下次再让你讲平衡二叉树,可别说不会了
Posted 波波Tea
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了下次再让你讲平衡二叉树,可别说不会了相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我前面写过一篇文章,是关于二叉查找树的结点插入的,详情请戳这里 ,并且在最后我揭露了这种插入算法的弊端,就是会导致树不平衡,而树越不平衡,查找操作的时间复杂度就越高,这显然是一种坏的插入算法。
今天我要讲的知识,就是来解决这个问题的。
平衡二叉树基本概念
平衡二叉树,也是一种二叉查找树,但它是平衡的,即左子树与右子树的高度差最多等于1。
平衡二叉树也叫AVL树,取自发明平衡二叉树算法的人的人名。
平衡因子BF:左子树深度减去右子树深度的值。平衡二叉树所有结点的平衡因子只能是-1,0,1。
最小不平衡子树:假设新插入了一个结点A,然后导致树不平衡了,距离结点A最近且BF绝对值大于1的那个结点为B,以B结点为根的树称为最小不平衡子树
平衡二叉树实现原理
在构建二叉查找树过程中,每插入一个结点,先检查是否破坏了树的平衡。若是,则找出最小不平衡子树,在保持二叉查找树特性的前提下,调整最小不平衡子树中各结点之间的链接关系,进行相应的旋转,使之达到新的平衡。
旋转分两种:左旋和右旋。右旋会减小BF,左旋增加BF。
上面的说辞比较抽象,下面就来具体一点的。为了更好地讲解原理,我们以依次插入结点3,2,1,4,5,6,7,10,9,8为例。
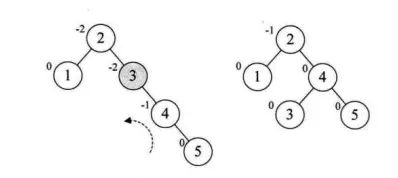
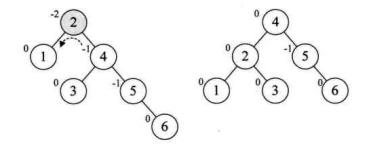
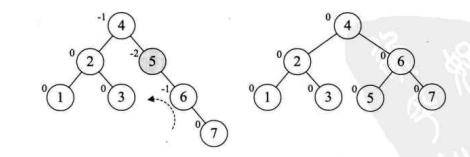
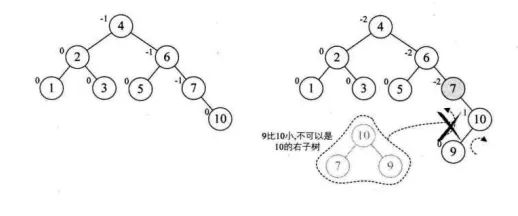
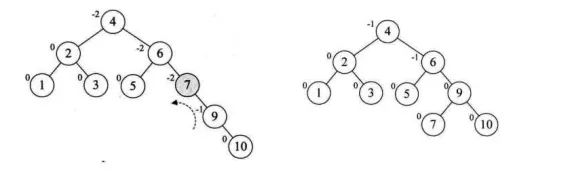
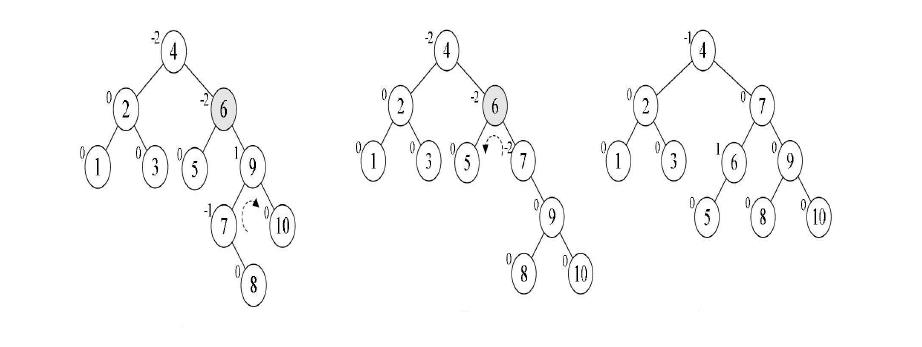
平衡二叉树代码实现
Ancestor:祖先类
AVLInsert:平衡二叉树结点插入核心实现
AVLMain:main方法所在类,包含示例程序
AVLNode:avl树结点类
AVLNode
import com.bobo.group.tree.draw.Drawable;
public class AVLNode implements Drawable {
private int val;
private AVLNode left;
private AVLNode right;
public AVLNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public AVLNode(int val, AVLNode left, AVLNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
//省略getter/setter方法
@Override
public String getValue() {
return String.valueOf(this.val);
}
@Override
public Drawable getLeftNode() {
return this.left;
}
@Override
public Drawable getRightNode() {
return this.right;
}
}/**
* 结点的祖先信息
*/
public class Ancestor {
private AVLNode ancestor;
private boolean isLeft;
public Ancestor(AVLNode ancestor) {
this.ancestor = ancestor;
}
public Ancestor(AVLNode ancestor, boolean isLeft) {
this.ancestor = ancestor;
this.isLeft = isLeft;
}
// 省略getter/setter方法
}import com.bobo.group.common.CommonUtil;
import com.bobo.group.tree.draw.DrawTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class AVLInsert {
//记录插入的每个结点
private List<AVLNode> avlNodes = new ArrayList<>();
//画二叉树对象
private DrawTree drawTree = new DrawTree();
//可变的根结点,因为根结点也会旋转
private AVLNode variableRoot;
//生成图片时计数
private int drawCounter=1;
//树偏移量数组,画图用
//private int[] offset_x_arr = new int[]{60,30,25,20,20,20,10,10};
private int[] offset_x_arr = new int[]{120,80,30,30,20,20,10,10};
/**
* 每插入一个结点,就画一次图
* @param key
*/
private void drawStep(int key){
drawTree.drawEntrance(variableRoot, CommonUtil.getResourceRoot()+"tree/avl/avlinsert_"+drawCounter+"_"+key+".png",false,offset_x_arr);
drawCounter++;
}
/**
* 平衡二叉树插入结点核心算法
* @param avlNode 当前结点
* @param key 要插入的关键字
* @param ancestorChain 祖先信息链
*/
private void insert(AVLNode avlNode,int key,List<Ancestor> ancestorChain){
if(key < avlNode.getVal()){
//新增一个祖先信息
ancestorChain.add(new Ancestor(avlNode,true));
//左孩子为null,则执行插入
if(avlNode.getLeft() == null){
AVLNode keyNode = new AVLNode(key);
avlNodes.add(keyNode);
avlNode.setLeft(keyNode);
//平衡算法
calculateBFAndRotate(ancestorChain);
//平衡后,画图
drawStep(key);
return;
}else{
//递归搜索
insert(avlNode.getLeft(),key,ancestorChain);
}
}
if(key > avlNode.getVal()){
//新增一个祖先信息
ancestorChain.add(new Ancestor(avlNode,false));
//右孩子为null,则执行插入
if(avlNode.getRight() == null){
AVLNode keyNode = new AVLNode(key);
avlNodes.add(keyNode);
avlNode.setRight(keyNode);
//平衡算法
calculateBFAndRotate(ancestorChain);
//平衡后,画图
drawStep(key);
return;
}else{
//递归搜索
insert(avlNode.getRight(),key,ancestorChain);
}
}
}
/**
* 计算平衡因子,如果有必要的话,还要旋转
* @param ancestorChain 祖先链
*/
private void calculateBFAndRotate(List<Ancestor> ancestorChain){
//ancestorChain持有的都是新插入的那个导致树不平衡的结点的祖先
// 祖先的顺序是:index为0时,为距离最远的祖先,index为size-1时,为距离最近的祖先
//所以,如果我们要找出最小不平衡子树,则需要从最近的祖先开始判断
for (int i = ancestorChain.size()-1;i >= 0;i--){
//当前祖先
AVLNode ancestorNode = ancestorChain.get(i).getAncestor();
boolean leftOfAncestor = ancestorChain.get(i).isLeft();
//分别计算当前祖先的左右子树深度
int leftDepth = searchDepth(ancestorNode.getLeft(),1);
int rightDepth = searchDepth(ancestorNode.getRight(),1);
//计算当前祖先的平衡因子
int bf = leftDepth-rightDepth;
//如果bf绝对值大于1,则表示树不平衡,需要进行相应的处理;否则,不做任何事情
if(Math.abs(bf) > 1){
//先判断当前祖先的子节点 与 当前祖先 的BF符号是否一致
AVLNode child = leftOfAncestor?ancestorNode.getLeft():ancestorNode.getRight();
int childLeftDepth = searchDepth(child.getLeft(),1);
int childRightDepth = searchDepth(child.getRight(),1);
int childBf = childLeftDepth-childRightDepth;
//符号不一致,以子结点为根结点进行旋转
if(childBf > 0 && bf < 0){
//右旋,旋转一个单位即可,应该没有特殊情况
rightRotate(ancestorNode,child,leftOfAncestor);
}else if(childBf < 0 && bf > 0){
//左旋
leftRotate(ancestorNode,child,leftOfAncestor);
}
//符号统一之后,再旋转当前结点
if(bf > 0){
// 右旋
if(i == 0){
//根结点的旋转特殊处理
AVLNode rootLeftRight = ancestorNode.getLeft().getRight();
AVLNode rootLeft = ancestorNode.getLeft();
rootLeft.setRight(ancestorNode);
ancestorNode.setLeft(rootLeftRight);
//更新可变根结点
variableRoot = rootLeft;
}else{
//非根结点处理,将当前祖先的父节点,当前祖先,当前祖先与其父节点的关系传给rightRotate方法
rightRotate(ancestorChain.get(i-1).getAncestor(),ancestorNode,ancestorChain.get(i-1).isLeft());
}
}else if(bf < 0){
// 左旋
if(i == 0){
//根结点的旋转特殊处理
AVLNode rootRightLeft = ancestorNode.getRight().getLeft();
AVLNode rootRight = ancestorNode.getRight();
rootRight.setLeft(ancestorNode);
ancestorNode.setRight(rootRightLeft);
//更新可变根结点
variableRoot = rootRight;
}else{
//非根结点处理,将当前祖先的父节点,当前祖先,当前祖先与其父节点的关系传给rightRotate方法
leftRotate(ancestorChain.get(i-1).getAncestor(),ancestorNode,ancestorChain.get(i-1).isLeft());
}
}
}
}
}
//左旋时,防止右节点的左孩子不为空
private void leftRotate(AVLNode parent,AVLNode node,boolean isLeft){
//由于是左旋,为了避免不满足二叉查找树特性,所以要先判断node的右孩子的左孩子是否为null
AVLNode nodeRightLeft = node.getRight().getLeft();
if(isLeft){
parent.setLeft(node.getRight());
parent.getLeft().setLeft(node);
node.setRight(nodeRightLeft);
}else{
parent.setRight(node.getRight());
parent.getRight().setLeft(node);
node.setRight(nodeRightLeft);
}
}
//右旋时,防止左节点的右孩子不为空
private void rightRotate(AVLNode parent,AVLNode node,boolean isLeft){
//由于是右旋,为了避免不满足二叉查找树特性,所以要先判断node的左孩子的右孩子是否为null
AVLNode nodeLeftRight = node.getLeft().getRight();
if(isLeft){
parent.setLeft(node.getLeft());
parent.getLeft().setRight(node);
node.setLeft(nodeLeftRight);
}else{
parent.setRight(node.getLeft());
parent.getRight().setRight(node);
node.setLeft(nodeLeftRight);
}
}
//查找树的深度
private int searchDepth(AVLNode avlNode, int depth){
if(avlNode == null){
return 0;
}
if(avlNode.getLeft() == null && avlNode.getRight() == null){
return depth;
}else if(avlNode.getLeft() == null){
return searchDepth(avlNode.getRight(),depth+1);
}else if(avlNode.getRight() == null){
return searchDepth(avlNode.getLeft(),depth+1);
}else{
int a = searchDepth(avlNode.getLeft(),depth+1);
int b = searchDepth(avlNode.getRight(),depth+1);
return a>b?a:b;
}
}
/**
* 平衡二叉树结点插入入口
* @param root 根结点
* @param keys 要插入的关键字数组
*/
public void insertEntrance(AVLNode root,int[] keys){
if(null == root){
root = new AVLNode(keys[0]);
variableRoot = root;
this.avlNodes.add(root);
for (int i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
List<Ancestor> parentPoints = new ArrayList<>();
insert(variableRoot,keys[i],parentPoints);
}
}else{
variableRoot = root;
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
List<Ancestor> parentPoints = new ArrayList<>();
insert(variableRoot,keys[i],parentPoints);
}
}
}
}AVLMain
public class AVLMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLInsert avlInsert = new AVLInsert();
avlInsert.insertEntrance(null,new int[]{3,2,1,4,5,6,7,10,9,8});
}
}平衡二叉树应该还挺重要的,它的算法有一定难度,不过掌握了思想之后,代码写起来就很快了。
今天就讲到这里了,明天的文章将开启新的知识。不过还是树。
以上是关于下次再让你讲平衡二叉树,可别说不会了的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章