SQL数据库批量添加数据
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SQL数据库批量添加数据相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ru如题
1、创建测试表,create table test_batch(id number, v_date date);
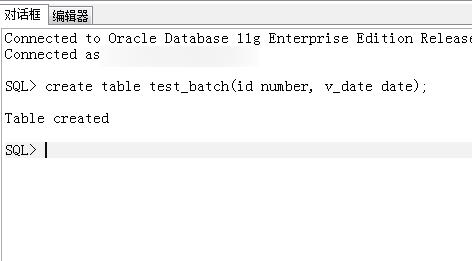
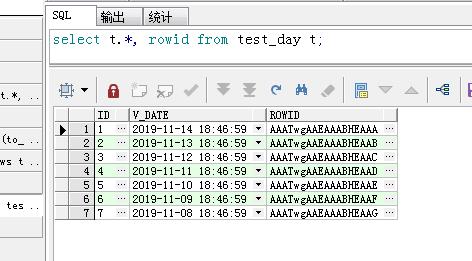
2、先看插入原始表数据;select t.*, rowid from test_day t;
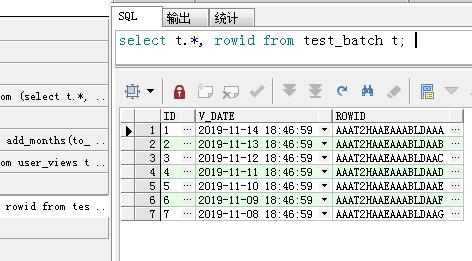
3、批量插入测试数据,insert into test_batch select * from test_day;commit;

4、查询表的记录,select t.*, rowid from test_batch t; 可以发现数据一致。批量添加数据完成。
一、针对批量插入数据,如果量不是太多,可以多条SQL语句运行就可以了,
类似下面的语句,当然可以使用excel 编辑后,复制到查询器中运行,
insert into table(a,b) values('1','a')
insert into table(a,b) values('2','b')
insert into table(a,b) values('3','c')
二、大量数批量插入,即数据表的移植,数据备份转换之类的,就需要工具,比如MSSQL的DTS工具,pb的数据通道 等等。这里介绍一下 DTS工具。
1、在SQL安装目录下开启导入和导出数据,即DTS。

2、选择一个批量的数据,可以是表,也可以是带分隔符的文件,或excel文档之类,如图中选择,导入的格式
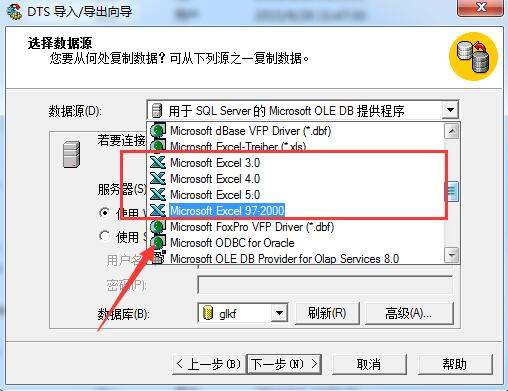
3、选择导入的目标

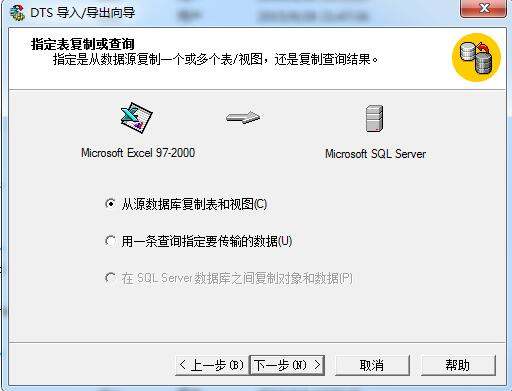
4、选择导入方式
5.具体的导入规则
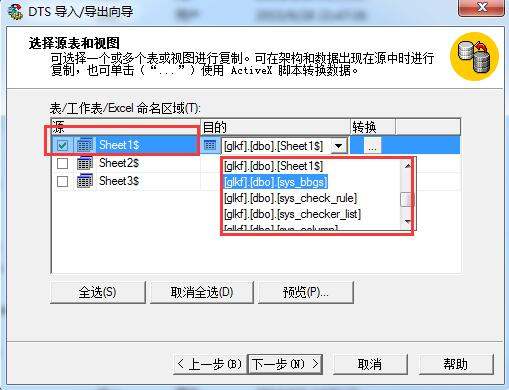
我们一般在EXCEL表上输入。。格式和数据库表一样。
完了。用SQL的导入向导导入。。
在EXCEL上输入可以自由弄格式。。。。
没有原始记录是什么办法都没有了。只有在excel上做快一点。
补充::
有表格就好办法。
【开始】-》【程序】->microsoft sql server-》导入和导入数据-》数据源为excel表。目的就是sql的表本回答被提问者采纳 参考技术C 下面的代码已验证过,直接在查询分析器里执行就可以了
create
table
#1
(
Time
datetime
)
--select
*
from
#1
declare
@i
int,@StartTime
datetime
select
@i
=
0,@StartTime
=
'2010-3-17
8:30:00'
while
@i
<
3
begin
insert
into
#1
values(dateadd(dd,@i,@StartTime))
set
@i=@i+1
end
select
*
from
#1
drop
table
#1 参考技术D 在表上做一个触发器。假设id是表的主键,t_time
时间字段,tb_name表名
declare
@id
int
declare
@n
int
declare
@t
datetime
select
@id=id,@t=t_time
from
inserted
select
@n
=count(*)
from
tb_name
if
@n=0
begin
select
@t=max(t_time)
from
tb_name
end
update
tb_name
set
t_time
=
dateadd(dd,1,@t)
where
id
=
@id
插入的时候一条一条插入就可以了
使用Batch批量添加数据
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JDBCTest {
@Test
public void testBatch(){
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try{
connection=JDBCTools.getConnection();
JDBCTools.beginTx(connection);
String sql="insert into customers values(?,?,?)";
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long beginTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++){
preparedStatement.setInt(1,i+100001);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "");
preparedStatement.setDate(3, new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
//preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//积攒SQL
preparedStatement.addBatch();
//当积攒到一定程度,就统一的执行一次,并且清空先前积攒的SQL
if((i+1)%300==0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
//若总条数不是批量数值的整数倍,则还需要再额外执行一次
if((100000%300)!=0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
long stopTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
JDBCTools.commit(connection);
System.out.println(beginTime-stopTime);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
JDBCTools.rollback(connection);
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
@Test
public void testBatchWithPreparedStatement(){
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try{
connection=JDBCTools.getConnection();
JDBCTools.beginTx(connection);
String sql="insert into customers values(?,?,?)";
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long beginTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++){
preparedStatement.setInt(1,i+100001);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "");
preparedStatement.setDate(3, new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
long stopTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
JDBCTools.commit(connection);
System.out.println(beginTime-stopTime);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
JDBCTools.rollback(connection);
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
以上是关于SQL数据库批量添加数据的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章