iOS进程间通信
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS进程间通信相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 线程间通信 :通过performSelector系列的方法 可以实现 各种线程间的通信(通信 :调用与传参)进程间通信:从一个App跳到另外一个App如从打地鼠练习跳转到卖票
卖票
首先添加一行info的myapp标示,这个标示表示当别个App要调用它时,要用到的表示
AppDelegate.m
打地鼠
练习图片爬虫
ViewController.m
高级IO中socketpair实现进程间通信以及重定向
sockpair实现进程间通信
我们以前学习的利用管道(此处为匿名管道)实现进程间通信,只能是单向的,一边只能读而另一边只能写,且只能在有血缘关系的进程间才能通信,若想实现双向通信就必须创建双向管道,而sockpair它的实现就是双向管道进行通信。它可以用来创建双向通信管道
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<string.h>
4 #include<sys/types.h>
5 #include<sys/socket.h>
6 #include<stdlib.h>
7 #include<errno.h>
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 int sv[2]={0,0};
12 char buf[1024];
13 int sock_pair=socketpair(AF_LOCAL,SOCK_STREAM,0,sv);
14 if(sock_pair < 0)
15 {
16 perror("socketpair");
17 exit(1);
18 }
19 pid_t id=fork();
20 if(id<0)
21 {
22 perror("fork");
23 return -1;24 }else if(id==0){ //child
25 close(sv[0]);
26 while(1)
27 {
28 memset(buf,‘\0‘,sizeof(buf));
29 strcpy(buf,"I‘m child");
30 write(sv[1],buf,strlen(buf));
31 ssize_t _size=read(sv[1],buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
32 if(_size<0)
33 {
34 perror("read");
35 return -2;
36 }else if(_size > 0)
37 {
38 buf[_size]=‘\0‘;
39 printf("father->child:%s\n",buf);
40 }
41 sleep(1);
42 }
43 close(sv[1]);
44
45 }else
46 {
47 close(sv[1]);
48 while(1)
49 {
50 ssize_t _size=read(sv[0],buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
51 if(_size<0)
52 {
53 perror("read");
54 exit(2);
55 }else if(_size >0)
56 {
57 buf[_size]=‘\0‘;
58 printf("child->father:%s\n",buf);
59 }
60 // memset(buf,‘\0‘,sizeof(buf));
61 strcpy(buf,"I‘m father");
62 write(sv[0],buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
63 }
64 close(sv[0]);
65 }
66 return 0;
67 }
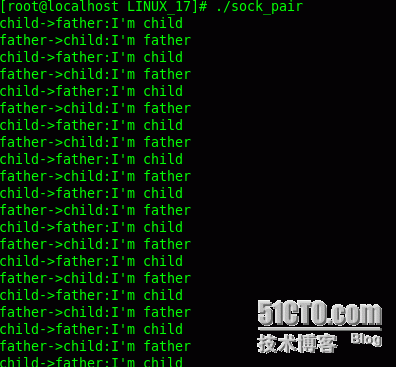
程序运行结果:
重定向:对文件描述符进行重定向
例:将一个文件中的内容打印到标准输出上,若关闭了标准输出文件描述符,此时再打开一个文件,文件描述符将为1,而此时第一个文件的内容将会被打印到文件中(即重定向)
若新创建一个进程文件描述符会从3(若0、1、2都不关)开始?
当打开一个终端时,该过程即为创建一个会话的过程,会有一个控制进程bash,也就是会话首进程,关联terminal终端后会默认填上标准输入、标准输出以及标准错误,因此在当下创建的进程都为子进程,又因子进程在创建时会继承父进程的文件描述符,因此创建一个进程后文件描述符会从3开始。
使用dup重定向:函数原型 int dup(int oldfd)
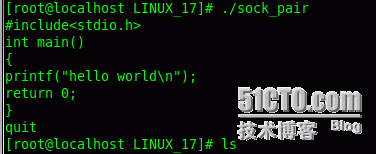
例:关闭1号文件描述符(标准输出),本应将标准输入的内容打印到标准输出上,重定向到了log文件中
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4 #include<fcntl.h>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<errno.h>
7 #include<sys/stat.h>
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 int fd=open("./log",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644);
12 if(fd<0)
13 {
14 perror("open");
15 exit(1);
16 }
17 close(1); //必须关闭要重定向的文件描述符
18 int newfd=dup(fd);
19 if(newfd <0)
20 {
21 perror("dup");
22 exit(2);
23 }24 char buf[1024];
25
26 while(1)
27 {
28 memset(buf,‘\0‘,sizeof(buf));
29 fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
30 if((strncmp("quit",buf,4))==0)
31 {
32 break;
33 }
34 printf("%s\n",buf);
35 //printf("hello world\n");
36 fflush(stdout);
37 }
38 close(newfd);
39
40 return 0;
41 }
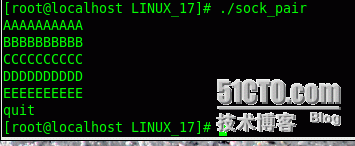
输入内容:
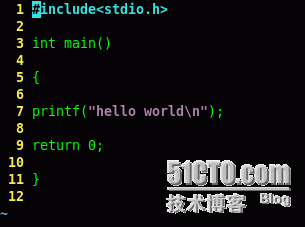
重定向到log文件中内容
int dup2(int oldfd,int newfd)
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4 #include<fcntl.h>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<errno.h>
7 #include<sys/stat.h>
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 int fd=open("./log",O_CREAT|O_RDWR,0644);
12 if(fd<0)
13 {
14 perror("open");
15 exit(1);
16 }
17 close(1); //可以不必关闭1号文件描述符
18 int newfd=dup2(fd,1);
19 if(newfd <0)
20 {
21 perror("dup");
22 exit(2);
23 }24 char buf[1024];
25 while(1)
26 {
27 memset(buf,‘\0‘,sizeof(buf));
28 fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
29 if((strncmp("quit",buf,4))==0)
30 {
31 break;
32 }
33 printf("%s",buf);
34 //printf("hello world\n");
35 fflush(stdout);
36 }
37 close(newfd);
38
39 return 0;
40 }
41
输入内容:
log文件中内容:
以上是关于iOS进程间通信的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章