实现一个简易的RPC
Posted 好好学java
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了实现一个简易的RPC相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
重磅资讯、干货,第一时间送达
今日推荐:
个人原创+1博客:
作者:黄青石
链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/huangqingshi/p/12289820.html
之前写了一些关于RPC原理的文章,但是觉得还得要实现一个。之前看到一句话觉得非常有道理,与大家共勉。不是“不要重复造轮子”,而是“不要发明轮子”,所以能造轮子还是需要造的。
这篇文章的梗概如下:
1. 介绍一下这篇RPC的大致梗概。
2. 说一下这篇文章需要的技术和实现。
3. 用测试用例测试一下。
一、梗概
这篇RPC主要提示了服务注册,服务发现,同步调用,异步调用,回调功能。这些功能已经足够学习RPC使用了,对其中的原理就了解的非常清楚了。
二、技术和实现
采用的技术有Netty, Zookeeper, Protostuff, Spring,Cglib,Log4j这些基本就能够达到这个功能。
Netty的作用就是用于客户端向服务端发送请求,服务端接收请求后进行处理,Netty是一个基于异步事件处理的程序,客户端和服务端采用的LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,这种解码方法是最通用的,也就是把长度写到数据包中,即 Length + Data,用这种解码方法解决拆包粘包的问题。
Zookeeper的作用是用于服务的注册,分布式解决方案中的很重要的一个工具。里边主要做两件事,一个是创建一个永久的节点,然后再永久的节点下边创建临时节点,用作服务的注册,同时写上对应的监听事件,如果服务下线或上线了,将进行服务上下线处理。
Protostuff是基于protoBuff的一种方案,这种方案可以在protoBuff的基础上省去对应的.proto文件,这样相对来讲会更方便一些。它的主要作用是将数据进行序列化和反序列化,相对于JDK自带的序列化方案,这种方案有更好更优的处理效率。
Spring主要是因为最近项目都比较流行Spring, 所以需要将Spring结合起来,这样才能更好的兼容大部分的工程,同时也了解一下Spring的各种机制,本篇主要采用的是自定义一个注解,然后将接口和方法添加上注解,添加好之后,在Spring启动的时候,获取该注解的类并且将其封闭到一个Map中,待后续使用。
Cglib的作用是动态代码,客户端将需要操作的接口类,方法,参数,参数进行进行封装,然后序列化后发给服务端,服务端收到请求之后将结合注册在Map中的Bean进行方法调用,采用的就是Cglib,关于动态代理我还写过一篇文章
Log4j用于配置进行日志输出。
接下来咱们一起看下代码片段:
下边的是Server的定义,里边主要有两个主要的功能,一个是Netty的初始化,采用上边说的将长度写到Length里边, Length占4个字节,剩下的就是数据。
效果如下,最大长度为64436即 64K,Length的长度为4个字节。将Request和Response进行解码和编码,这个含义是直接将实际的数据转化为真实的Request。
* +------------+--------------------+
* | Length | Actual Content |
* | 0x00000C | "HELLO, WORLD" |
* +------------+--------------------+
还有一个比较重要的就是在启动初始化的时候,将注解RPCServer的类获取且封装起来,放到Map里边用于后续的调用。
package com.hqs.server; import com.hqs.client.RPCClientHandler; import com.hqs.codec.RPCDecoder; import com.hqs.codec.RPCEncoder; import com.hqs.protocol.Request; import com.hqs.protocol.Response; import com.hqs.registry.ServiceDiscovery; import com.hqs.registry.ServiceRegistry; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioserverSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder; import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class RPCServer implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean { private String serverAddress; private ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry; private Map<String, Object> handlerMap = new HashMap<>(); private static ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor; private EventLoopGroup bossGroup = null; private EventLoopGroup workerGroup = null; public RPCServer(String serverAddress) { this.serverAddress = serverAddress;
} public RPCServer(String serverAddress, ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry) { this.serverAddress = serverAddress; this.serviceRegistry = serviceRegistry;
}
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
start();
}
@Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
Map<String, Object> serverBeanMap = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(RPCService.class); if(!MapUtils.isEmpty(serverBeanMap)) { for(Object serviceBean : serverBeanMap.values()) {
String interfaceName = serviceBean.getClass().getAnnotation(RPCService.class).value().getName();
handlerMap.put(interfaceName, serviceBean);
}
}
} public void start() throws InterruptedException { if(bossGroup == null && workerGroup == null) {
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65536, 0, 4, 0, 0))
.addLast(new RPCDecoder(Request.class))
.addLast(new RPCEncoder(Response.class))
.addLast(new RPCServerHandler(handlerMap));
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
String[] address = serverAddress.split(":");
String host = address[0]; int port = Integer.parseInt(address[1]);
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(host, port).sync();
System.out.println("servier 启动"); if(serviceRegistry != null) {
serviceRegistry.register(serverAddress);
}
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
} public static void submit(Runnable task) { if(threadPoolExecutor == null) { synchronized (RPCServer.class) { if(threadPoolExecutor == null) {
threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(16, 16, 600L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(65536));
}
}
}
threadPoolExecutor.submit(task);
} public RPCServer addService(String interfaceName, Object serviceBean) { if(!handlerMap.containsKey(interfaceName)) {
handlerMap.put(interfaceName, serviceBean);
} return this;
}
}
下面是异步调用接口和动态代理接口,用于进行接口异步调用,实现动态代理。
package com.hqs.proxy; import com.hqs.async.RPCFuture; public interface AsyncObjectProxy {
RPCFuture call(String funcName, Object... args);
}
client端的代理采用的是JDK的代理机制,在初始化ObjectProxy的时候,将需要代理的类传入,这样如果类在调用方法的时候,首先会调用里边的invoke方法,这样就可以在invoke里边进行数据请求的初始化工作了。
package com.hqs.proxy; import com.hqs.ConnectionManager; import com.hqs.async.RPCFuture; import com.hqs.client.RPCClientHandler; import com.hqs.protocol.Request; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.UUID; public class ObjectProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, AsyncObjectProxy{ private Class<T> clazz; public ObjectProxy(Class<T> clazz) { this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override public RPCFuture call(String funcName, Object... args) {
RPCClientHandler handler = ConnectionManager.getInstance().chooseHandler();
Request request = createRquest(this.clazz.getName(), funcName, args);
RPCFuture future = handler.sendRequest(request); return future;
}
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if (Object.class == method.getDeclaringClass()) {
String name = method.getName(); if ("equals".equals(name)) { return proxy == args[0];
} else if ("hashCode".equals(name)) { return System.identityHashCode(proxy);
} else if ("toString".equals(name)) { return proxy.getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(proxy)) +
", with InvocationHandler " + this;
} else { throw new IllegalStateException(String.valueOf(method));
}
}
Request request = new Request();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setClassName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameters(args);
Class[] parameterTypes = new Class[args.length]; for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
parameterTypes[i] = getClassType(args[i]);
}
request.setParameterTypes(parameterTypes);
System.out.println("requestId:" + request.getRequestId() + " className:" + request.getClassName());
RPCClientHandler handler = ConnectionManager.getInstance().chooseHandler();
RPCFuture future = handler.sendRequest(request); return future.get();
} private Request createRquest(String className, String methodName, Object[] args) {
Request request = new Request();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setClassName(className);
request.setMethodName(methodName);
request.setParameters(args);
Class[] parameterTypes = new Class[args.length]; for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
parameterTypes[i] = getClassType(args[i]);
}
request.setParameterTypes(parameterTypes);
System.out.println("requestId:" + request.getRequestId() + " className:" + className); return request;
} private Class<?> getClassType(Object obj) {
Class<?> classType = obj.getClass();
String typeName = classType.getName(); switch (typeName) { case "java.lang.Integer": return Integer.TYPE; case "java.lang.Long": return Long.TYPE; case "java.lang.Float": return Float.TYPE; case "java.lang.Double": return Double.TYPE; case "java.lang.Character": return Character.TYPE; case "java.lang.Boolean": return Boolean.TYPE; case "java.lang.Short": return Short.TYPE; case "java.lang.Byte": return Byte.TYPE;
} return classType;
}
}
异步回调方法接口和异步处理类RPCFuture,该类实现了Future类,这个类里有的方法大家应该比较常用。cancel(), isCancelled(), isDone(), get(), get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit),其中get是同步调用,什么时候执行完成之后什么时候继续执行后续操作,get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)用于在某个时间内不给到回执的话,将会不丢弃掉请求。
package com.hqs.async; public interface AsyncRPCCallback { void success(Object result); void fail(Exception e);
} package com.hqs.async; import com.hqs.client.RPCClient; import com.hqs.protocol.Request; import com.hqs.protocol.Response; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException; import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * 用于实现异步调用 */
public class RPCFuture implements Future<Object> { private Sync sync; private Request request; private Response response; private long startTime; private long responseTimeThreshold = 5000L; private List<AsyncRPCCallback> pendingCallbacks = new ArrayList<>(); private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public RPCFuture(Request request) { this.sync = new Sync(); this.request = request; this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { return false;
}
@Override public boolean isCancelled() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override public boolean isDone() { return sync.isDone();
}
@Override public Object get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
sync.acquire(1); if(this.response != null) { return this.response.getResult();
} return null;
}
@Override public Object get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { boolean success = sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout)); if(success) { if(this.response != null) { return this.response.getResult();
} return null;
} return new RuntimeException("Timeout exception. Request id: " + this.request.getRequestId() + ". Request class name: " + this.request.getClassName() + ". Request method: " + this.request.getMethodName());
} public void done(Response response) { this.response = response;
sync.release(1);
invokeCallbacks(); long responseTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; if(responseTime > responseTimeThreshold) {
System.out.println("Service response time is too slow. Request id = " + response.getRequestId());
}
} private void invokeCallbacks() {
lock.lock(); try { for( AsyncRPCCallback asyncRPCCallback : pendingCallbacks) {
runCallback(asyncRPCCallback);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} public RPCFuture addCallback(AsyncRPCCallback callback) {
lock.lock(); try { if(isDone()) {
runCallback(callback);
} else { this.pendingCallbacks.add(callback);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
} return this;
} private void runCallback(final AsyncRPCCallback callback) { final Response response = this.response;
RPCClient.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() { if(!response.isError()) {
callback.success(response.getResult());
} else {
callback.fail(new RuntimeException("Response error", new Throwable(response.getError())));
}
}
});
} static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { //future status
private final int done = 1; private final int pending = 0;
@Override protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) { return getState() == done;
}
@Override protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) { if(getState() == pending) { if(compareAndSetState(pending, done)) { return true;
} else { return false;
}
} else { return true;
}
} public boolean isDone() { return getState() == done;
}
}
}
服务的注册和服务发现类,里边包括了zk的连接,设置ZK的监听,创建永久节点和临时节点。
package com.hqs.registry; import org.apache.zookeeper.*; import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; public class ServiceRegistry { private CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); private String registryAddress; public ServiceRegistry(String registryAddress) { this.registryAddress = registryAddress;
} public void register(String data) { if(data != null) {
ZooKeeper zk = connectServer(); if(zk != null) {
AddRootNode(zk);
createNode(zk, data);
}
}
} private ZooKeeper connectServer() {
ZooKeeper zk = null; try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(registryAddress, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, new Watcher() {
@Override public void process(WatchedEvent event) { if(event.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected) {
latch.countDown();
}
}
});
latch.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return zk;
} private void AddRootNode(ZooKeeper zk) { try {
Stat s = zk.exists(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH, false); if(s == null) {
zk.create(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH, new byte[0], ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} private void createNode(ZooKeeper zk, String data) { try { byte[] dataBytes= data.getBytes();
String path = zk.create(Constant.ZK_DATA_PATH, dataBytes, ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);
System.out.println("createNode:path" + path + " data:" + data);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.hqs.registry; import com.hqs.ConnectionManager; import org.apache.zookeeper.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; public class ServiceDiscovery { private CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); private volatile List<String> dataList = new ArrayList<>(); private String registryAddress; private ZooKeeper zooKeeper; public ServiceDiscovery(String registryAddress) { this.registryAddress = registryAddress;
zooKeeper = connectServer(); if(zooKeeper != null) { try {
watchNode(zooKeeper);
} catch (Exception e) { try {
watchNode(zooKeeper);
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} private ZooKeeper connectServer() {
ZooKeeper zk = null; try {
zk = new ZooKeeper(registryAddress, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, new Watcher() {
@Override public void process(WatchedEvent event) { if(event.getState() == Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected) {
latch.countDown();
}
}
});
latch.await();
} catch (Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return zk;
} private void watchNode(final ZooKeeper zk) { try {
List<String> nodeList = zk.getChildren(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH, new Watcher() {
@Override public void process(WatchedEvent event) { if(event.getType() == Event.EventType.NodeDataChanged) {
watchNode(zk);
}
}
});
List<String> dataList = new ArrayList<>(); for(String node : nodeList) { byte[] bytes = zk.getData(Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH + "/" + node, false, null);
dataList.add(new String(bytes));
} this.dataList = dataList;
UpdateConnectServer();
} catch (KeeperException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} private void UpdateConnectServer() {
ConnectionManager.getInstance().UpdateConnectedServer(dataList);
} public void close() { if(zooKeeper != null) { try {
zooKeeper.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
三、测试
大部分代码功能已经在上边描述了,当然还有很多细节需要了解,比如AQS,RentrantLock,Condition,这个需要自行了解一下。下边咱们来看一下测试用例。
启动zookeeper,然后启动RPCBootServiceWithSpring,将下边每个测试的类进行调用,依次是同步调用,异步调用,同步callback调用。
package com.hqs.spring; import com.hqs.HelloService; import com.hqs.async.AsyncRPCCallback; import com.hqs.async.RPCFuture; import com.hqs.client.RPCClient; import com.hqs.proxy.AsyncObjectProxy; import com.hqs.registry.ServiceDiscovery; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:client.xml") public class ServiceTest { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServiceTest.class);
@Autowired private RPCClient rpcClient;
@Test public void syncTest() {
HelloService helloService = rpcClient.create(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.sayHi("hqs");
System.out.println(result);
Assert.assertEquals("Hi hqs", result);
}
@Test public void asyncInvokeTest() {
ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery = new ServiceDiscovery("127.0.0.1:2181");
RPCClient rpcClient = new RPCClient(serviceDiscovery);
AsyncObjectProxy asyncClient = rpcClient.createAsync(HelloService.class);
RPCFuture future = asyncClient.call("sayHi", "hqs"); try {
String result = (String) future.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Assert.assertEquals("Hi hqs", result);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test public void syncCallbackTest() {
ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery = new ServiceDiscovery("127.0.0.1:2181");
RPCClient rpcClient = new RPCClient(serviceDiscovery);
AsyncObjectProxy asyncClient = rpcClient.createAsync(HelloService.class);
RPCFuture future = asyncClient.call("sayHi", "hqs"); final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
future.addCallback(new AsyncRPCCallback() {
@Override public void success(Object result) {
System.out.println("result:" + result.toString());
Assert.assertEquals("Hi hqs", result);
latch.countDown();
}
@Override public void fail(Exception e) {
System.out.println("fail:" + e.getMessage());
latch.countDown();
}
}); try {
latch.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@After public void setTear() { if (rpcClient != null) {
rpcClient.stop();
}
}
}
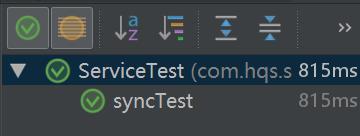
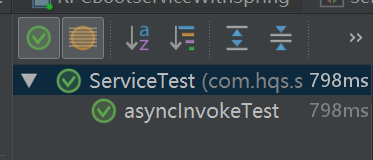
运行上边的结果都通过了,说明能正常运行。
如果想要看更详细的代码访问:https://github.com/stonehqs/MyNettyRpc
欢迎指正。
以上是关于实现一个简易的RPC的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章