_cr.total_cost()) {
325 cost_cr.SetTotalCost(cost);
326 cost_cr.SetPrePoint(pre_col[r_pre]);
327 }
328 }
329}
330
331
// 获取代价值最小的速度数据
332Status DpStGraph::RetrieveSpeedProfile(SpeedData*
const speed_data) {
333
// 最小代价值
334
double min_cost =
std::numeric_limits<
double>::infinity();
335
// 最优终点(即包含最小代价值的节点)
336
const StGraphPoint* best_end_point =
nullptr;
337
// cost_table_.back()存储的是最后一个时间采样值上不同距离的代价值
338
for (
const StGraphPoint& cur_point : cost_table_.back()) {
339
if (!
std::isinf(cur_point.total_cost()) &&
340 cur_point.total_cost() < min_cost) {
341 best_end_point = &cur_point;
342 min_cost = cur_point.total_cost();
343 }
344 }
345
// 对于cost_table_中的每一行,即第一个、第二个、...、最后一个时间采样值上的
346
// 代价值数组,其最后一个元素存储的是本级时间采样值上的最小代价节点。
347
// 将这些节点与现有最优终点best_end_point比较,
348
// 不断更新最小代价值min_cost和最优终点best_end_point,
349
// 直至找到全局最优终点
350
for (
const
auto& row : cost_table_) {
351
const StGraphPoint& cur_point = row.back();
352
if (!
std::isinf(cur_point.total_cost()) &&
353 cur_point.total_cost() < min_cost) {
354 best_end_point = &cur_point;
355 min_cost = cur_point.total_cost();
356 }
357 }
358
359
// 寻找最优终点失败
360
if (best_end_point ==
nullptr) {
361
const
std::
string msg =
"Fail to find the best feasible trajectory.";
362 AERROR << msg;
363
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
364 }
365
366
// 设置最优终点的速度数据,并顺藤摸瓜找出其连接的倒数第二个、倒数第三个直到第一个时间节点
367
// 分别设置这些时间节点的速度数据
368
std::
vector
speed_profile;
369
const StGraphPoint* cur_point = best_end_point;
370
while (cur_point !=
nullptr) {
371 SpeedPoint speed_point;
372 speed_point.set_s(cur_point->point().s());
373 speed_point.
set_t(cur_point->point().t());
374 speed_profile.emplace_back(speed_point);
375 cur_point = cur_point->pre_point();
376 }
377
// 将速度数据按起点到终点的顺序重新排列
378
std::reverse(speed_profile.begin(), speed_profile.end());
379
380
// 若速度数据中起始点的时间(t)或距离(s)大于编译器定义的最小双精度浮点数(即起点的时间t
381
// 或距离s不为0),则视结果为错误输出。
382
constexpr
double kEpsilon =
std::numeric_limits<
double>::epsilon();
383
if (speed_profile.front().t() > kEpsilon ||
384 speed_profile.front().s() > kEpsilon) {
385
const
std::
string msg =
"Fail to retrieve speed profile.";
386 AERROR << msg;
387
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
388 }
389
390
// 设置最终的速度数据
391 speed_data->set_speed_vector(speed_profile);
392
return Status::OK();
393}
394
395
// 计算第一、二、三、四个节点之间的连接代价
396
double DpStGraph::CalculateEdgeCost(
const STPoint& first,
const STPoint& second,
397
const STPoint& third,
const STPoint& forth,
398
const
double speed_limit) {
399
return dp_st_cost_.GetSpeedCost(third, forth, speed_limit) +
400 dp_st_cost_.GetAccelCostByThreePoints(second, third, forth) +
401 dp_st_cost_.GetJerkCostByFourPoints(first, second, third, forth);
402}
403
404
// 为第二列(即第三个时间采样值上的代价数组)计算连接代价
405
double DpStGraph::CalculateEdgeCostForSecondCol(
const
uint32_t row,
406
const
double speed_limit) {
407
double init_speed = init_point_.v();
408
double init_acc = init_point_.a();
409
const STPoint& pre_point = cost_table_[
0][
0].point();
410
const STPoint& curr_point = cost_table_[
1][row].point();
411
return dp_st_cost_.GetSpeedCost(pre_point, curr_point, speed_limit) +
412 dp_st_cost_.GetAccelCostByTwoPoints(init_speed, pre_point,
413 curr_point) +
414 dp_st_cost_.GetJerkCostByTwoPoints(init_speed, init_acc, pre_point,
415 curr_point);
416}
417
418
// 为第三列(即第四个时间采样值上的代价数组)计算连接代价
419
double DpStGraph::CalculateEdgeCostForThirdCol(
const
uint32_t curr_row,
420
const
uint32_t pre_row,
421
const
double speed_limit) {
422
double init_speed = init_point_.v();
423
const STPoint& first = cost_table_[
0][
0].point();
424
const STPoint& second = cost_table_[
1][pre_row].point();
425
const STPoint& third = cost_table_[
2][curr_row].point();
426
return dp_st_cost_.GetSpeedCost(second, third, speed_limit) +
427 dp_st_cost_.GetAccelCostByThreePoints(first, second, third) +
428 dp_st_cost_.GetJerkCostByThreePoints(init_speed, first, second, third);
429}
<左右滑动以查看完整代码>
以上是"动态规划及其在Apollo项目Planning模块的应用"的全部内容,更多话题讨论、技术交流可以扫描下方二维码添加『Apollo小哥哥』为好友,进开发者交流群。



* 以上内容为开发者原创,不代表百度官方言论。
内容来自开发者CSDN:


以上是关于开发者说丨动态规划及其在Apollo项目Planning模块的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章

