Vue3.0 dom diff 算法
Posted Web手艺人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Vue3.0 dom diff 算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在讲 diff 算法之前我们先来了解一下虚拟 DOM。
什么是虚拟 DOM
虚拟 DOM(virtual DOM )简单点讲就是用普通 js 对象来描述 DOM 结构,因为不是真实 DOM,所以称之为虚拟 DOM。
虚拟 DOM 的优点
抽象了原本的渲染过程,实现了跨平台的能力
减少了频繁操作真实的 DOM 带来的巨大开销。因为如果没有虚拟 DOM, 要改变页面展示的内容,只能通过遍历查询 DOM 树的方式找到需要修改的 DOM, 然后修改样式行为或者结构,这种方式开销是很大的。当使用虚拟 DOM 时,每次 DOM 的更改就变成了对 js 对象的属性的增删改查,这样查找 js 对象的属性变化要比查询 DOM 树的性能开销小。
虚拟 DOM 与 diff 算法的关系
找出新旧两个虚拟 DOM 的不同之处然后更新,其他的不更新,找出的过程就是 diff 算法。我们应该以最小的时间最大可能的找出新旧两个虚拟 DOM 的不同之处的最小集,以减少开销,提高性能,可见 diff 算法在 DOM 更新中的重要性。
Vue3 虚拟 DOM 基础的对比流程
Vue3.0 与 Vue2.x 的 diff 方法基本上没太大区别,都是从根节点开始,同级虚拟 DOM 做比较,然后递归比较子元素节点。
当数据变化,Vue 会调用 `render` 方法,`render` 方法会通过 `patch` 方法做新旧虚拟 DOM (以下称 vnode) 的对比。
render 方法
如果新 vnode 为null,则卸载老元素节点;
新 vnode 不为 null,需要做 patch 比较;
const render = (vnode, container) => {// 当新的 vnode 为null 时,卸载掉当前容器上的 vnode 节点// 否则进行 patch,更新 domif (vnode == null) {unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true);} else {patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container);}container._vnode = vnode;};
patch 的简单概括
1. 首先对比新旧节点元素的标签类型是否一样,如果不一样,则删除旧节点,挂载新节点。(比如:旧节点为 `<div>` 标签,新节点为 `<p>` 标签,不管两者有没有子元素,都是删除旧元素 `<div>` 标签,然后挂载新元素 `<p>` 标签),完成更新流程。
2. 如果新旧元素标签类型一样,则先遍历找出标签上属性的不同,然后找到子节点继续对比。
patch 方法(简略的代码)
/*** @param `n1` 代表旧虚拟 DOM,* @param `n2` 新虚拟 DOM,* @param `container` 是父容器* @param `anchor` 是参照节点容器*/const patch = (n1, n2, container, anchor = null) {// 如果新的节点标签类型与旧的节点标签类型不一样,则卸载旧的if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {// 卸载旧节点unmount(n1);n1 = null;}const {type, ref, shapeFlag} = n2;// 根据标签的类型分别执行相应的新节点更新流程switch (type) {case Text:processText(n1, n2, container, anchor);break;default:// shapeFlag 节点类型标识if (shapeFlag & 1 /* ELEMENT */) {processElement(n1, n2, container, anchor);} else if (shapeFlag & 6 /* COMPONENT */) {processComponent(n1, n2, container, anchor);}}}
processElement 方法
1. 新旧 vnode 标签 及 key 不一样时 直接卸载老元素
2. 新旧 vnode 标签 及 key 一样时,调用 patchElement 对比新旧 vnode 不同
const processElement = (n1, n2, container, anchor) => {// 挂载新节点if (n1 == null) {mountElement(n2, container, anchor);}// 当元素的标签类型一样时,对比元素else {patchElement(n1, n2, parentComponent);}};
patchElement 方法
在对比 vnode 时,先对比属性,再对比子元素 vnode
const patchElement = (n1, n2, parentComponent) => {const el = (n2.el = n1.el);const oldProps = n1.props || {};const newProps = n2.props || {};// 对比找出属性的不同patchProps(el, n2, oldProps, newProps, parentComponent);// 对比子节点patchChildren(n1, n2, el, null, parentComponent);};
patchProps 属性的对比
1. 循环遍历新老 vnode 属性
2. 新老 vnode 属性不一样 则新 vnode 属性覆盖老 vnode 属性
3. 老 vnode 属性有, 而新 vnode 属性没有时,删除掉老 vnode 上的属性
const patchProps = (el, vnode, oldProps, newProps, parentComponent) => {if (oldProps !== newProps) {// 新属性存在,则新属性覆盖老属性或添加新属性for (const key in newProps) {const next = newProps[key];const prev = oldProps[key];if (next !== prev) {hostPatchProp(el, key, prev, next);}}// 如果老的属性存在,而新属性不存在,则删除老属性if (oldProps !== {}) {for (const key in oldProps) {if (!(key in newProps)) {hostPatchProp(el, key, oldProps[key], null);}}}}};
patchChildren 子节点的对比
子节点的对比存在以下几种情况:
1. 老的是文本,新的是文本 -> 新的覆盖老的;
2. 老的是数组,新的是文本 -> 新的覆盖老的;
3. 老的是文本,新的是数组 -> 移除老的,生成新的节点挂载;
4. 老的是数组,新的是数组 -> diff 算法
const patchChildren = (n1, n2, container, anchor) => {const c1 = n1 && n1.children;const prevShapeFlag = n1 ? n1.shapeFlag : 0;const c2 = n2.children;const { patchFlag, shapeFlag } = n2;// 如果新的是有 keyif (patchFlag & 128 /* KEYED_FRAGMENT */) {patchKeyedChildren(c1, c2, container, anchor);return;}// 如果新的没有 keyelse if (patchFlag & 256 /* UNKEYED_FRAGMENT */) {patchUnkeyedChildren(c1, c2, container, anchor);return;}// 新的是文本,老的是数组,删除老的元素,增加新的文本元素if (shapeFlag & 8 /* TEXT_CHILDREN */) {// text children fast pathif (prevShapeFlag & 16 /* ARRAY_CHILDREN */) {unmountChildren(c1, parentComponent, parentSuspense);}if (c2 !== c1) {hostSetElementText(container, c2);}}else {// 老的是文本 新的是数组,删除掉老的,生成新的节点挂载 ...}};
到这里我们看到 `patchUnkeyedChildren`、 `patchKeyedChildren` 这两个方法:
`patchUnkeyedChildren`: 无 key 的子元素比较;
`patchKeyedChildren`: 有 key 的子元素比较;
无 key 的情况:
1. 找出新旧 children 数量共有的最大 length 值 然后对于公共部分,进行 patch。
2. 如果老节点数量 > 新的节点数量 ,移除多出来的节点。
3. 如果新的节点数量 > 老节点的数量,挂载多出来的新节点。
const patchUnkeyedChildren = (c1, c2, container, anchor) => {c1 = c1 || [];c2 = c2 || [];const oldLength = c1.length;const newLength = c2.length;// 找出新旧 children 的共有的最大 length 值;const commonLength = Math.min(oldLength, newLength);let i;// 循环遍历公共长度内的每个节点,然后 patch;for (i = 0; i < commonLength; i++) {const nextChild = c2[i];patch(c1[i], nextChild, container, null);}// 老节点数量 > 新节点数量,删除老节点上多出来的节点if (oldLength > newLength) {unmountChildren(c1, container, commonLength);}// 新节点的数量 > 老节点的数量,挂载多出来的新节点else {mountChildren(c2, container, commonLength);}};
下面开始 `patchKeyedChildren` 有 key 的子元素比较,这里才开始 Vue 的核心 diff 算法。
核心 diff 算法拆解:
先初始化需要的变量
const patchKeyedChildren = (c1, c2, container, parentAnchor) => {let i = 0; // 初始索引值const l2 = c2.length; // 新 vnode 的数量let e1 = c1.length - 1; // 老 vnode 的最后一个节点的索引let e2 = l2 - 1; // 新 vnode 的最后一个节点的索引}
第一步:从头部比较
从头部开始遍历对比,首先对比 key 与 type 是否相同,相同则 patch, 否则跳出遍历,初始索引变为跳出索引的下一个索引值:
// 1. sync from start// (a b) c// (a b) d ewhile (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {const n1 = c1[i];const n2 = c2[i];if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {patch(n1, n2, container, null);}else {break;}i++;}
对应的代码图示:
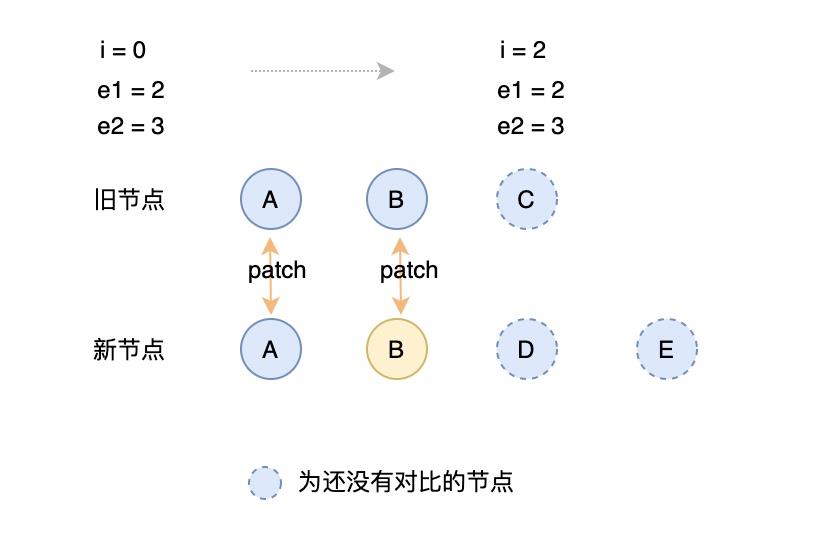
第二步:从尾部比较
从尾部开始遍历对比,对比 key 与 type 是否相同,相同则 patch, 否则跳出遍历,新、老 vnode 的最后一个节点的索引为各自当前未对比的最后一个值的索引值。
// 2. sync from end// a (b c)// d e (b c)while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {const n1 = c1[e1];const n2 = c2[e2];if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {patch(n1, n2, container, null);}else {break;}e1--;e2--;};
对应的代码图示:
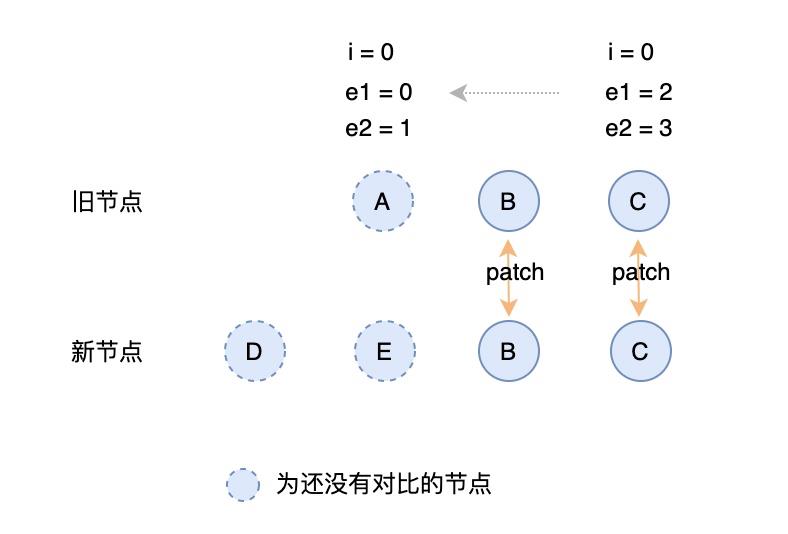
第三步:有新增的元素 添加新增的元素
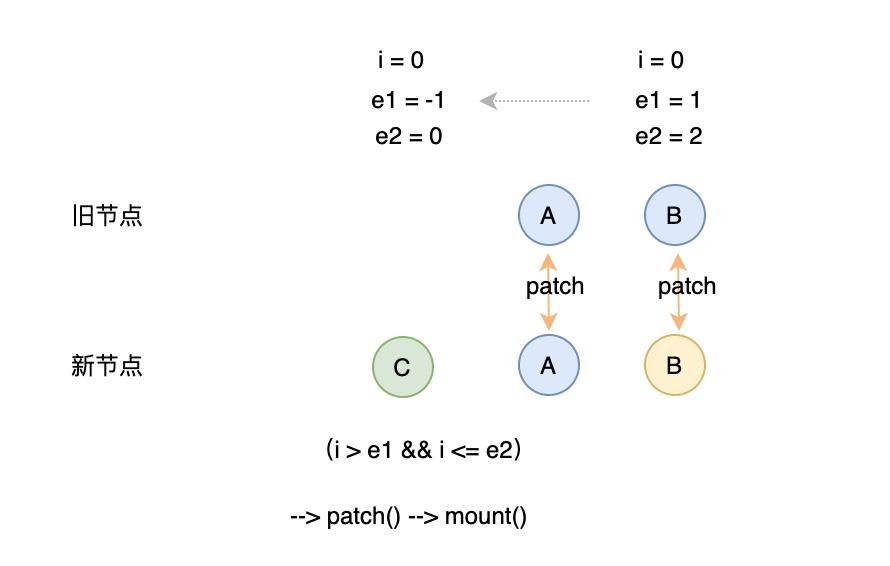
判断依据:头尾比较完成后 旧 vnode 没有待比较的了,而新 vnode 还有待比较的,这时需要往容器里挂载这个新的元素
// 3. common sequence + mount// (a b)// (a b) c// i = 2, e1 = 1, e2 = 2// (a b)// c (a b)// i = 0, e1 = -1, e2 = 0if (i > e1) {if (i <= e2) {const nextPos = e2 + 1;const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? c2[nextPos].el : parentAnchor;while (i <= e2) {patch(null, c2[i], container, anchor);i++;}}}
头部对比后尾部新增:
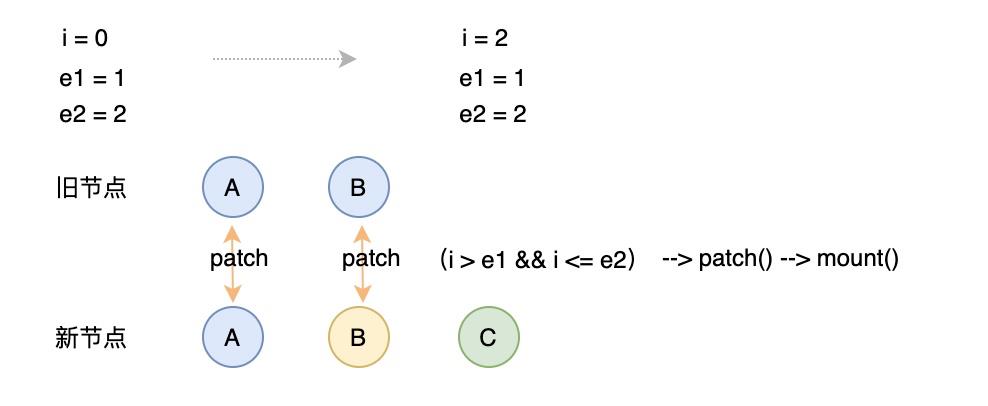
尾部对比后头部新增:
第四步 有删除的元素
判断依据:头尾比较完成后 旧 vnode 还有有待比较的,而新 vnode 已经全比较完成了,需要删除旧元素
// 4. common sequence + unmount// (a b) c// (a b)// i = 2, e1 = 2, e2 = 1// a (b c)// (b c)// i = 0, e1 = 0, e2 = -1else if (i > e2) {while (i <= e1) {unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);i++;}}
头部对比后尾部删除:
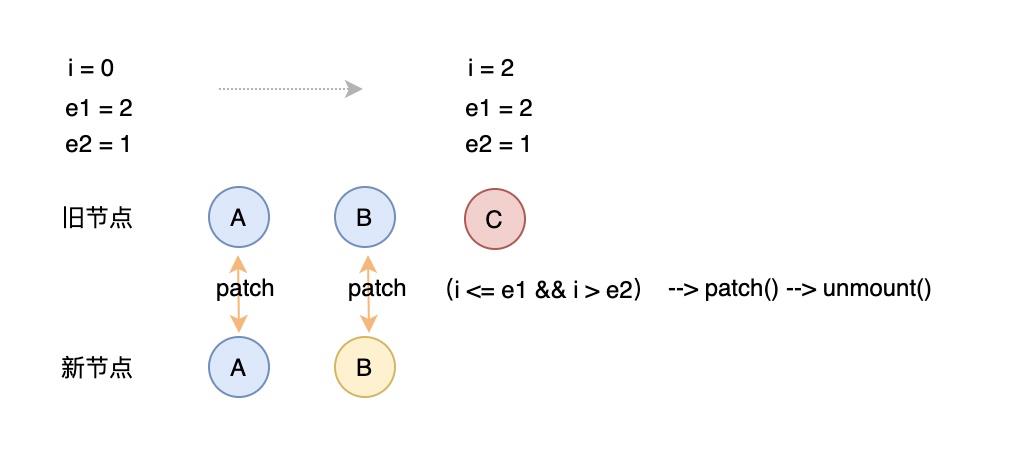
尾部对比后头部删除:
第五步 以上四种情况后剩余的无规律的情况比较
旧节点:a, b, c, d, e, f, g
新节点:a, b, e, d, c, h, f, g
首先经过 1、2步的比较后 vnode 的对比示意图如下:
5-1:循环遍历新 vnode,构建一个新节点的 key: index 的映射表
keyToNewIndexMap: {e: 2, d:3, c: 4, h: 5}
5-2: 生成一个未 patch 的新节点的位置与老节点的索引对应关系的数组:newIndexToOldIndexMap: [0, 0, 0, 0];
遍历未 patch 的老 vnode ,并找到与新节点索引位置的对应关系,更新这个对应关系数组
无规律比较的整体代码
// 5. unknown sequence// [i ... e1 + 1]: a b [c d e] f g// [i ... e2 + 1]: a b [e d c h] f g// i = 2, e1 = 4, e2 = 5else {const s1 = i; // 第一步之后老节点开始的索引const s2 = i; // 第一步之后新节点开始的索引// 5.1 构建一个新节点的 key: index 的映射表// keyToNewIndexMap: {e: 2, d:3, c: 4, h: 5}const keyToNewIndexMap = new Map();for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {const nextChild = c2[i];if (nextChild.key != null) {if ( keyToNewIndexMap.has(nextChild.key)) {warn(`Duplicate keys found during update:`, JSON.stringify(nextChild.key), `Make sure keys are unique.`);}keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i);}}// 5.2 loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch// matching nodes & remove nodes that are no longer presentlet j;// 在此步骤已经 patch 过的新节点的数量let patched = 0;// 待 patch 的新节点的数量const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1;let moved = false;// used to track whether any node has movedlet maxNewIndexSoFar = 0;// works as Map<newIndex, oldIndex>// Note that oldIndex is offset by +1// and oldIndex = 0 is a special value indicating the new node has// no corresponding old node.// used for determining longest stable subsequence// 未 patch 的新节点的位置与老节点的索引对应关系的数组// 初始化时都为 0// newIndexToOldIndexMap: [0, 0, 0, 0]const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched);for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++)newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0;// 遍历未 patch 的老 vnodefor (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {const prevChild = c1[i];// 老的节点有 新的节点已经没有了 此时直接卸载老节点if (patched >= toBePatched) {// all new children have been patched so this can only be a removalunmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);continue;}// 新的索引let newIndex;if (prevChild.key != null) {newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key);}else {// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same typefor (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 &&isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j])) {newIndex = j;break;}}}// 老的节点有 新的节点已经没有了 此时直接卸载老节点if (newIndex === undefined) {unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);}// 更新新节点的位置与老节点的索引对应关系的数组else {newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1;if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex;}// 标识有做移动的元素else {moved = true;}patch(prevChild, c2[newIndex], container, null);patched++;}}// 5.3 move and mount// 使用 getSequence 生成一个最长递增子序列,这样有效减少不必要元素的删除、增加。const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap): [];j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1;// 反向遍历插入 或 移动新的节点for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {const nextIndex = s2 + i;const nextChild = c2[nextIndex];const anchor = nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? c2[nextIndex + 1].el : parentAnchor;if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {// mount newpatch(null, nextChild, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG);}else if (moved) {// move if:// There is no stable subsequence (e.g. a reverse)// OR current node is not among the stable sequenceif (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {move(nextChild, container, anchor, 2 /* REORDER */);}else {j--;}}}}
getSequence 生成最长递增子序列
这个方法是 vue3.0 最核心的算法,其中使用了贪心 及 二分查找,最终的时间复杂度为 O(nlogn)。
详细的演示:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_increasing_subsequence
function getSequence(arr) {const p = arr.slice();const result = [0];let i, j, u, v, c;const len = arr.length;for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {const arrI = arr[i];if (arrI !== 0) {j = result[result.length - 1];if (arr[j] < arrI) {p[i] = j;result.push(i);continue;}u = 0;v = result.length - 1;// 二分查找while (u < v) {c = ((u + v) / 2) | 0;if (arr[result[c]] < arrI) {u = c + 1;}else {v = c;}}if (arrI < arr[result[u]]) {if (u > 0) {p[i] = result[u - 1];}result[u] = i;}}}u = result.length;v = result[u - 1];while (u-- > 0) {result[u] = v;v = p[v];}return result;}
时间仓促,第五步中无规则 vnode 对比没来得及画图,后续画好后补充。
本文只是从主体流程上梳理了一下 Vue3.0 的 diff 流程,其中很多细节代码忽略了,有兴趣欢迎同学们补充修正。
整体 Vue3.0 的 DOM diff 算法与 Vue2.x 区别不是特别大,区别一:
1. 没有了 2.x 中 头尾、尾头的比较方式
2. Vue3.0 中在 compile 流程中为 vnode 增加了 patchFlag 标识,使其在标识不产生变化的节点不再进行 diff,这样在复杂结构的页面中能提升性能。
以上是关于Vue3.0 dom diff 算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章