R语言日历图(完)
Posted 气象水文科研猫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了R语言日历图(完)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
往期R语言日历图推文超链接:
1 《》
2 《》
3 《》
4 《》
5 《》
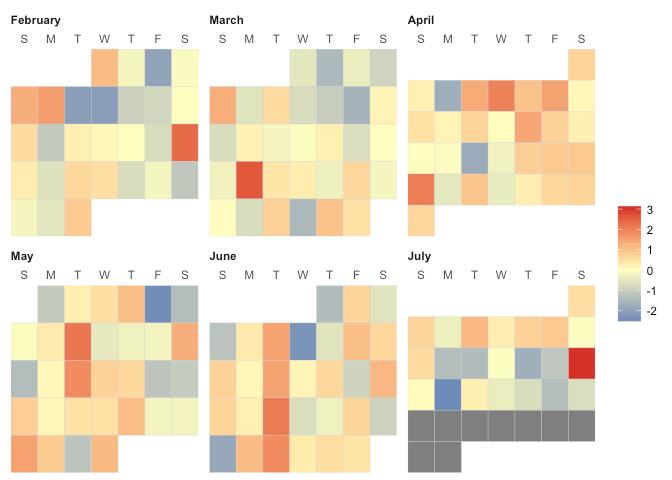
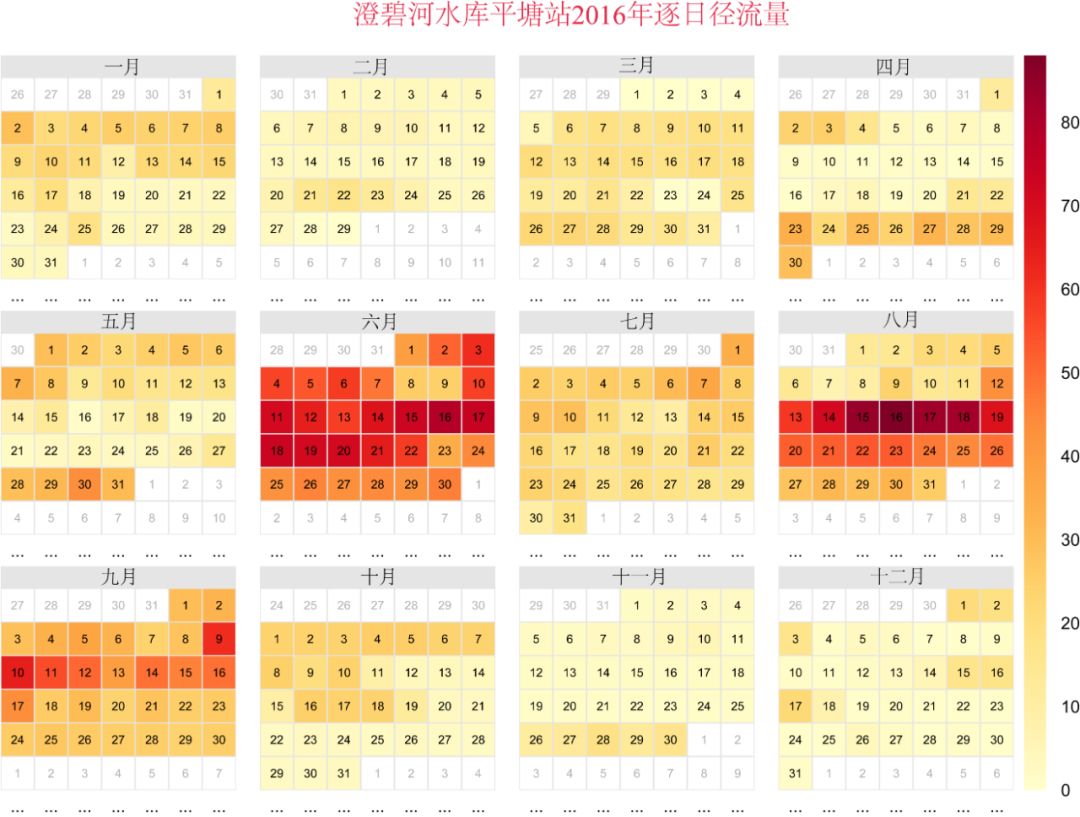
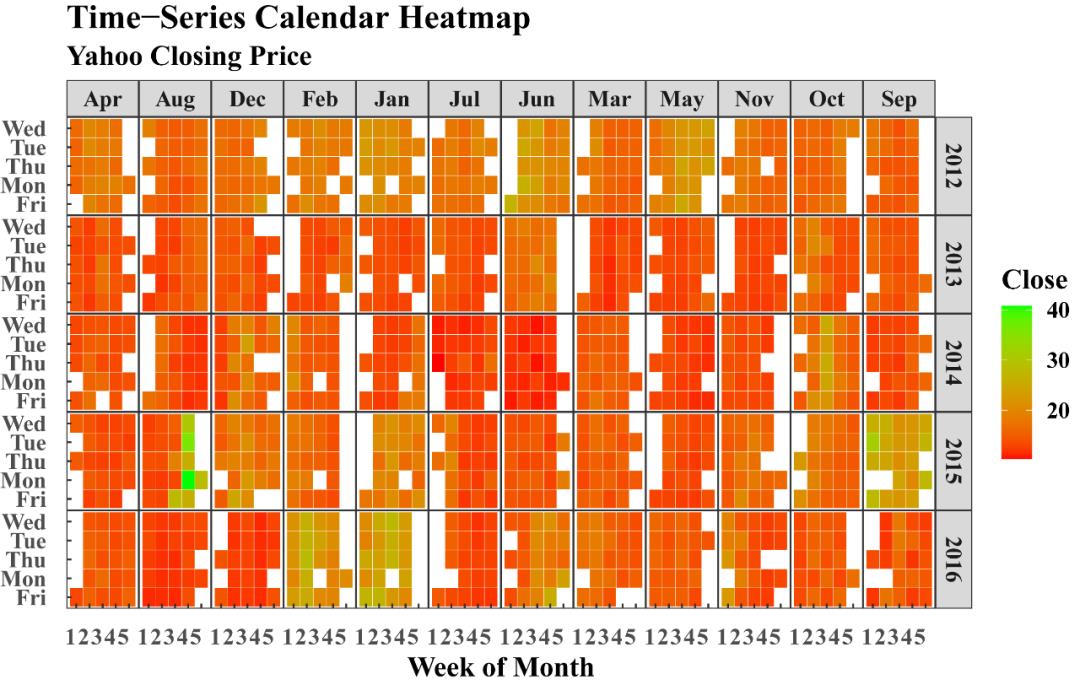
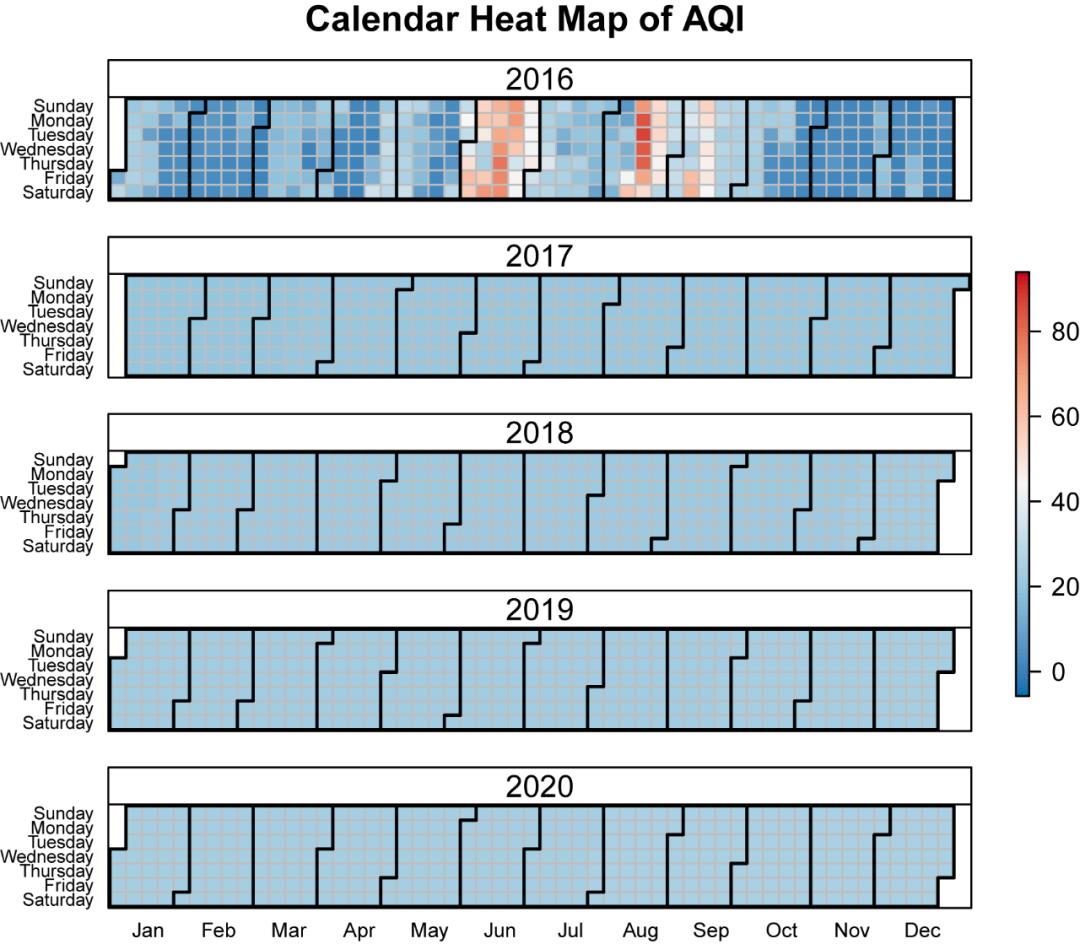
ggplot(data = dat, aes(date = date, fill = ValueCol))+stat_calendar_heatmap() +scale_fill_gradientn(colours = rev(brewer.pal(11, "Spectral"))) +scale_x_continuous(name = NULL, breaks = MonthLabels$meanWkofYr, labels = MonthLabels$month, expand = c(0,0)) +facet_wrap(~Year,ncol = 1)+theme_bw()+ # 去除地图灰色背景theme(panel.grid.major=element_line(colour=NA),panel.background = element_rect(fill = "transparent",colour = NA),plot.background = element_rect(fill = "transparent",colour = NA),panel.grid.minor = element_blank())+ # 去除地图网格theme(axis.ticks.length=unit(0, "cm"),axis.text.x = element_text(margin=unit(c(0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5), "cm")),axis.text.y = element_text(margin=unit(c(0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5), "cm")) )+theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=0,hjust=1), # 旋转坐标轴label的方向text = element_text(size = 13, face = "bold", family="serif"),panel.spacing = unit(0,"lines"))+scale_y_discrete(expand = c(0,0))+scale_y_continuous(name = NULL,breaks = seq(7, 1, -1), labels = c("Mon", "Tue", "Wed","Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun")) +scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0,0),breaks = seq(7, 1, -1), labels = c("Mon", "Tue", "Wed","Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"))+theme(legend.key.height = grid::unit(2.3, "cm"))
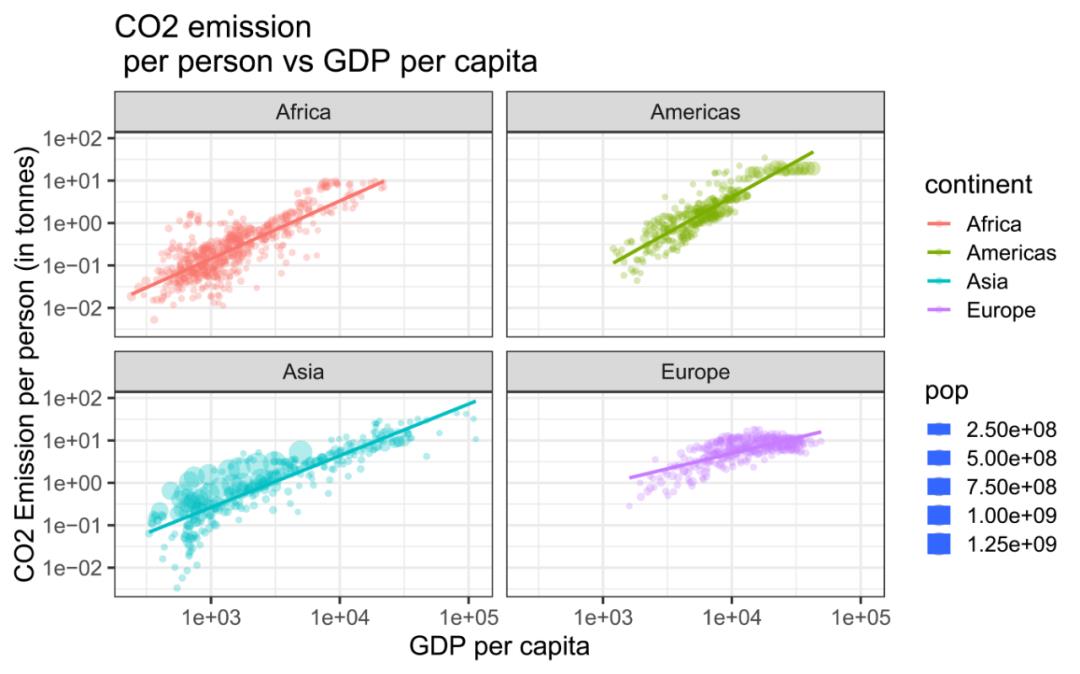
setwd('F:/Rpeng/29')library(tidyverse)library(ggplot2)theme_set(theme_bw())gapminder_co2 <- read.csv('co2.csv',header = T)gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point()gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point()+labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita")+theme_bw(base_size = 16)gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point() +labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_x_log10()gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point() + labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point(alpha=0.3) +labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2, color=continent)) +geom_point(alpha=0.5) + labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point(alpha=0.5, aes(color=continent,size=pop)) + labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point(alpha=0.5, aes(color=continent,size=pop)) + labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()+geom_smooth(method=lm,se=FALSE)gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2,color=continent,size=pop)) +geom_point(alpha=0.5) + labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()+geom_smooth(method=lm,se=FALSE)set.seed(143)gapminder_co2 %>% ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2)) +geom_point(alpha=0.5, aes(color=continent,size=pop)) +labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()+geom_smooth(method=lm,se=FALSE) +ggrepel::geom_text_repel(data = gapminder_co2 %>% filter(gdpPercap>12000 | gdpPercap < 1000) %>%sample_n(20),aes(label = country))gapminder_co2 %>% filter(continent!="Oceania") %>%ggplot(aes(x=gdpPercap,y=co2,color=continent,size=pop)) +geom_point(alpha=0.3) +labs(x="GDP per capita", y= "CO2 Emission per person (in tonnes)",title="CO2 emission per person vs GDP per capita") +scale_y_log10()+scale_x_log10()+geom_smooth(method=lm,se=FALSE)+facet_wrap(~continent, ncol=2)+theme(strip.text.x = element_text(size=12, color="blue",angle=0),strip.background = element_rect(colour="blue", fill="white"),axis.text = element_text(size=12))
以上是关于R语言日历图(完)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章