用Perl读取Excel文件,Spreadsheet::Read.pm库介绍
Posted ExASIC
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了用Perl读取Excel文件,Spreadsheet::Read.pm库介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Excel是IC设计验证中常用的配置文件格式。与yaml、json、xml等专业格式比起来,Excel人人都会用,无需培训。
Spreadsheet::Read介绍
Spreadsheet::Read库支持读取csv、ods、xls、xlsx等文件格式。
1use Spreadsheet::Read;
2my $book = ReadData ("test.csv", sep => ";");
3my $book = ReadData ("test.ods");
4my $book = ReadData ("test.xls");
5my $book = ReadData ("test.xlsx");
其实Read.pm并没有那么厉害,它只是把Spreadsheet::XLSX和Spreadsheet::ParseExcel包了一层,统一了各种格式的读取数据的接口和数据存储结构。
读取csv或excel文件后,Read.pm把数据按下面的结构存储。$book是一个数组指针,$book[0]是一些整体的信息,如一共有几张sheet,每个sheet的label名等。$book[1]~$book[n]保存着实际sheet里的信息和数据。
1$book = [
2 # Entry 0 is the overall control hash
3 { sheets => 2,
4 sheet => {
5 "Sheet 1" => 1,
6 "Sheet 2" => 2,
7 },
8 parsers => [ {
9 type => "xls",
10 parser => "Spreadsheet::ParseExcel",
11 version => 0.59,
12 }],
13 error => undef,
14 },
15 # Entry 1 is the first sheet
16 { parser => 0,
17 label => "Sheet 1",
18 maxrow => 2,
19 maxcol => 4,
20 cell => [ undef,
21 [ undef, 1 ],
22 [ undef, undef, undef, undef, undef, "Nugget" ],
23 ],
24 attr => [],
25 merged => [],
26 active => 1,
27 A1 => 1,
28 B5 => "Nugget",
29 },
30 # Entry 2 is the second sheet
31 { parser => 0,
32 label => "Sheet 2",
33 ...
每个sheet里,具体保存了label名、实际使用的最大行和最大列(即有效数据的最后一行和最后一列)、单元格里的数据等。
其中单元格里的数据是一个二维数组cell[col][row]。为了使用更方便,cell数组的0行0列留空了,没使用。实际数据从1行1列开始。例如:cell[1][1]就是A1里面的值。
注意:列在前、行在后。
SpreadSheet::Read的例子
假设,我们有Excel文件Book1.xlsx,内容如下:
读取Excel的脚本如下:
1#!/usr/bin/perl -w
2
3use strict;
4use Spreadsheet::Read;
5
6my $excelfilename = "Book1.xlsx";
7my $book_ref = ReadData("$excelfilename");
8my @book = @{$book_ref};
9
10#info
11my %info = %{$book[0]};
12my $pages = $info{sheets};
13print("Total $pages sheets
");
14
15#sheet 1
16my %sheet = %{$book[1]};
17
18my $label = $sheet{'label'};
19print("process $label ...
");
20
21my $maxrow = $sheet{'maxrow'};
22my $maxcol = $sheet{'maxcol'};
23print("max row: $maxrow, max col: $maxcol
");
24
25#get cells
26my $cellref = $sheet{'cell'};
27my @cell = @{$cellref};
28
29
30for(my $r=1; $r<=$maxrow; $r++){
31 for(my $c=1; $c<=$maxcol; $c++){
32 if(defined($cell[$c][$r])){
33 print($cell[$c][$r] . " ");
34 }else{
35 print("undefined ");
36 }
37 }
38 print("
");
39}
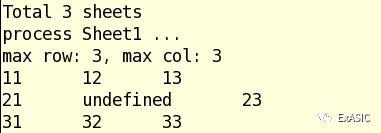
测试结果如下,共有3页sheet,只读取了第一个sheet,输出内容与Excel原文件相同。

细心的朋友可能注意到上面代码中有个defined(),那么defined($cell[$c][$r])是做什么的?有可能什么情况下会出现undefined?我们实验发现两种情况出输出undefined。
情况一:单元格里没有值
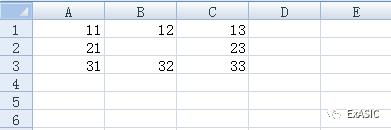
情况二:合并单元格
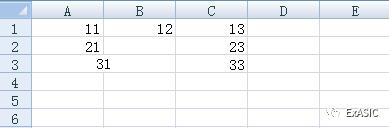
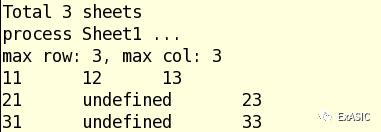
A3和B3合并后,A3可以读出值,而B3是undefined。考虑更通用的情况,如果多个单元格合并,数值保存在左上角,其余单元格都是undefined。
更多资源
Spreadsheet::Read的作者还基于此库做了一些示例应用:
其中,
ss2tk是在tk中显示excel文件,
ssdiff可以对比两个excel的差异,
xls2cvs可以格式转换,
xlscat显示全部或指定的部分内容,
xlsgrep显示正则匹配到的单元格内容等。
github链接:
https://github.com/Tux/Spreadsheet-Read/tree/master/examples
欢迎关注ExASIC
分享数字集成电路设计中的经验和方法
分享让工作更轻松
以上是关于用Perl读取Excel文件,Spreadsheet::Read.pm库介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
perl tk将界面输入的汉字不能输出到读取的EXCEL表格