了解gRPC一篇就够了
Posted 牛儿吃草仗剑天涯
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了了解gRPC一篇就够了相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。


gRPC是什么?
一个高性能,开源,通用的RPC框架,将移动和HTTP/2放在首位(跟传统rpc定位不同),支持负载均衡、健康检查、身份验证。移动设备和浏览器可以直连,google开源。
前置知识:gRPC的数据序列化协议Protocol Buffers
简单使用:
安装
brew install protobuf
#go版本的protubuf插件
go get -v -u github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
协议简介
message SearchResponse {
/* 注释 */
message Result {
string url = 1; //1为字段标号
singular string title = 2; //singular0个或一个字段内容
repeated string snippets = 3; //repeated任意重复内容
}
repeated Result results = 1; //结构体嵌套
}
service SearchService {
rpc Search (SearchRequest) returns (SearchResponse); //定义服务方法
}
使用简介:
1、创建message.proto
syntax = "proto3";
package tutorial;
import "google/protobuf/timestamp.proto";
message Person {
string name = 1;
int32 id = 2; // Unique ID number for this person.
string email = 3;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0;
HOME = 1;
WORK = 2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
string number = 1;
PhoneType type = 2;
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 4; //实际会生成数组
google.protobuf.Timestamp last_updated = 5;
}
// Our address book file is just one of these.
message AddressBook {
repeated Person people = 1;
}
2、生成stub
protoc -I=./ --go_out=./ ./message.proto
3、加密与解密
package main
import (
"github.com/golang/protobuf/proto"
"github.com/e421083458/test_grpc/proto_test/message"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
)
var (
fileName string = "message.buffer"
)
func main() {
peoples:=[]*message.Person{
&message.Person{
Name:"test",
},
}
book := &message.AddressBook{
People:peoples,
}
// Write the new address book back to disk.
out, err := proto.Marshal(book)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to encode address book:", err)
}
if err := ioutil.WriteFile(fileName, out, 0644); err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to write address book:", err)
}
bts,err:=ioutil.ReadFile(fileName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to read address book:", err)
}
newBook:=&message.AddressBook{}
if err:=proto.Unmarshal(bts,newBook);err!=nil{
log.Fatalln("Failed to decode address book:", err)
}
log.Println(book)
log.Println(newBook)
}
proto encoding原理
查看加密文件
1、首先创建一个协议文件:
syntax = "proto3";
message Message {
int32 id = 1;
}
2、创建一个序列化程序
func main() {
m:=&message.Message{
Id:1,
}
out, err := proto.Marshal(m)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to encode address book:", err)
}
if err := ioutil.WriteFile("test.txt", out, 0644); err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Failed to write address book:", err)
}
}
3、写入文件后用二进制打开文件:
vim -b test.txt
:%!xxd
查看16进制:
0000000: 0896 01 ...
上面是啥意思?
要了解以上啥意思,首先要了解Varint
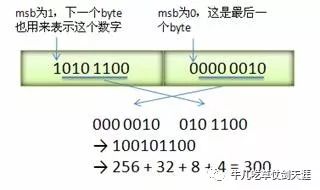
1、Varint 编码表示法
每个 byte 的最高位 bit 有特殊的含义,如果该位为 1,表示后续的 byte 也是该数字的一部分,如果该位为 0,则结束。其他的 7 个 bit 都用来表示数字。因此小于 128 的数字都可以用一个 byte 表示。大于 128 的数字,会用两个字节
例如整数1的表示,仅需一个字节:
0000 0001
例如300的表示,需要两个字节:
1010 1100 | 0000 0010
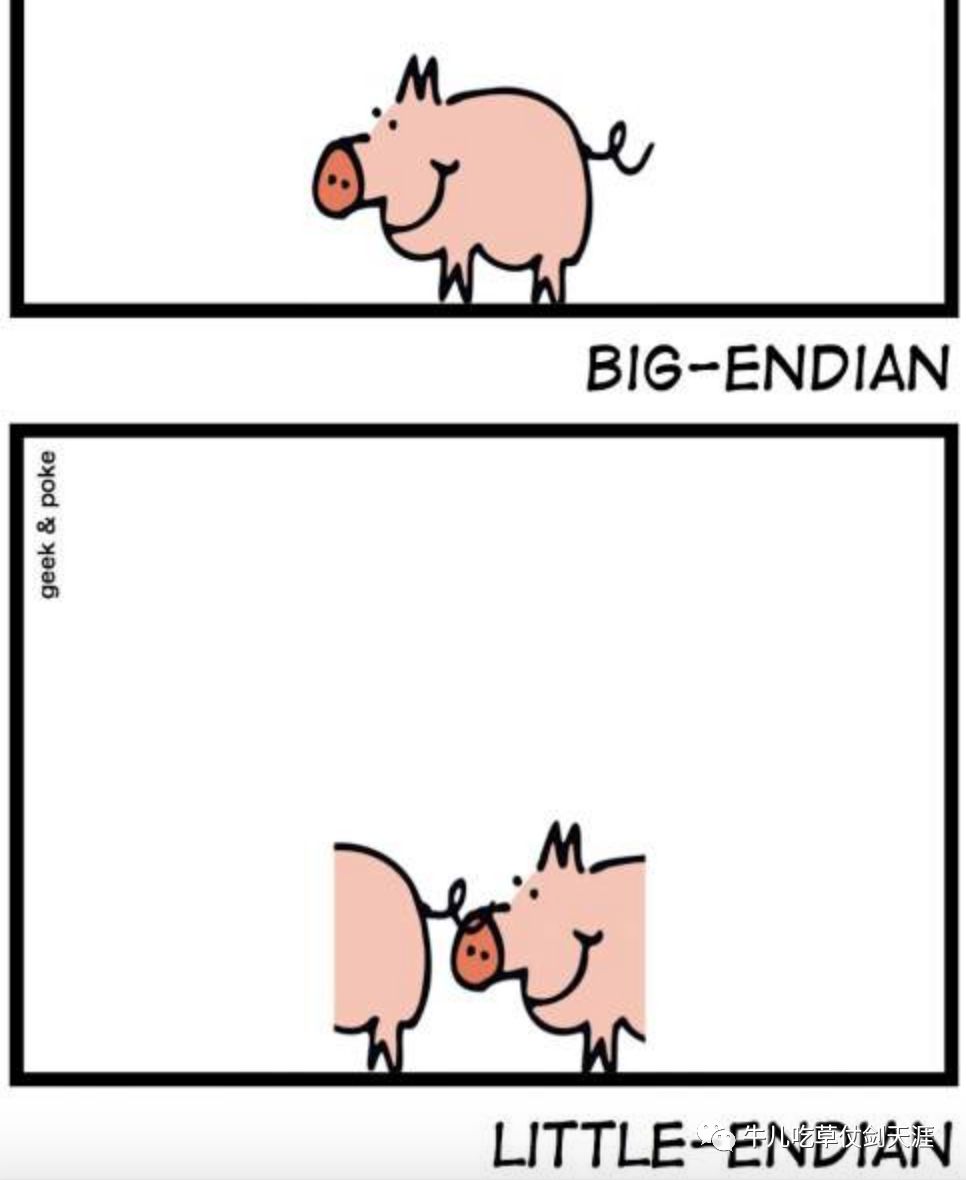
字节序采用 little-endian 的方式
ps:
大端字节序:高位字节在前,低位字节在后,这是人类读写数值的方法。
小端字节序:低位字节在前,高位字节在后,即以0x1122形式储存。
https://www.cnblogs.com/gremount/p/8830707.html
2、key的定义:
(field_number << 3) | wire_type
0 000 1000 首位为标识位,后三位为wire_type:0
>>3
0 000 0001 数字标签为1
得出wire_type为0,右移3位得到,数字标签。
3、wire_type定义

4、解码96 01
96 01 = 1001 0110 0000 0001
→ 000 0001 ++ 001 0110 (drop the msb and reverse the groups of7 bits)
→ 10010110
→ 2 + 4 + 16 + 128 = 150
gRPC
rpc原理
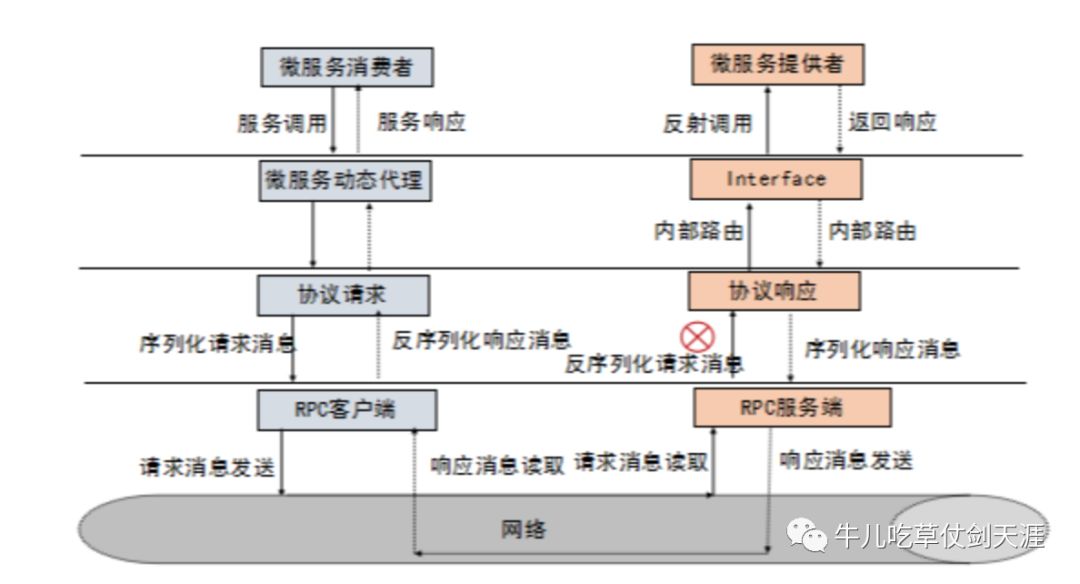
grpc原理
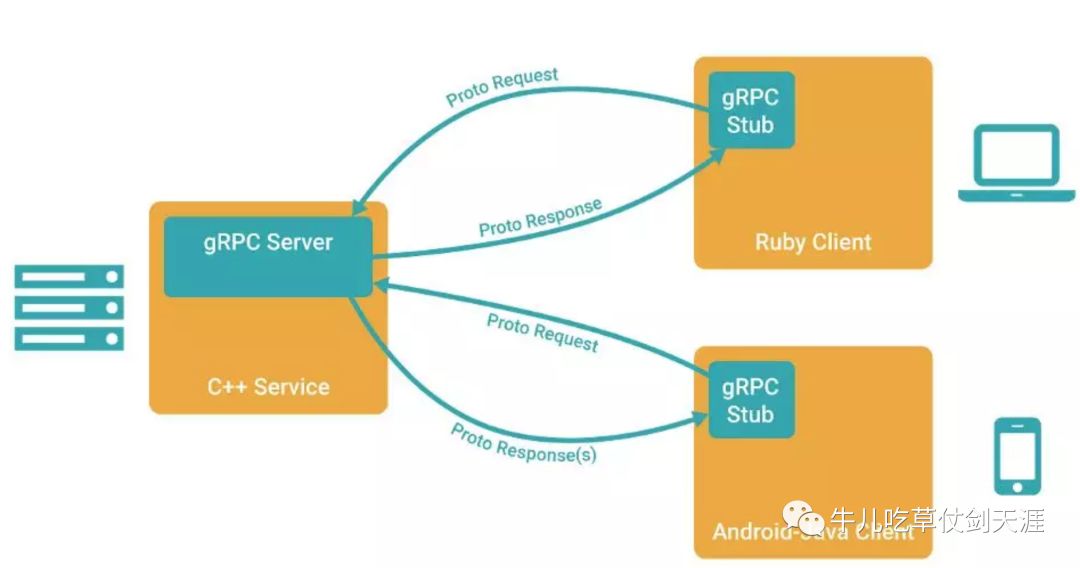
1、客户端(gRPC Stub)调用 A 方法,发起 RPC 调用。
2、对请求信息使用 Protobuf 进行对象序列化压缩(IDL)。
3、服务端(gRPC Server)接收到请求后,解码请求体,进行业务逻辑处理并返回。
4、对响应结果使用 Protobuf 进行对象序列化压缩(IDL)。
5、客户端接受到服务端响应,解码请求体。回调被调用的 A 方法,唤醒正在等待响应(阻塞)的客户端调用并返回响应结果。
基本使用:
0、安装gRPC及依赖
安装gRPC,一定要在gopath里安装,因为需要安装执行文件
go get -v -u google.golang.org/grpc
1、 一元RPC普通用法
定义协议
syntax = "proto3";
package helloworld;
service Greeter {
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
创建stub
protoc -I ../helloworld --go_out=plugins=grpc:../helloworld ../helloworld/helloworld.proto
创建服务器
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "google.golang.org/grpc/examples/helloworld/helloworld"
)
const (
port = ":50051"
)
type server struct{}
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloRequest)(*pb.HelloReply, error) {
log.Printf("Received: %v", in.Name)
return &pb.HelloReply{Message: "Hello " + in.Name}, nil
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
创建客户端
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"time"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "google.golang.org/grpc/examples/helloworld/helloworld"
)
const (
address = "localhost:50051"
defaultName = "world"
)
func main() {
conn, err := grpc.Dial(address, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewGreeterClient(conn)
name := defaultName
if len(os.Args) > 1 {
name = os.Args[1]
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
r, err := c.SayHello(ctx, &pb.HelloRequest{Name: name})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not greet: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("Greeting: %s", r.Message)
}
2、流式请求
协议定义
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "io.grpc.examples.routeguide";
option java_outer_classname = "RouteGuideProto";
package routeguide;
service RouteGuide {
rpc GetFeature(Point) returns (Feature) {}
rpc ListFeatures(Rectangle) returns (stream Feature) {}
rpc RouteChat(stream RouteNote) returns (stream RouteNote) {}
}
message Point {
int32 latitude = 1;
int32 longitude = 2;
}
message Rectangle {
Point lo = 1;
Point hi = 2;
}
message Feature {
string name = 1;
Point location = 2;
}
message RouteNote {
Point location = 1;
string message = 2;
}
message RouteSummary {
int32 point_count = 1;
int32 feature_count = 2;
int32 distance = 3;
int32 elapsed_time = 4;
}
创建stub
protoc -I ./ --go_out=plugins=grpc:./ ./route_guide.proto
服务器实现
func (s *routeGuideServer) ListFeatures(rect *pb.Rectangle, stream pb.RouteGuide_ListFeaturesServer) error {
for _, feature := range s.savedFeatures {
if inRange(feature.Location, rect) {
if err := stream.Send(feature); err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
return nil
}
func (s *routeGuideServer) RouteChat(stream pb.RouteGuide_RouteChatServer) error {
for {
in, err := stream.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
return nil
}
if err != nil {
return err
}
key := serialize(in.Location)
s.mu.Lock()
s.routeNotes[key] = append(s.routeNotes[key], in)
rn := make([]*pb.RouteNote, len(s.routeNotes[key]))
copy(rn, s.routeNotes[key])
s.mu.Unlock()
for _, note := range rn {
if err := stream.Send(note); err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
}
客户端实现
func runRouteChat(client pb.RouteGuideClient) {
notes := []*pb.RouteNote{
{Location: &pb.Point{Latitude: 0, Longitude: 1}, Message: "First message"},
{Location: &pb.Point{Latitude: 0, Longitude: 3}, Message: "Sixth message"},
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(),10*time.Second)
defer cancel()
stream, err := client.RouteChat(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("%v.RouteChat(_) = _, %v", client, err)
}
waitc := make(chan struct{})
go func() {
for {
in, err := stream.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
close(waitc)
return
}
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to receive a note : %v", err)
}
log.Printf("Got message %s at point(%d, %d)", in.Message,in.Location.Latitude, in.Location.Longitude)
}
}()
for _, note := range notes {
if err := stream.Send(note); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to send a note: %v", err)
}
}
stream.CloseSend()
<-waitc
}
特性:
1、鉴权认证
func main() {
flag.Parse()
fmt.Printf("server starting on port %d... ", *port)
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair(testdata.Path("server1.pem"), testdata.Path("server1.key"))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to load key pair: %s", err)
}
opts := []grpc.ServerOption{
grpc.UnaryInterceptor(ensureValidToken),
grpc.Creds(credentials.NewServerTLSFromCert(&cert)),
}
s := grpc.NewServer(opts...)
ecpb.RegisterEchoServer(s, &ecServer{})
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
2、超时关闭
func main() {
flag.Parse()
conn, err := grpc.Dial(*addr, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewEchoClient(conn)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(),10*time.Second)
stream, err := c.BidirectionalStreamingEcho(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error creating stream: %v", err)
}
// Send some test messages.
if err := sendMessage(stream, "hello"); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error sending on stream: %v", err)
}
if err := sendMessage(stream, "world"); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("error sending on stream: %v", err)
}
recvMessage(stream, codes.OK)
recvMessage(stream, codes.OK)
log.Println("cancelling begin")
cancel()
log.Println("cancelling after")
time.Sleep(30*time.Second)
log.Println("sleep done")
sendMessage(stream, "closed")
recvMessage(stream, codes.Canceled)
}
3、定义拦截器
func main() {
flag.Parse()
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
// Create tls based credential.
creds, err := credentials.NewServerTLSFromFile(testdata.Path("server1.pem"), testdata.Path("server1.key"))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to create credentials: %v", err)
}
//定义拦截器
s := grpc.NewServer(grpc.UnaryInterceptor(unaryInterceptor), grpc.StreamInterceptor(streamInterceptor))
// Register EchoServer on the server.
ecpb.RegisterEchoServer(s, &server{})
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
func unaryInterceptor(ctx context.Context, req interface{}, info *grpc.UnaryServerInfo, handler grpc.UnaryHandler) (interface{}, error){
// authentication (token verification)
md, ok := metadata.FromIncomingContext(ctx)
if !ok {
return nil, errMissingMetadata
}
if !valid(md["authorization"]) {
return nil, errInvalidToken
}
m, err := handler(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
logger("RPC failed with error %v", err)
}
return m, err
}
4、负载均衡支持
func main() {
pickfirstConn, err := grpc.Dial(
fmt.Sprintf("%s:///%s", exampleScheme, exampleServiceName),
// grpc.WithBalancerName("pick_first"), // "pick_first" is the default, so this DialOption is not necessary.
grpc.WithInsecure(),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer pickfirstConn.Close()
fmt.Println("--- calling helloworld.Greeter/SayHello with pick_first ---")
makeRPCs(pickfirstConn, 10)
fmt.Println()
// Make another ClientConn with round_robin policy.
roundrobinConn, err := grpc.Dial(
fmt.Sprintf("%s:///%s", exampleScheme, exampleServiceName),
grpc.WithBalancerName("round_robin"), // This sets the initial balancing policy.
grpc.WithInsecure(),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer roundrobinConn.Close()
fmt.Println("--- calling helloworld.Greeter/SayHello with round_robin ---")
makeRPCs(roundrobinConn, 10)
}
➜ client git:(master) go run main.go
--- calling helloworld.Greeter/SayHello with pick_first ---
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
--- calling helloworld.Greeter/SayHello with round_robin ---
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50052)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50052)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50052)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50052)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50051)
this is examples/load_balancing (from :50052)
客户端与服务端交互
没有配置成功wireshark,所以盗图,以下也是http2的交互流程
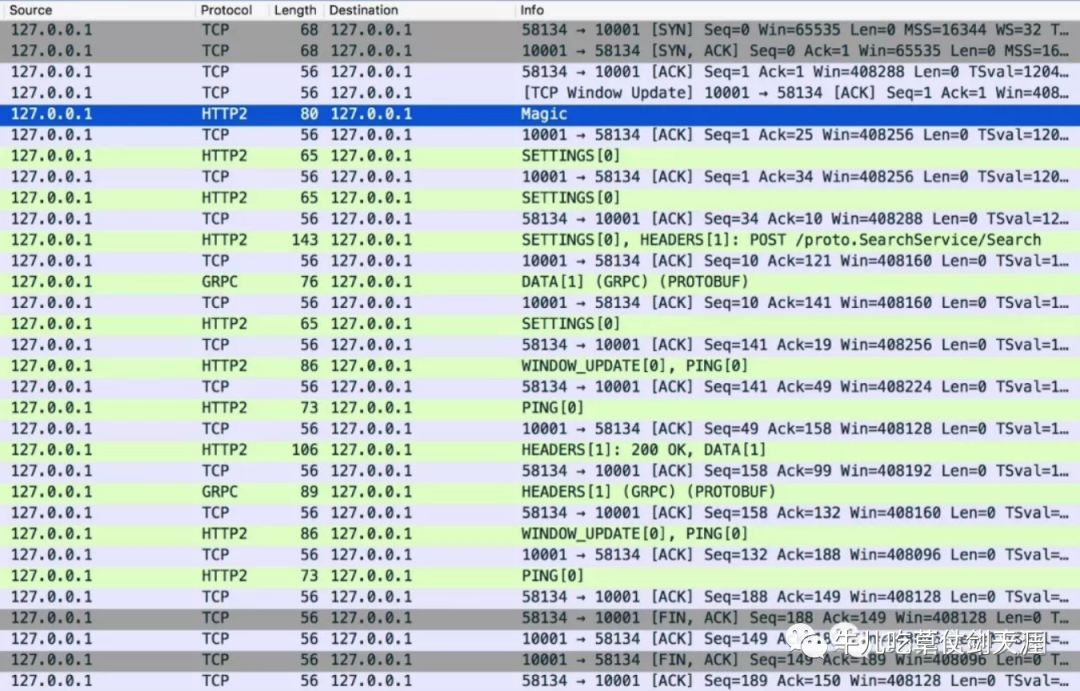
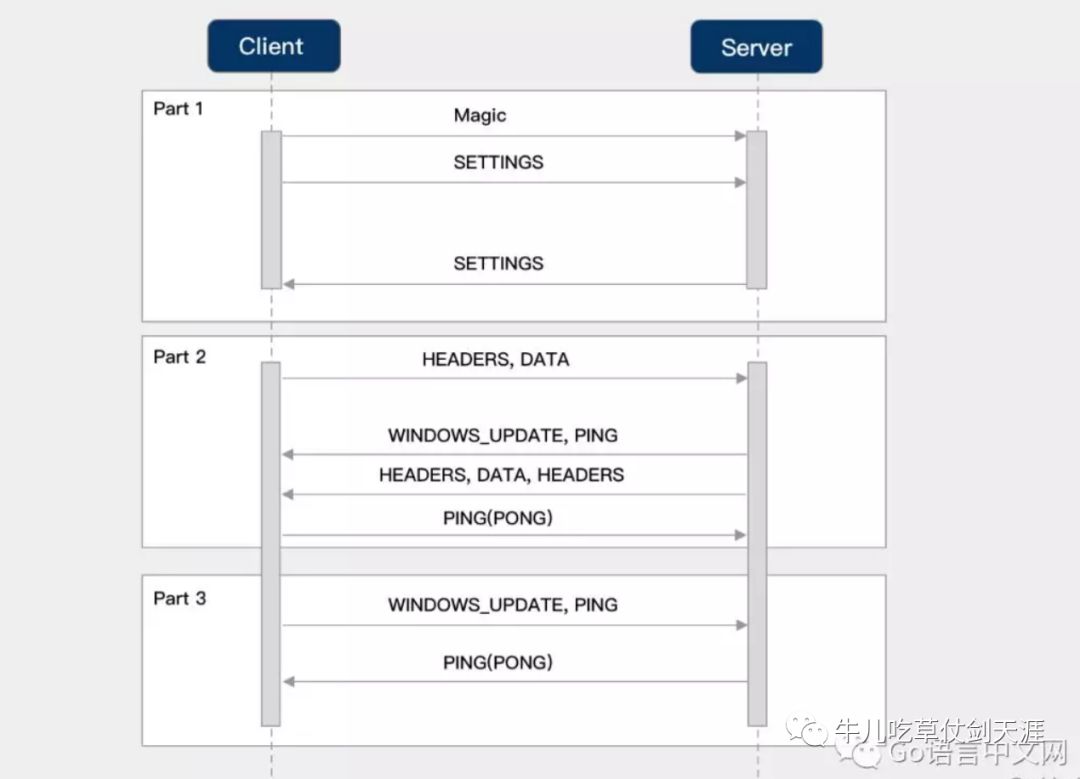
在建立连接之前,客户端/服务端都会发送连接前言(Magic+SETTINGS),确立协议和配置项。
在传输数据时,是会涉及滑动窗口(WINDOW_UPDATE)等流控策略的。
传播 gRPC 附加信息时,是基于 HEADERS 帧进行传播和设置;而具体的请求/响应数据是存储的 DATA 帧中的。
请求/响应结果会分为 HTTP 和 gRPC 状态响应两种类型。
客户端发起 PING,服务端就会回应 PONG,反之亦可。
源码分析:
1、服务端
初始化及注册
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
注册链条
func (s *Server) RegisterService(
func (s *Server) register(
srv := &service{
server: ss,
md: make(map[string]*MethodDesc),
sd: make(map[string]*StreamDesc),
mdata: sd.Metadata,
}
for i := range sd.Methods {
d := &sd.Methods[i]
srv.md[d.MethodName] = d
}
for i := range sd.Streams {
d := &sd.Streams[i]
srv.sd[d.StreamName] = d
}
s.m[sd.ServiceName] = srv
监听 触发休眠机制,若为第一次失败那么休眠 5ms,否则翻倍,再次失败则不断翻倍直至上限休眠时间 1s
func (s *Server) Serve(lis net.Listener) error {
...
var tempDelay time.Duration
for {
rawConn, err := lis.Accept()
if err != nil {
if ne, ok := err.(interface {
Temporary() bool
}); ok && ne.Temporary() {
if tempDelay == 0 {
tempDelay = 5 * time.Millisecond
} else {
tempDelay *= 2
}
if max := 1 * time.Second; tempDelay > max {
tempDelay = max
}
...
timer := time.NewTimer(tempDelay)
select {
case <-timer.C:
case <-s.quit:
timer.Stop()
return nil
}
continue
}
...
return err
}
tempDelay = 0
s.serveWG.Add(1)
go func() {
s.handleRawConn(rawConn)
s.serveWG.Done()
}()
}
}
服务从监听到方法被调用到的整个链条
func (s *Server) Serve(
func (s *Server) handleRawConn(
func (s *Server) serveStreams(
func (s *Server) handleStream(
//拿到注册的方法
srv, knownService := s.m[service]
if knownService {
if md, ok := srv.md[method]; ok {
s.processUnaryRPC(t, stream, srv, md, trInfo)
return
}
if sd, ok := srv.sd[method]; ok {
s.processStreamingRPC(t, stream, srv, sd, trInfo)
return
}
}
2、客户端
初始化
func main() {
//在非阻塞情况下,不会真正做连接。它只控制设置作用
conn, err := grpc.Dial(address, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewGreeterClient(conn)
name := defaultName
if len(os.Args) > 1 {
name = os.Args[1]
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
r, err := c.SayHello(ctx, &pb.HelloRequest{Name: name})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not greet: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("Greeting: %s", r.Message)
}
调用方法链
func (c *greeterClient) SayHello(
func (cc *ClientConn) Invoke(
func invoke(ctx context.Context, method string, req, reply interface{}, cc *ClientConn, opts ...CallOption) error {
cs, err := newClientStream(ctx, unaryStreamDesc, cc, method, opts...)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if err := cs.SendMsg(req); err != nil {
return err
}
return cs.RecvMsg(reply)
}
newClientStream 获取传输层 Trasport 并组合封装到 ClientStream 中返回,在这块会涉及负载均衡、超时控制、 Encoding、 Stream 的动作,与服务端基本一致的行为。
func newClientStream(
func (cs *clientStream) newAttemptLocked(
func (cc *ClientConn) getTransport(ctx context.Context, failfast bool, method string) (transport.ClientTransport,func(balancer.DoneInfo), error) {
t, done, err := cc.blockingpicker.pick(ctx, failfast, balancer.PickOptions{
FullMethodName: method,
})
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, toRPCErr(err)
}
return t, done, nil
}
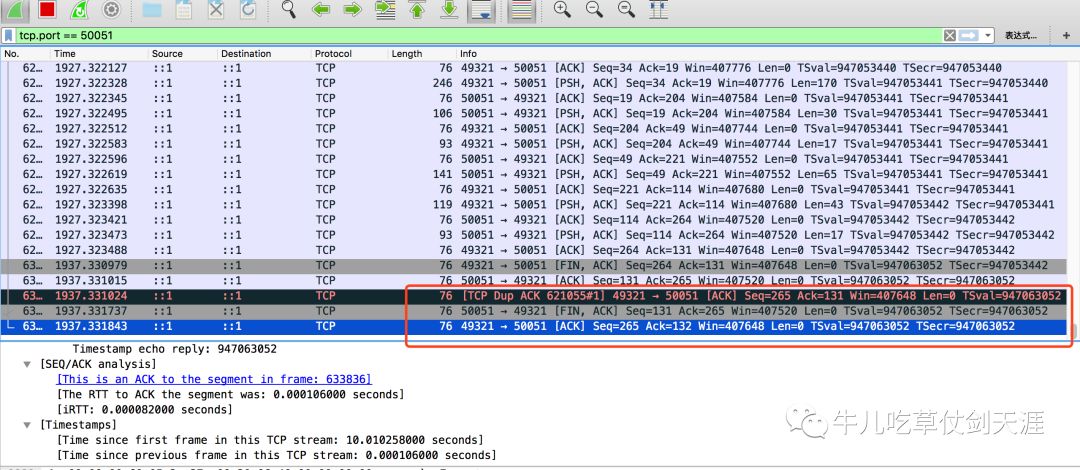
cancel 请求是怎么往下游传递的?context下游是怎么传递的?
实际是执行了FIN的包的传递
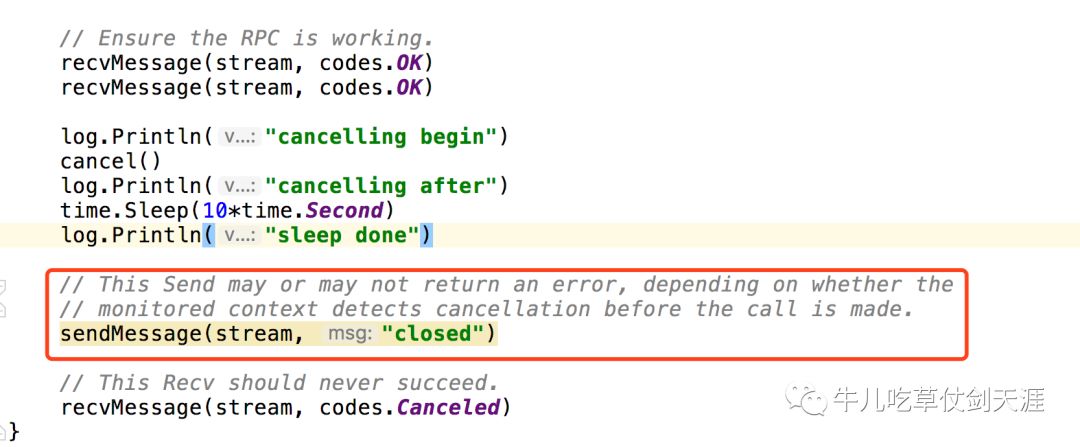
执行红框内sendMessage之前
执行之后
gRPC生态:
https://github.com/grpc/grpc-community
grpc-gateway
前置准备
go get -v -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
go get -v -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger
go get -v -u github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
简单使用
1、定义协议文件
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}
service YourService {
rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {}
}
2、添加注解
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}
service YourService {
rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/v1/example/echo"
body: "*"
};
}
}
3、构建gprc桩
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I.
-I$GOPATH/src
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis
--go_out=plugins=grpc:.
path/to/your_service.proto
4、构建服务器
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I.
-I$GOPATH/src
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis
--grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true:.
path/to/your_service.proto
5、构建代理服务器&编写代码
package main
import (
"context" // Use "golang.org/x/net/context" for Golang version <= 1.6
"flag"
"net/http"
"github.com/golang/glog"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/runtime"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
gw "github.com/e421083458/test_grpc/grpc_gateway/example"
)
var (
grpcServerEndpoint = flag.String("grpc-server-endpoint", "localhost:50051", "gRPC server endpoint")
)
func run() error {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
opts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()}
err := gw.RegisterYourServiceHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, mux, *grpcServerEndpoint, opts)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return http.ListenAndServe(":8081", mux)
}
func main() {
flag.Parse()
defer glog.Flush()
if err := run(); err != nil {
glog.Fatal(err)
}
}
6、生成swgger文档
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I.
-I$GOPATH/src
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis
--swagger_out=logtostderr=true:.
path/to/your_service.proto
测试:
➜ ~ curl 'http://127.0.0.1:8081/v1/example/echo' -d '{"value":"foo"}'
{"value":"Hellofoo"}%
gRPC在前端的调用支持
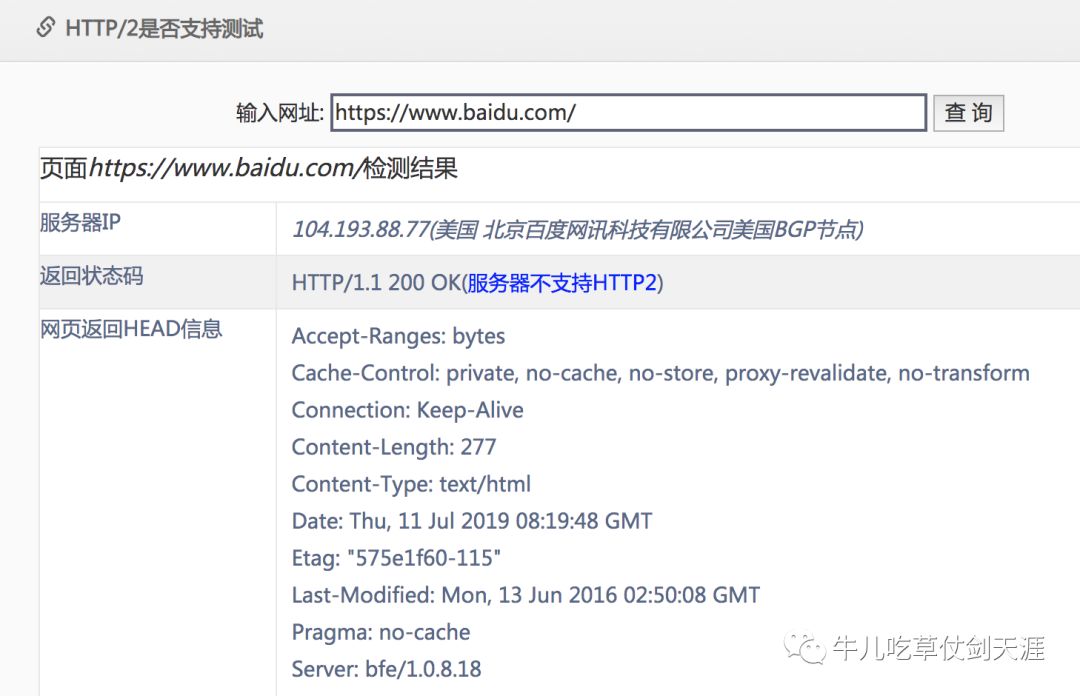
话外音:使用grpc你就能等同于接入了流行趋势
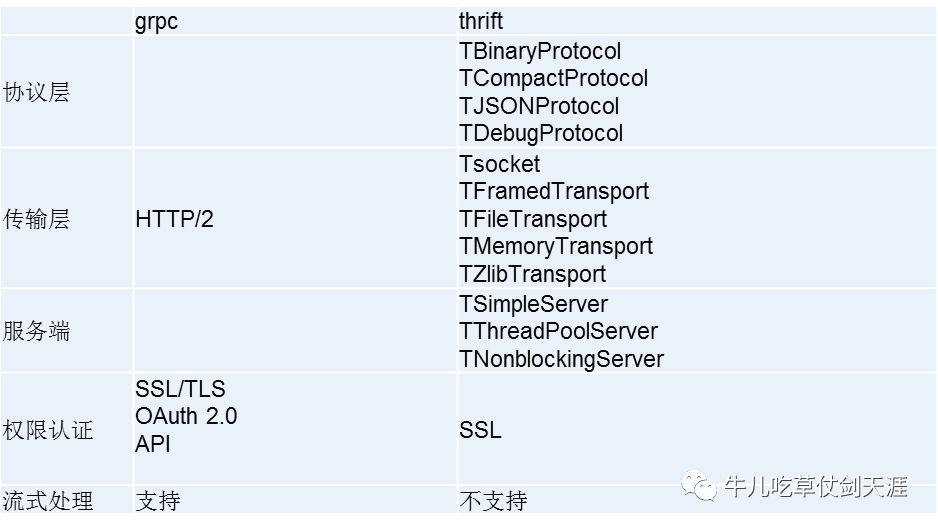
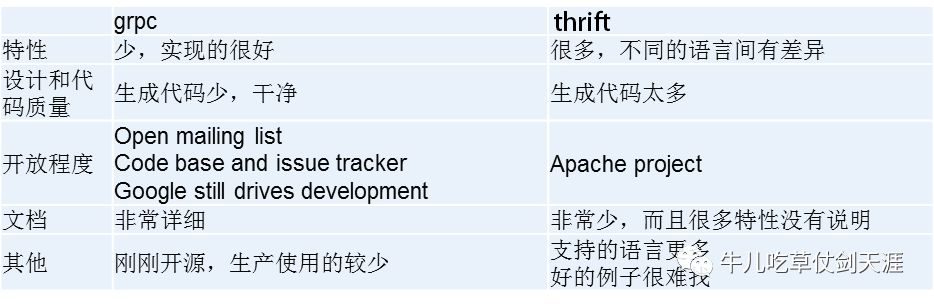
gRPC VS Thrift
特点对比
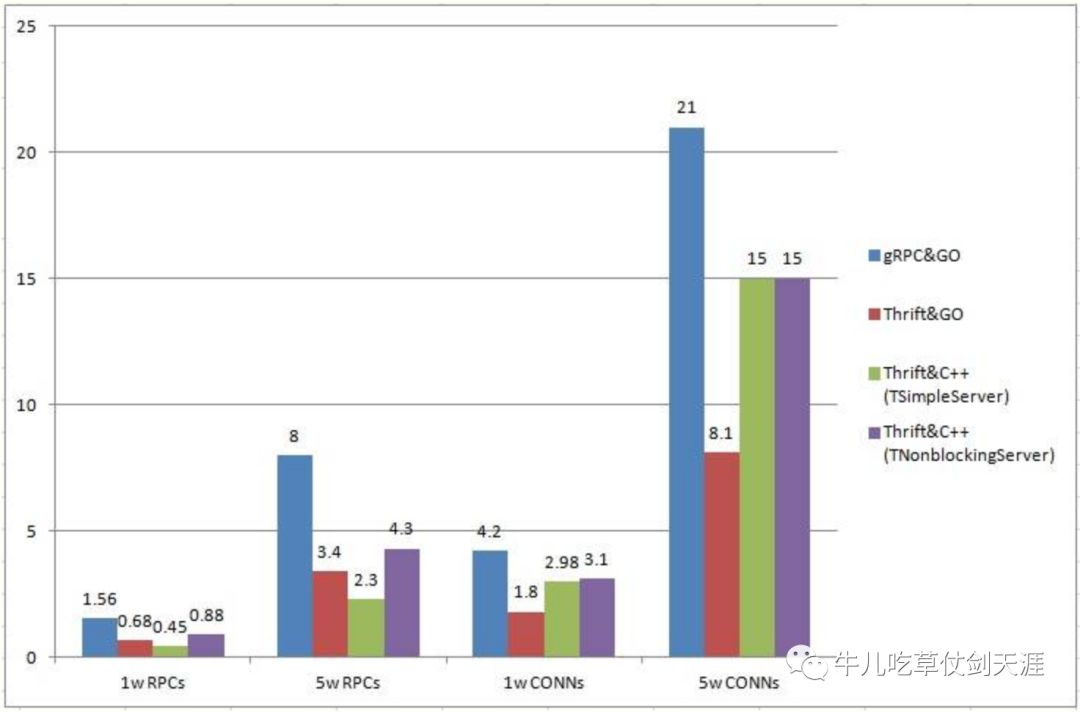
性能对比
单线程请求耗时:1w或5w次请求
多线程请求耗时:1、4核
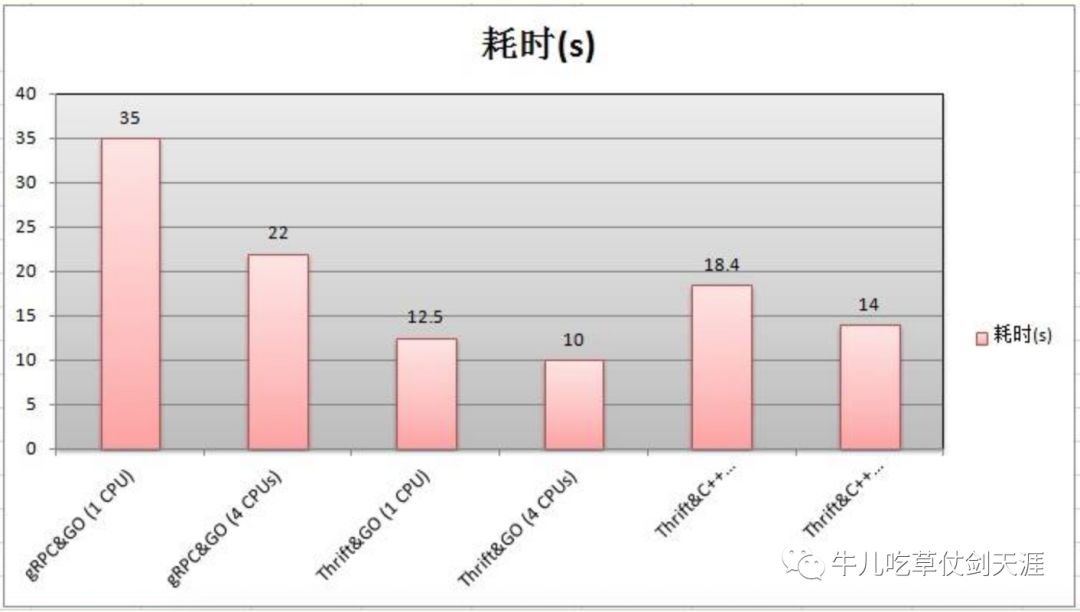
热度对比
从上面对比看来,gRPC热度只高不减。为什么性能一般的gRPC还这么受人喜爱。我感觉是因为gRPC专注于移动领域并且从根源上使用了http2协议。当你使用移动设备、或者浏览器 浏览网络时不是那一丝毫耗时产生的影响。而是http1.1本身有并发问题导致的。
参考文档:
安装protobuf
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21383435/article/details/81035852
Protocol Buffers 3 简明教程
https://juejin.im/post/5b852d476fb9a019e4505873
protobuf官方手册
https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/gotutorial
proto encoding原理
https://www.cnblogs.com/shitouer/archive/2013/04/12/google-protocol-buffers-encoding.html
大端字节序与小端字节序
https://www.cnblogs.com/gremount/p/8830707.html
js中 与,或,以及异或的二进制使用
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39460408/article/details/80797231
grpc快速开始
https://grpc.io/docs/quickstart/go/
grpc-web
https://www.npmjs.com/package/grpc-web
从实践到原理,带你参透 gRPC
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-1aPHIDfwWCkQyT8Yhfv7Q##
以上是关于了解gRPC一篇就够了的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章