论文推荐最新十篇机器翻译相关论文—自然语言推理无监督神经机器翻译多任务学习局部卷积图卷积多语种机器翻译
Posted 专知
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了论文推荐最新十篇机器翻译相关论文—自然语言推理无监督神经机器翻译多任务学习局部卷积图卷积多语种机器翻译相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【导读】专知内容组整理了最近十篇机器翻译(Machine Translation)相关文章,为大家进行介绍,欢迎查看!
1. The Best of Both Worlds: Combining Recent Advances in Neural Machine Translation(The Best of Both Worlds:结合神经机器翻译的最新进展)
机构:George Mason University
摘要:The past year has witnessed rapid advances in sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) modeling for Machine Translation (MT). The classic RNN-based approaches to MT were first out-performed by the convolutional seq2seq model, which was then out-performed by the more recent Transformer model. Each of these new approaches consists of a fundamental architecture accompanied by a set of modeling and training techniques that are in principle applicable to other seq2seq architectures. In this paper, we tease apart the new architectures and their accompanying techniques in two ways. First, we identify several key modeling and training techniques, and apply them to the RNN architecture, yielding a new RNMT+ model that outperforms all of the three fundamental architectures on the benchmark WMT'14 English to French and English to German tasks. Second, we analyze the properties of each fundamental seq2seq architecture and devise new hybrid architectures intended to combine their strengths. Our hybrid models obtain further improvements, outperforming the RNMT+ model on both benchmark datasets.
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月26日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/35b5d2a4eb8254c3c7e08ebeda58e699
2. On the Evaluation of Semantic Phenomena in Neural Machine Translation Using Natural Language Inference(利用自然语言推理对神经机器翻译中的语义现象进行评价)
机构:Johns Hopkins University
摘要:We propose a process for investigating the extent to which sentence representations arising from neural machine translation (NMT) systems encode distinct semantic phenomena. We use these representations as features to train a natural language inference (NLI) classifier based on datasets recast from existing semantic annotations. In applying this process to a representative NMT system, we find its encoder appears most suited to supporting inferences at the syntax-semantics interface, as compared to anaphora resolution requiring world-knowledge. We conclude with a discussion on the merits and potential deficiencies of the existing process, and how it may be improved and extended as a broader framework for evaluating semantic coverage.
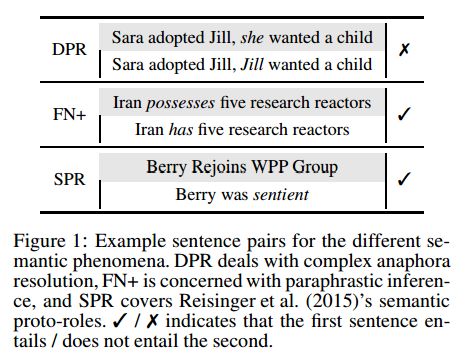
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月26日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/34040751380262ad0fc15a43e4ebef1e
3. Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation with Weight Sharing(权重共享的无监督神经机器翻译)
机构:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
摘要:Unsupervised neural machine translation (NMT) is a recently proposed approach for machine translation which aims to train the model without using any labeled data. The models proposed for unsupervised NMT often use only one shared encoder to map the pairs of sentences from different languages to a shared-latent space, which is weak in keeping the unique and internal characteristics of each language, such as the style, terminology, and sentence structure. To address this issue, we introduce an extension by utilizing two independent encoders but sharing some partial weights which are responsible for extracting high-level representations of the input sentences. Besides, two different generative adversarial networks (GANs), namely the local GAN and global GAN, are proposed to enhance the cross-language translation. With this new approach, we achieve significant improvements on English-German, English-French and Chinese-to-English translation tasks.
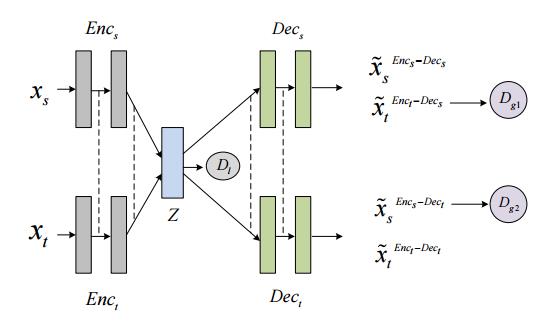
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月24日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/d8155e035fcb62f192b632d5df9385cc
4.Scheduled Multi-Task Learning: From Syntax to Translation(多任务学习:从语法到翻译)
摘要:Neural encoder-decoder models of machine translation have achieved impressive results, while learning linguistic knowledge of both the source and target languages in an implicit end-to-end manner. We propose a framework in which our model begins learning syntax and translation interleaved, gradually putting more focus on translation. Using this approach, we achieve considerable improvements in terms of BLEU score on relatively large parallel corpus (WMT14 English to German) and a low-resource (WIT German to English) setup.
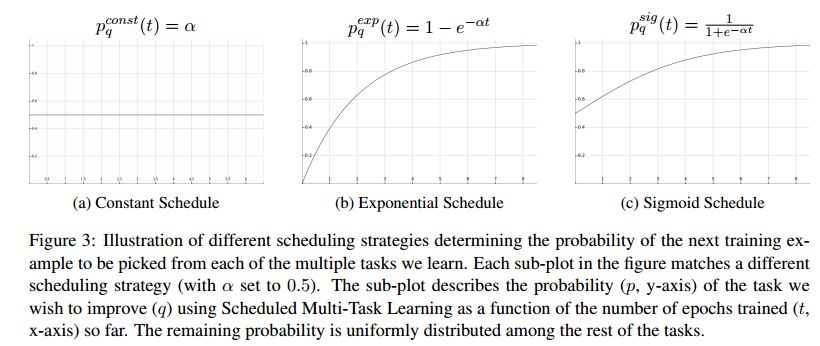
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月24日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/eff202d4507474c7ca1bf5080b714fa2
5. QANet: Combining Local Convolution with Global Self-Attention for Reading Comprehension(QANet: 局部卷积与整体自我关注相结合的阅读理解)
机构:Carnegie Mellon University
摘要:Current end-to-end machine reading and question answering (Q&A) models are primarily based on recurrent neural networks (RNNs) with attention. Despite their success, these models are often slow for both training and inference due to the sequential nature of RNNs. We propose a new Q&A architecture called QANet, which does not require recurrent networks: Its encoder consists exclusively of convolution and self-attention, where convolution models local interactions and self-attention models global interactions. On the SQuAD dataset, our model is 3x to 13x faster in training and 4x to 9x faster in inference, while achieving equivalent accuracy to recurrent models. The speed-up gain allows us to train the model with much more data. We hence combine our model with data generated by backtranslation from a neural machine translation model. On the SQuAD dataset, our single model, trained with augmented data, achieves 84.6 F1 score on the test set, which is significantly better than the best published F1 score of 81.8.
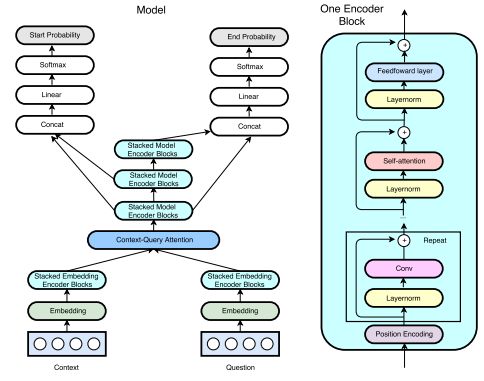
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月23日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/b0977e98a1f13b9062fd4f567771a259
6. Exploiting Semantics in Neural Machine Translation with Graph Convolutional Networks(利用图卷积网络对神经机器翻译中的语义进行挖掘)
机构:University of Amsterdam,University of Edinburgh
摘要:Semantic representations have long been argued as potentially useful for enforcing meaning preservation and improving generalization performance of machine translation methods. In this work, we are the first to incorporate information about predicate-argument structure of source sentences (namely, semantic-role representations) into neural machine translation. We use Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) to inject a semantic bias into sentence encoders and achieve improvements in BLEU scores over the linguistic-agnostic and syntax-aware versions on the English--German language pair.
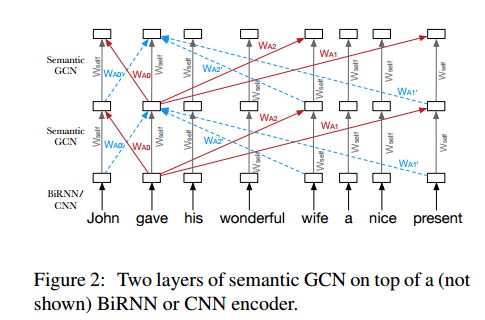
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月23日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/1db2982d6a8e07e79738729e2bba6a03
7. A neural interlingua for multilingual machine translation(多语种机器翻译的神经网络语言)
摘要:We incorporate an explicit neural interlingua into a multilingual encoder-decoder neural machine translation (NMT) architecture. We demonstrate that our model learns a true interlingua by performing direct zero-shot translation (without using pivot translation), and by using the interlingual sentence embeddings to train an English Yelp review classifier that, through the mediation of the interlingua, can also classify French and German reviews. Furthermore, we show that, despite using a smaller number of parameters than a pairwise collection of bilingual NMT models, our interlingual approach produces comparable BLEU scores for each language pair in WMT15.
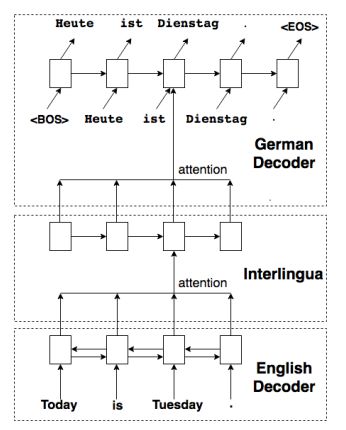
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月23日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/3ec4928148c73dba62d0369705ca5845
8. Phrase-Based & Neural Unsupervised Machine Translation(基于短语和神经的无监督机器翻译)
机构:Universite Le Mans,Sorbonne Universites
摘要:Machine translation systems achieve near human-level performance on some languages, yet their effectiveness strongly relies on the availability of large amounts of bitexts, which hinders their applicability to the majority of language pairs. This work investigates how to learn to translate when having access to only large monolingual corpora in each language. We propose two model variants, a neural and a phrase-based model. Both versions leverage automatic generation of parallel data by backtranslating with a backward model operating in the other direction, and the denoising effect of a language model trained on the target side. These models are significantly better than methods from the literature, while being simpler and having fewer hyper-parameters. On the widely used WMT14 English-French and WMT16 German-English benchmarks, our models respectively obtain 27.1 and 23.6 BLEU points without using a single parallel sentence, outperforming the state of the art by more than 11 BLEU points.
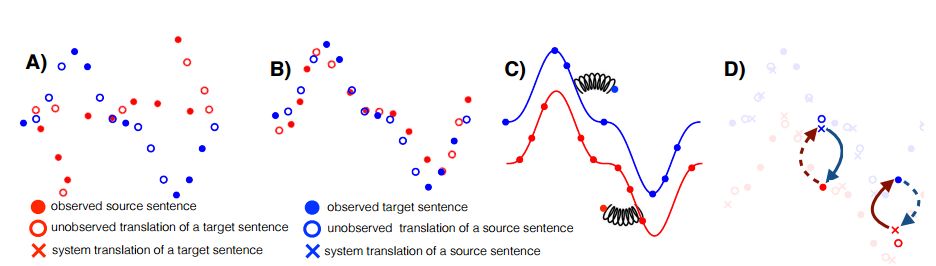
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月21日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/27909b8105443ec48f9d5e42c436a6d7
9. ParaNMT-50M: Pushing the Limits of Paraphrastic Sentence Embeddings with Millions of Machine Translations(ParaNMT-50M: 通过数百万次机器翻译突破释义句嵌入的限制)
机构:Carnegie Mellon University
摘要:We describe PARANMT-50M, a dataset of more than 50 million English-English sentential paraphrase pairs. We generated the pairs automatically by using neural machine translation to translate the non-English side of a large parallel corpus, following Wieting et al. (2017). Our hope is that ParaNMT-50M can be a valuable resource for paraphrase generation and can provide a rich source of semantic knowledge to improve downstream natural language understanding tasks. To show its utility, we use ParaNMT-50M to train paraphrastic sentence embeddings that outperform all supervised systems on every SemEval semantic textual similarity competition, in addition to showing how it can be used for paraphrase generation.
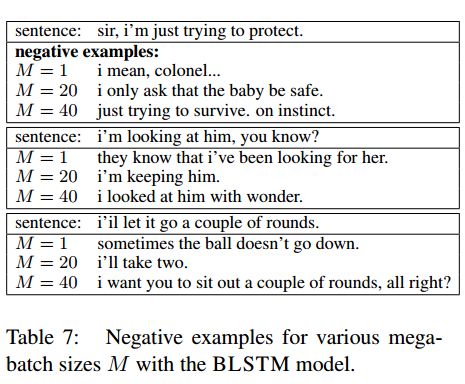
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月21日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/07dba57ecb2c7c89fcb52c30c2a329aa
10.Evaluating Discourse Phenomena in Neural Machine Translation(评价神经机器翻译中的语篇现象)
机构: University of Edinburgh,University of Zurich
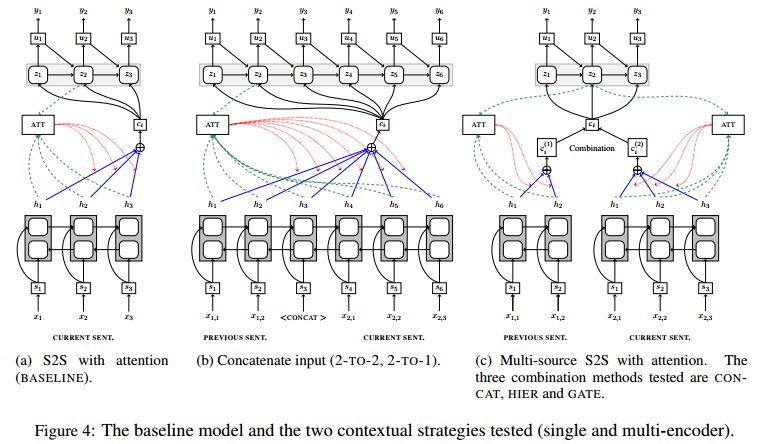
摘要:For machine translation to tackle discourse phenomena, models must have access to extra-sentential linguistic context. There has been recent interest in modelling context in neural machine translation (NMT), but models have been principally evaluated with standard automatic metrics, poorly adapted to evaluating discourse phenomena. In this article, we present hand-crafted, discourse test sets, designed to test the models' ability to exploit previous source and target sentences. We investigate the performance of recently proposed multi-encoder NMT models trained on subtitles for English to French. We also explore a novel way of exploiting context from the previous sentence. Despite gains using BLEU, multi-encoder models give limited improvement in the handling of discourse phenomena: 50% accuracy on our coreference test set and 53.5% for coherence/cohesion (compared to a non-contextual baseline of 50%). A simple strategy of decoding the concatenation of the previous and current sentence leads to good performance, and our novel strategy of multi-encoding and decoding of two sentences leads to the best performance (72.5% for coreference and 57% for coherence/cohesion), highlighting the importance of target-side context.
期刊:arXiv, 2018年4月20日
网址:
http://www.zhuanzhi.ai/document/a20f794a231d81b37da6bcc19fbafa98
-END-
专 · 知
人工智能领域主题知识资料查看与加入专知人工智能服务群:
点击上面图片加入会员
请PC登录www.zhuanzhi.ai或者点击阅读原文,注册登录专知,获取更多AI知识资料!
点击“阅读原文”,使用专知
以上是关于论文推荐最新十篇机器翻译相关论文—自然语言推理无监督神经机器翻译多任务学习局部卷积图卷积多语种机器翻译的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
数十篇推荐系统论文被批无法复现:源码数据集均缺失,性能难达预期