Mybatis和mybatis-spring一级缓存
Posted APPZone
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Mybatis和mybatis-spring一级缓存相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题图:By 迹_Jason
目录
1.mybatis的几个核心概念 2.mybatis一级缓存应用及源码分析 3.mybatis-spring一级缓存应用及分析
1、Mybatis的几个核心概念
mybatis的官方简介 http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html

核心概念
1.SqlSession : 代表和数据库的一次会话,向用户提供了操作数据库的方法。 2.MappedStatement: 代表要发往数据库执行的指令,可以理解为是Sql的抽象表示。 3.Executor: 具体用来和数据库交互的执行器,接受MappedStatement作为参数。 4.映射接口: 在接口中会要执行的Sql用一个方法来表示,具体的Sql写在映射文件中。 5.映射文件: 可以理解为是Mybatis编写Sql的地方,通常来说每一张单表都会对应着一个映射文件,在该文件中会定义Sql语句入参和出参的形式。
2、一级缓存
一级缓存的简绍
在系统代码的运行中,我们可能会在一个数据库会话中,执行多次查询条件完全相同的Sql,鉴于日常应用的大部分场景都是读多写少,这重复的查询会带来一定的网络开销,同时select查询的量比较大的话,对数据库的性能是有比较大的影响的。
如果是mysql数据库的话,在服务端和Jdbc端都开启预编译支持的话,可以在本地JVM端缓存Statement,可以在Mysql服务端直接执行Sql,省去编译Sql的步骤,但也无法避免和数据库之间的重复交互。
Mybatis提供了一级缓存的方案来优化在数据库会话间重复查询的问题。实现的方式是每一个SqlSession中都持有了自己的缓存,一种是SESSION级别,即在一个Mybatis会话中执行的所有语句,都会共享这一个缓存。一种是STATEMENT级别,可以理解为缓存只对当前执行的这一个statement有效。如果用一张图来代表一级查询的查询过程的话,可以用下图表示:
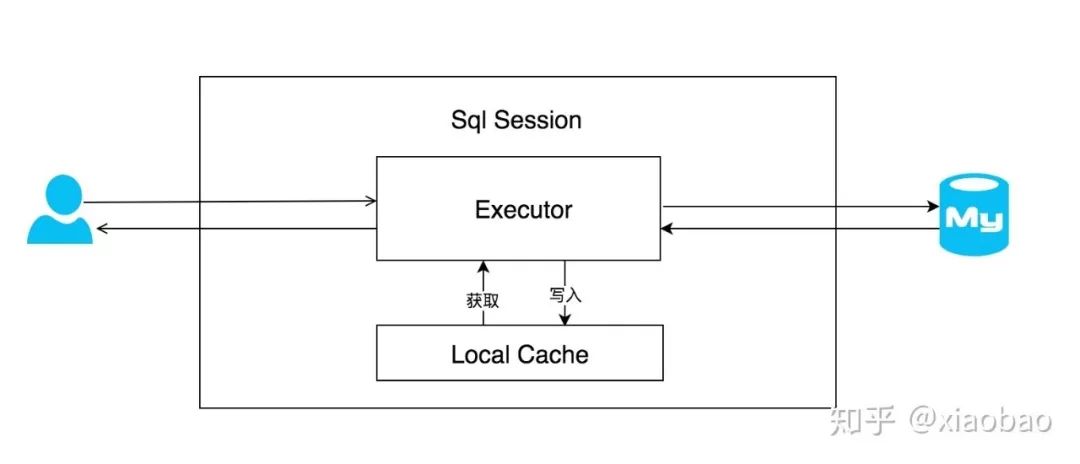
每一个SqlSession中持有了自己的Executor,每一个Executor中有一个Local Cache。当用户发起查询时,Mybatis会根据当前执行的MappedStatement生成一个key,去Local Cache中查询,如果缓存命中的话,返回。如果缓存没有命中的话,则写入Local Cache,最后返回结果给用户。
一级缓存工作流程和源码分析
工作流程

主要步骤如下: 1.对于某个Select Statement,根据该Statement生成key。 2.判断在Local Cache中,该key是否用对应的数据存在。 3.如果命中,则跳过查询数据库,继续往下走。 4.如果没命中,回去数据库中查询,然后写入到Local Cache中
源码分析 https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases
对于mybatis中有很多Executor执行器,在一级缓存中我主要学习BaseExecutor。
一级缓存Local Cache的查询和写入是在Executor内部完成的。在阅读BaseExecutor的代码后,我们也发现Local Cache就是它内部的一个成员变量,如下代码所示:
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
protected Transaction transaction;
protected Executor wrapper;
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads;
//存储缓存对象
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
}
BaseExecutor成员变量之一的PerpetualCache,就是对Cache接口最基本的实现,其实现非常的简内部持有了hashmap,对一级缓存的操作其实就是对这个hashmap的操作。
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
BaseExecutor的query核心方法,主要的功能是查库写缓存。
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//从缓存中获取
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//查不到的话,就从数据库查,在queryFromDatabase中,会对localcache进行写入。
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear();
//判断一级缓存级别是否是STATEMENT级别,如果是的话,就清空缓存,这也就是STATEMENT级别的一级缓存无法共享localCache的原因
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
最后确认一下insert/delete/update方法,缓存就会刷新的原因。
DefaultSqlSession类中的执行方法,发现所有的方法都执行了update。
@Override
public int insert(String statement, Object parameter) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
@Override
public int update(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//update方法也是委托给了Executor执行
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
@Override
public int delete(String statement) {
return update(statement, null);
}
@Override
public int delete(String statement, Object parameter) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
BaseExecutor的执行方法如下:
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//清理缓存
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
总结 1.Mybatis一级缓存的生命周期和SqlSession一致。 2.Mybatis的缓存没有更新缓存和缓存过期的概念,同时只是使用了默认的hashmap,也没有做容量上的限定。 3.Mybatis的一级缓存最大范围是SqlSession内部,有多个SqlSession或者分布式的环境下,有操作数据库写的话,会引起脏数据,建议是把一级缓存的默认级别设定为Statement,即不使用一级缓存。
mybatis-spring 一级缓存
mybatis-spring官方文档 http://www.mybatis.org/spring/sqlsession.html#
官方文档摘要
Using an SqlSession In MyBatis you use the SqlSessionFactory to create an SqlSession. Once you have a session, you use it to execute your mapped statements, commit or rollback connections and finally, when it is no longer needed, you close the session. With MyBatis-Spring you don't need to use SqlSessionFactory directly because your beans can be injected with a thread safe SqlSession that automatically commits, rollbacks and closes the session based on Spring's transaction configuration.
大概的意思是说:mybatis-spring中的sqlsession通过spring去管理,
前面说到mybatis的一级缓存生效的范围是sqlsession,是为了在sqlsession没有关闭时,业务需要重复查询相同数据使用的。一旦sqlsession关闭,则由这个sqlsession缓存的数据将会被清空。
spring对mybatis的sqlsession的使用是由template控制的,sqlsession又被spring当作resource放在当前线程的上下文里(threadlocal),spring通过mybatis调用数据库的过程如下: 1.需要访问数据 2.spring检查到了这种需求,于是去申请一个mybatis的sqlsession,并将申请到的sqlsession与当前线程绑定,放入threadlocal里面 3.template从threadlocal获取到sqlsession,去执行查询 4.查询结束,清空threadlocal中与当前线程绑定的sqlsession,释放资源 5.又需要访问数据 6.返回到步骤2
结论:
通过以上步骤后发现,同一线程里面两次查询同一数据所使用的sqlsession是不相同的,所以mybatis结合spring后,mybatis的一级缓存失效了。
希望对大家有所帮助!
以上是关于Mybatis和mybatis-spring一级缓存的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章