Flutter异步编程
Posted 小菜与老鸟
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Flutter异步编程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
A future (lower case “f”) is an instance of the Future (capitalized “F”) class. A future represents the result of an asynchronous operation, and can have two states: uncompleted or completed. https://dart.dev/codelabs/async-await

final future1 = http.get("httts://www.google.com");
final future2 = SharedPreferences.getInstance();
···
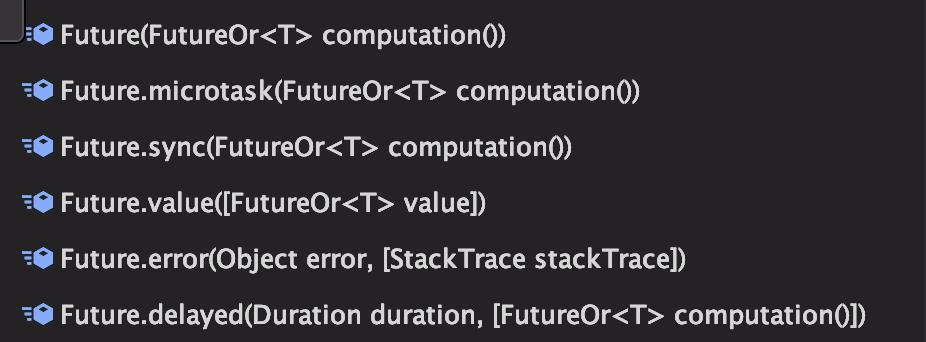
/// factory Future(FutureOr<T> computation())
/// 创建一个包含调用computation结果的future。
final myFuture = Future(() {
return "HelloFlutter!";
});
/// factory Future.microtask(FutureOr<T> computation())
/// 创建一个future,scheduleMicrotask将computation放到微任务调用处理,然后返回结果。
final myFuture = Future.microtask(() {
return "HelloFlutter!";
});
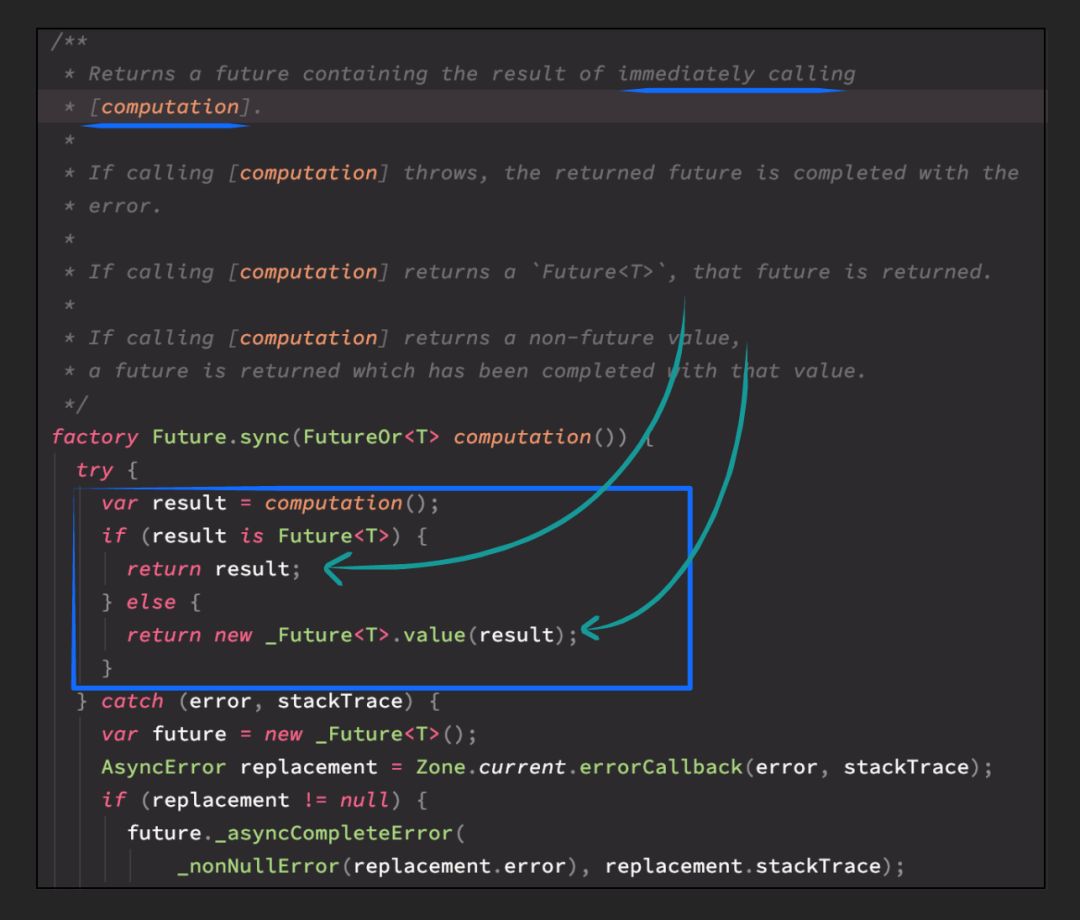
/// factory Future.sync(FutureOr<T> computation())
/// 创建一个future,包含立即调用computation的结果。
/// 如果结果类型为Future<T>,则直接返回
/// 如果不为Future<T>,则会创建并返回一个已经完成的future,值value为result
final myFuture = Future.sync(() {
return "HelloFlutter";
});
/// factory Future.value([FutureOr<T> value])
/// 创建一个值为value的成功态future。
final myFuture = Future.value("HelloFlutter!");
/// factory Future.error(Object error, [StackTrace stackTrace])
/// 创建一个error的失败态future,可选参数为堆栈信息
final myFuture = Future.error(Exception());
/// factory Future.delayed(Duration duration, [FutureOr<T> computation()])
/// 创建一个延时执行computation的future
final myFuture = Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 2), () => "HelloFlutter!");
// main.dartvoid main() {runFuturesDemo();}// futures_demo.dartvoid runFuturesDemo() async {print("runFuturesDemo start...");// future1 ------------------------------------Future future1 = new Future(() => null);future1.then((_) {print("future1 then 1");}).catchError((e) {print("future1 catchError");}).whenComplete(() {print("future1 whenComplete");});// future2 ------------------------------------Future future2 = Future(() {print("future2 init");});future2.then((_) {print("future2 then");future1.then((_) {print("future1 then3");});}).catchError((e) {print("future2 catchError");}).whenComplete(() {print("future2 whenComplete");});future1.then((_) {print("future1 then2");});// future3 ------------------------------------Future future3 = Future.microtask(() {print("future3 init");});// future4 ------------------------------------Future future4 = Future.sync(() {print("future4 init");});// future5 ------------------------------------Future future5 = Future(() {print("future5 init");});// future6 ------------------------------------Future future6 = Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 3), () {print("future6 init");});print("runFuturesDemo end...");}
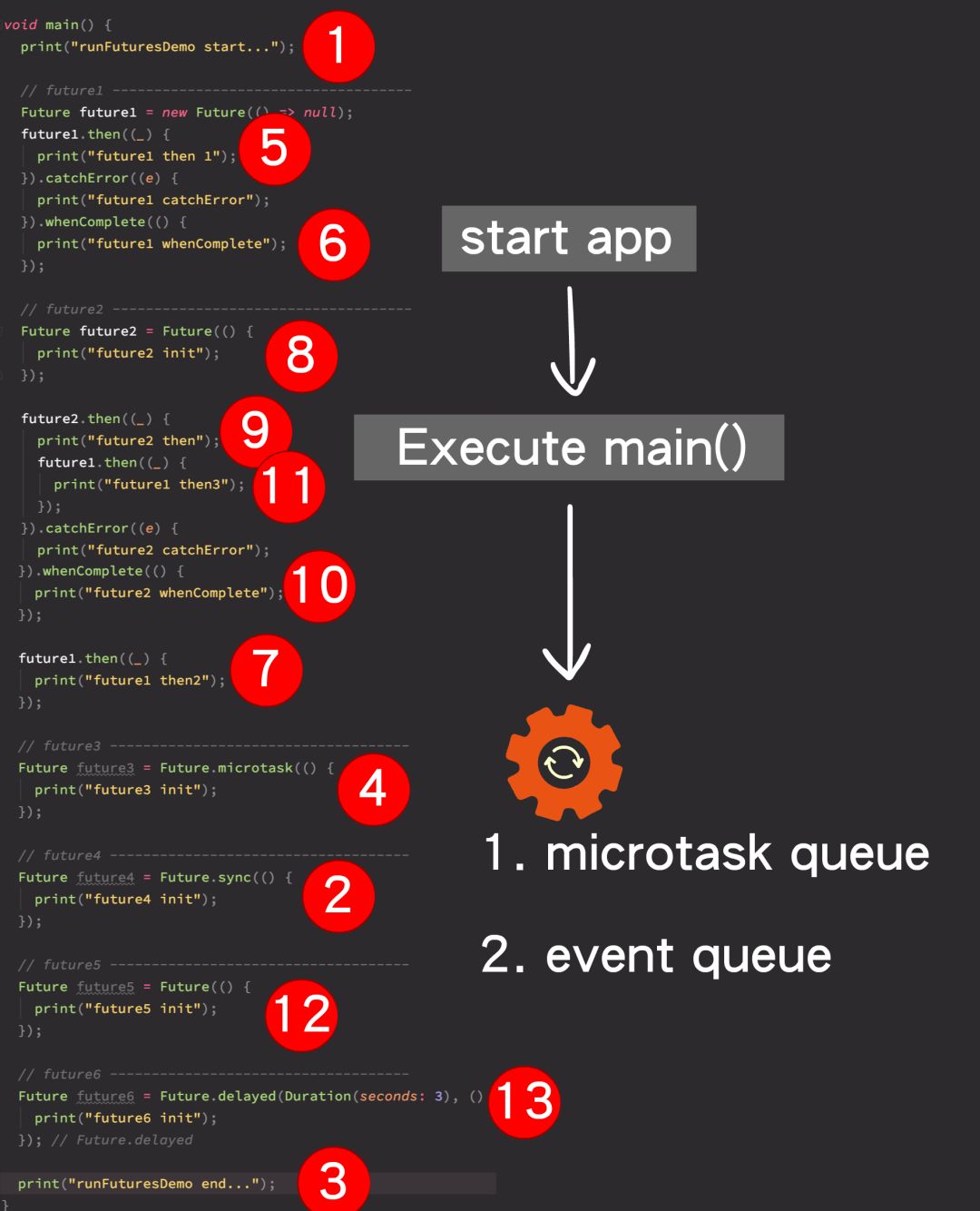
事实a)执行 main 函数,在 main 里面会往 microtask queue 和 event queue 中添加任务和事件, 包括注册一些回调,结束后,开启event loop
事实b)事件循环中 microtask queue 优先级 > event queue 优先级
事实c)从上面工厂方法 Future.sync 源码截图中可以看到,先同步执行computation(于是打印"future4 init"),根据 computation() 返回值视情况进行 Future 封箱(如果 compuation() 返回值为 Future<T>,直接返回,如果不是,则使用 _Future.value 将结果封箱)。
事实d)为什么 7 排在 8 前面?
我们看源码 then 的注释:
Future<R> then<R>(FutureOr<R> onValue(T value), {Function onError});
* Register callbacks to be called when this future completes.** When this future completes with a value,* the [onValue] callback will be called with that value.* If this future is already completed, the callback will not be called* immediately, but will be scheduled in a later microtask.
因为 future1 已经 completed 了,所以 future1 在7这个位置再次用 then 注册的 callback 回调会被放在 microtask 中执行。microtask的优先级高,所以 7 会在 8 前面打印。
事实e)为什么 11 排在 9 后面而不是 7 后面?
future2 在 event queue 事件队列中排在了 future1 后面,future2 init 执行完毕后,交给 then 的回调处理,此时位置 11 处,即 future1 使用 then 注册的 callback 在 future2 的 then 的 callback 里面,所以会处在 9 后面而不是 7 后面。
flutter: runFuturesDemo start...flutter: future4 initflutter: runFuturesDemo end...flutter: future3 initflutter: future1 then 1flutter: future1 whenCompleteflutter: future1 then2flutter: future2 initflutter: future2 thenflutter: future2 whenCompleteflutter: future1 then3flutter: future5 initflutter: future6 init
new Future(() { doSomething(); return result; });
Future doStuff(){
return someAsyncOperation().then((result) {
return someOtherAsyncOperation(result);
});
}
Future queryName(int id) {
// 创建一个completer
var completer = new Completer();
// 查询数据库,然后根据成功或者失败执行相应的callback回调,这个过程是异步的
database.query("select name from user where id = $id", (results) {
completer.complete(results);
}, (error) {
completer.completeError(error);
});
// return 在query结果出来之前就会被执行
return completer.future;
}
void runFuturesDemo2() async {
try {
final name = await queryName(100);
print("id 100 user name is $name");
} catch (e) {
print(e.toString());
} finally {
print("finally finished.");
}
}
void runFuturesDemo2() {
queryName(100).then((name) {
print("id 100 user name is $name");
}, onError: (e) {
print(e.toString());
}).whenComplete(() {
print("finally finished.");
});
}
以上是关于Flutter异步编程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章