深入解决异步编程Promise对象的学习
Posted 码小巴
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深入解决异步编程Promise对象的学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.什么是Promise
简单来说Promise是异步编程的一种解决方案
Promise是ES6中的特性。
什么是异步操作?
网络请求中,对端服务器处理需要时间,信息传递过程需要时间,不像我们本地调用算术函数一样,这里的网络请求不是同步的有时延, 不能立即得到结果。
== 如何处理异步事件?==
对于网络请求这种,一般会使用回调函数,在服务器端传给我数据成功后,调用回调函数。例如Ajax调用。
$.ajax({sucess:function(){...}})
如果碰到嵌套网络请求,例如第一次网络请求成功后回调函数再次发送网络请求,这种代码就会让人含难受。
$.ajax({sucess:function(){$.ajax({...})}})
如果还需要再次的网络请求,那么又要嵌套一层,这样的代码层次不分明很难读,也容易出问题。
2.Promise的基本使用
什么时候使用Promise
解决异步请求冗余这样的问题,promise就是这样封装移步请求的。
Promise对象
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>{})
Promise对象的参数是一个函数(resolve,reject) => {},这个函数又有两个参数分别是resolve和reject。这两个参数本身也是函数,后面还有回调函数then(func)的参数也是一个函数。
模拟定时器的异步事件
用定时器模拟网络请求,定时一秒为网络请求事件,用console.log()表示需要执行的代码。
//1.使用setTimeout模拟嵌套的第三次网络请求setTimeout(() => {//第一次请求console.log("hello wk")//第一次处理代码setTimeout(() => {//第二次请求console.log("hello meng")//第二次处理代码setTimeout(() => {//第三次请求console.log("hello vue")//第三次处理代码},1000)},1000)},1000)
一层套一层,看起来是不是很绕。
使用promise来处理异步操作
//参数 -> 函数// resolve和reject本身也是函数//then()的参数也是一个函数new Promise((reslove,reject) => {setTimeout(() => {//第一次网络请求resolve()},1000)}).then(() => {console.log("hello wk")//第一次处理代码return new promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {//第二次网络请求resolve()},1000).then(() => {console.log("hello vuejs")//第二次处理代码return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {//第三次网络请求resolve()}, 1000)}).then(() => {console.log("hello java")//第三次处理代码})})})})
是不是觉得代码还要更复杂了?仔细看看第一个如果使用了多个就找不到对应的关系了。相反第二个流程就很清楚了,调用resolve()就能跳转发到then()方法就能执行处理代码,then()回调的返回值又是一个promise对象。层次很明显,只要是then()必然是执行处理代码,如果还有嵌套必然就是返回了一个promise对象,这样调用就像Java中的StringBuffer的append()方法一样,链式调用。
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('success')}, 1000).then(success => {console.log(success)})})
setTimeout()模拟的是网络请求,而then()执行的是网络请求后的代码,这就将网络请求和请求得到的响应后的操作分离了,每个地方干自己的事情。在resolve中传参了,那么在then()方法中的参数就有这个参数,例如data。
网络请求中也会有失败情况?例如网络堵塞。
如何处理失败情况,此时就要用到reject()
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {reject('error message')}, 1000).catch(error => {console.log(error)})})
此时reject(error),catch()方法捕获到reject()中的error。
合起来
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {// 成功的时候调用resolve()// resolve('hello world')// 失败的时候调用reject()reject('error message')}, 1000).then(success => {console.log(success)}).catch(error => {console.log(error)})})
拿ajax来举例子:
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {$.ajax({success:function(){// 成功的时候调用resolve()// resolve('hello world')// 失败的时候调用reject()reject('error message')}}).then(success => {console.log(success)}).catch(error => {console.log(error)})})
3.Promise的三种状态
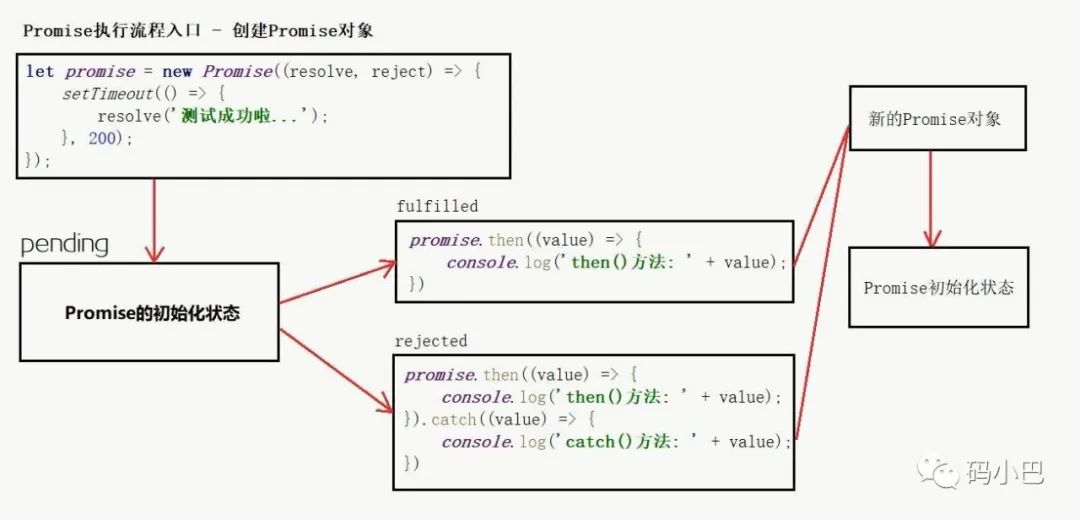
pending:等待状态,比如正在进行的网络请求还未响应,或者定时器还没有到时间
fulfill:满足状态,当我们主动回调了resolve函数,就处于满足状态,并会回调then()
reject:拒绝状态,当我们主动回调reject函数,就处于该状态,并且会回调catch()

4.Promies的链式调用
网络请求响应结果为 hello ,打印hello
处理:hello world ,打印hello world
处理:hello world,vuejs ,打印hello world,vuejs
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('hello')}, 1000)}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印helloreturn new Promise(resolve => {resolve(res + ' world')}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello worldreturn new Promise(resolve => {resolve(res + ',vuejs')}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello world,vuejs})})})
链式调用就是then()方法的返回值返回一个Promise对象继续调用then(),此外还有简写Promise.resolve()。
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('hello')}, 1000)}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印helloreturn Promise.resolve(res + ' world')}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello worldreturn Promise.resolve(res + ',vuejs')}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello world,vuejs})
还可以直接省略掉Promise.resolve()
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('hello')}, 1000)}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印helloreturn res + ' world'}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello worldreturn res + ',vuejs'}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello world,vuejs})
如果中途发生异常,可以通过catch()捕获异常
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('hello')}, 1000)}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印helloreturn res + ' world'}).then(res => {console.log(res)// return Promise.reject('error message')//发生异常throw 'error message' //抛出异常}).then(res => {console.log(res)//打印hello world,vuejs}).catch(error => {console.log(error)})
也可以通过throw抛出异常,类似java
throw 'error message' //抛出异常5.Promies的all使用
有这样一个情况,一个业务需要请求2个地方(A和B)的数据,只有A和B的数据都拿到才能走下一步。
ajax实现
$.ajax({...//结果AresultA = truecallback()})$.ajax({...//结果BresultB = truecallback()})//回调函数function callback(){if(resultA&&resultB){...}}
由于不知道网络请求A和网络请求B哪个先返回结果,所以需要定义一个函数只有2个请求都返回数据才回调成功。
Promise实现
Promise.all([new Promise((resolve, resjct) => {$.ajax({url: 'url1',success: function (data) {resolve(data)}})}),new Promise((resolve, resjct) => {$.ajax({url: 'url2',success: function (data) {resolve(data)}})}).then(results => {console.log(results)})])
上面是伪代码,只是包装了ajax,ajaxA和ajaxB的结果都放在resolve()中,Promise将其放在results中了,使用setTimeout模拟。
Promise.all([new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {// 请求Aresolve('结果A')}, 1000)}),new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {// 请求Bresolve('结果B')}, 1000)})]).then(results => {console.log(results)})

文末点击阅读原文有技术免费电子书分享给大家哦。
以上是关于深入解决异步编程Promise对象的学习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章