Java中Math方法举例
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java中Math方法举例相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我已经知道了
Math.sqrt是开平方根
Math.random()是生成0-1之间的随机数
那么请高手帮我列举一下常用的Math方法
最好可以告知一下作用是什么 谢谢啦
就需要知道 Math什么方法 可以表示指数、对数、三角函数等 并且 语句代码是什么
与 StrictMath 类的某些数值方法不同,并不是 Math 类的所有等效函数的实现都定义为返回逐位相同的结果。这一宽限允许在不要求严格可重复性的地方实现更好的性能。
默认情况下,很多 Math 方法仅调用 StrictMath 中的等效方法来完成它们的实现。代码生成器鼓励使用特定于平台的本机库或者在可用的地方使用微处理器指令,来提供对 Math 方法的更高性能的实现。这种更高性能的实现仍然必须遵守 Math 的规范。
实现规范的质量涉及到两种属性,即返回结果的准确性和方法的单调性。浮点 Math 方法的准确性根据 ulp(units in the last place,最后一位的进退位)来衡量。对于一个给定的浮点格式,特定实数值的 ulp 是将该数值括起来的两个浮点值的差。讨论方法的准确性是从整体上考虑的,而不是针对具体的参数,引用的 ulp 数是为了考虑参数的最差情况的误差。如果一个方法的误差总是小于 0.5 ulp,则该方法始终返回最接近准确结果的浮点数;这种方法就是正确舍入。一种正确舍入的方法通常能得到最佳的浮点近似值,然而,对于很多浮点方法来说,进行正确的舍入有些不切实际。相反,对于 Math 类来说,有些方法允许误差在 1 或 2 ulp 的范围内。在非正式情况下,对于 1 ulp 的误差范围,当准确结果是可表示的数值时,应该按照计算结果返回准确结果;否则,返回将准确结果括起来的两个浮点值。对于值很大的准确结果,括号的一端可以是无穷大。除了个别参数的准确性之外,维护不同参数的方法之间的正确关系也很重要。因此,大多数误差大于 0.5 ulp 的方法都要求是半单调的:只要数学函数是非递减的,浮点近似值就是非递减的;同样地,只要数学函数是非递增的,浮点近似值就是非递增的。不是所有准确性为 1 ulp 的近似值都能自动满足单调性要求。
方法摘要
static double abs(double a)
返回 double 值的绝对值。
static float abs(float a)
返回 float 值的绝对值。
static int abs(int a)
返回 int 值的绝对值。
static long abs(long a)
返回 long 值的绝对值。
static double acos(double a)
返回角的反余弦,范围在 0.0 到 pi 之间。
static double asin(double a)
返回角的反正弦,范围在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 之间。
static double atan(double a)
返回角的反正切,范围在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 之间。
static double atan2(double y, double x)
将矩形坐标 (x, y) 转换成极坐标 (r, theta)。
static double cbrt(double a)
返回 double 值的立方根。
static double ceil(double a)
返回最小的(最接近负无穷大)double 值,该值大于或等于参数,并且等于某个整数。
static double cos(double a)
返回角的三角余弦。
static double cosh(double x)
返回 double 值的双曲线余弦。
static double exp(double a)
返回欧拉数 e 的 double 次幂的值。
static double expm1(double x)
返回 ex -1。
static double floor(double a)
返回最大的(最接近正无穷大)double 值,该值小于或等于参数,并且等于某个整数。
static double hypot(double x, double y)
返回 sqrt(x2 +y2),没有中间溢出或下溢。
static double IEEEremainder(double f1, double f2)
按照 IEEE 754 标准的规定,对两个参数进行余数运算。
static double log(double a)
返回(底数是 e)double 值的自然对数。
static double log10(double a)
返回 double 值的底数为 10 的对数。
static double log1p(double x)
返回参数与 1 的和的自然对数。
static double max(double a, double b)
返回两个 double 值中较大的一个。
static float max(float a, float b)
返回两个 float 值中较大的一个。
static int max(int a, int b)
返回两个 int 值中较大的一个。
static long max(long a, long b)
返回两个 long 值中较大的一个。
static double min(double a, double b)
返回两个 double 值中较小的一个。
static float min(float a, float b)
返回两个 float 值中较小的一个。
static int min(int a, int b)
返回两个 int 值中较小的一个。
static long min(long a, long b)
返回两个 long 值中较小的一个。
static double pow(double a, double b)
返回第一个参数的第二个参数次幂的值。
static double random()
返回带正号的 double 值,大于或等于 0.0,小于 1.0。
static double rint(double a)
返回其值最接近参数并且是整数的 double 值。
static long round(double a)
返回最接近参数的 long。
static int round(float a)
返回最接近参数的 int。
static double signum(double d)
返回参数的符号函数;如果参数是零,则返回零;如果参数大于零,则返回 1.0;如果参数小于零,则返回 -1.0。
static float signum(float f)
返回参数的符号函数;如果参数是零,则返回零;如果参数大于零,则返回 1.0;如果参数小于零,则返回 -1.0。
static double sin(double a)
返回角的三角正弦。
static double sinh(double x)
返回 double 值的双曲线正弦。
static double sqrt(double a)
返回正确舍入的 double 值的正平方根。
static double tan(double a)
返回角的三角正切。
static double tanh(double x)
返回 double 值的双曲线余弦。
static double toDegrees(double angrad)
将用弧度测量的角转换为近似相等的用度数测量的角。
static double toRadians(double angdeg)
将用度数测量的角转换为近似相等的用弧度测量的角。
static double ulp(double d)
返回参数的 ulp 大小。
static float ulp(float f)
返回参数的 ulp 大小。 参考技术A 可以直接通过Math.方法的形式执行以下方法:
static double log(double a) :返回(底数是 e)double 值的自然对数。
static double log10(double a) :返回 double 值的底数为 10 的对数。
static double log1p(double x) :返回参数与 1 的和的自然对数。
static double max(double a, double b) :返回两个 double 值中较大的一个。
static float max(float a, float b) :返回两个 float 值中较大的一个。
static double abs(double a) :返回 double 值的绝对值。
static float abs(float a) :返回 float 值的绝对值。
static int abs(int a) :返回 int 值的绝对值。
static long abs(long a) :返回 long 值的绝对值。
static double acos(double a) :返回角的反余弦,范围在 0.0 到 pi 之间。
static double asin(double a) :返回角的反正弦,范围在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 之间。
static double atan(double a) :返回角的反正切,范围在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 之间。
static double atan2(double y, double x) :将矩形坐标 (x, y) 转换成极坐标 (r, theta)。
static double cbrt(double a) : 返回 double 值的立方根。
static double ceil(double a) :返回最小的(最接近负无穷大)double 值,该值大于或等于参数,并且等于某个整数。
static double cos(double a) : 返回角的三角余弦。
static double cosh(double x) :返回 double 值的双曲线余弦。
static double exp(double a) : 返回欧拉数 e 的 double 次幂的值。
static double floor(double a) :返回最大的(最接近正无穷大)double 值,该值小于或等于参数,并且等于某个整数。
static double hypot(double x, double y) :返回 sqrt(x2 +y2),没有中间溢出或下溢。 参考技术B sin
public static double sin(double a)Returns the trigonometric sine of an angle. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN or an infinity, then the result is NaN.
If the argument is zero, then the result is a zero with the same sign as the argument.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - an angle, in radians.
Returns:
the sine of the argument.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
cos
public static double cos(double a)Returns the trigonometric cosine of an angle. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN or an infinity, then the result is NaN.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - an angle, in radians.
Returns:
the cosine of the argument.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tan
public static double tan(double a)Returns the trigonometric tangent of an angle. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN or an infinity, then the result is NaN.
If the argument is zero, then the result is a zero with the same sign as the argument.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - an angle, in radians.
Returns:
the tangent of the argument.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
asin
public static double asin(double a)Returns the arc sine of an angle, in the range of -pi/2 through pi/2. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN or its absolute value is greater than 1, then the result is NaN.
If the argument is zero, then the result is a zero with the same sign as the argument.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - the value whose arc sine is to be returned.
Returns:
the arc sine of the argument.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
acos
public static double acos(double a)Returns the arc cosine of an angle, in the range of 0.0 through pi. Special case:
If the argument is NaN or its absolute value is greater than 1, then the result is NaN.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - the value whose arc cosine is to be returned.
Returns:
the arc cosine of the argument.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
atan
public static double atan(double a)Returns the arc tangent of an angle, in the range of -pi/2 through pi/2. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN, then the result is NaN.
If the argument is zero, then the result is a zero with the same sign as the argument.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - the value whose arc tangent is to be returned.
Returns:
the arc tangent of the argument.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
toRadians
public static double toRadians(double angdeg)Converts an angle measured in degrees to an approximately equivalent angle measured in radians. The conversion from degrees to radians is generally inexact.
Parameters:
angdeg - an angle, in degrees
Returns:
the measurement of the angle angdeg in radians.
Since:
1.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
toDegrees
public static double toDegrees(double angrad)Converts an angle measured in radians to an approximately equivalent angle measured in degrees. The conversion from radians to degrees is generally inexact; users should not expect cos(toRadians(90.0)) to exactly equal 0.0.
Parameters:
angrad - an angle, in radians
Returns:
the measurement of the angle angrad in degrees.
Since:
1.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
exp
public static double exp(double a)Returns Euler's number e raised to the power of a double value. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN, the result is NaN.
If the argument is positive infinity, then the result is positive infinity.
If the argument is negative infinity, then the result is positive zero.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - the exponent to raise e to.
Returns:
the value ea, where e is the base of the natural logarithms.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
log
public static double log(double a)Returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a double value. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN or less than zero, then the result is NaN.
If the argument is positive infinity, then the result is positive infinity.
If the argument is positive zero or negative zero, then the result is negative infinity.
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - a number greater than 0.0.
Returns:
the value ln a, the natural logarithm of a.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sqrt
public static double sqrt(double a)Returns the correctly rounded positive square root of a double value. Special cases:
If the argument is NaN or less than zero, then the result is NaN.
If the argument is positive infinity, then the result is positive infinity.
If the argument is positive zero or negative zero, then the result is the same as the argument.
Otherwise, the result is the double value closest to the true mathematical square root of the argument value.
Parameters:
a - a value.
Returns:
the positive square root of a. If the argument is NaN or less than zero, the result is NaN.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IEEEremainder
public static double IEEEremainder(double f1,
double f2)Computes the remainder operation on two arguments as prescribed by the IEEE 754 standard. The remainder value is mathematically equal to f1 - f2 × n, where n is the mathematical integer closest to the exact mathematical value of the quotient f1/f2, and if two mathematical integers are equally close to f1/f2, then n is the integer that is even. If the remainder is zero, its sign is the same as the sign of the first argument. Special cases:
If either argument is NaN, or the first argument is infinite, or the second argument is positive zero or negative zero, then the result is NaN.
If the first argument is finite and the second argument is infinite, then the result is the same as the first argument.
Parameters:
f1 - the dividend.
f2 - the divisor.
Returns:
the remainder when f1 is divided by f2.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ceil
public static double ceil(double a)Returns the smallest (closest to negative infinity) double value that is not less than the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. Special cases:
If the argument value is already equal to a mathematical integer, then the result is the same as the argument.
If the argument is NaN or an infinity or positive zero or negative zero, then the result is the same as the argument.
If the argument value is less than zero but greater than -1.0, then the result is negative zero.
Note that the value of Math.ceil(x) is exactly the value of -Math.floor(-x).
Parameters:
a - a value.
Returns:
the smallest (closest to negative infinity) floating-point value that is not less than the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
floor
public static double floor(double a)Returns the largest (closest to positive infinity) double value that is not greater than the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. Special cases:
If the argument value is already equal to a mathematical integer, then the result is the same as the argument.
If the argument is NaN or an infinity or positive zero or negative zero, then the result is the same as the argument.
Parameters:
a - a value.
Returns:
the largest (closest to positive infinity) floating-point value that is not greater than the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
rint
public static double rint(double a)Returns the double value that is closest in value to the argument and is equal to a mathematical integer. If two double values that are mathematical integers are equally close, the result is the integer value that is even. Special cases:
If the argument value is already equal to a mathematical integer, then the result is the same as the argument.
If the argument is NaN or an infinity or positive zero or negative zero, then the result is the same as the argument.
Parameters:
a - a double value.
Returns:
the closest floating-point value to a that is equal to a mathematical integer.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
atan2
public static double atan2(double y,
double x)Converts rectangular coordinates (x, y) to polar (r, theta). This method computes the phase theta by computing an arc tangent of y/x in the range of -pi to pi. Special cases:
If either argument is NaN, then the result is NaN.
If the first argument is positive zero and the second argument is positive, or the first argument is positive and finite and the second argument is positive infinity, then the result is positive zero.
If the first argument is negative zero and the second argument is positive, or the first argument is negative and finite and the second argument is positive infinity, then the result is negative zero.
If the first argument is positive zero and the second argument is negative, or the first argument is positive and finite and the second argument is negative infinity, then the result is the double value closest to pi.
If the first argument is negative zero and the second argument is negative, or the first argument is negative and finite and the second argument is negative infinity, then the result is the double value closest to -pi.
If the first argument is positive and the second argument is positive zero or negative zero, or the first argument is positive infinity and the second argument is finite, then the result is the double value closest to pi/2.
If the first argument is negative and the second argument is positive zero or negative zero, or the first argument is negative infinity and the second argument is finite, then the result is the double value closest to -pi/2.
If both arguments are positive infinity, then the result is the double value closest to pi/4.
If the first argument is positive infinity and the second argument is negative infinity, then the result is the double value closest to 3*pi/4.
If the first argument is negative infinity and the second argument is positive infinity, then the result is the double value closest to -pi/4.
If both arguments are negative infinity, then the result is the double value closest to -3*pi/4.
A result must be within 2 ulps of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
y - the ordinate coordinate
x - the abscissa coordinate
Returns:
the theta component of the point (r, theta) in polar coordinates that corresponds to the point (x, y) in Cartesian coordinates.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pow
public static double pow(double a,
double b)Returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument. Special cases:
If the second argument is positive or negative zero, then the result is 1.0.
If the second argument is 1.0, then the result is the same as the first argument.
If the second argument is NaN, then the result is NaN.
If the first argument is NaN and the second argument is nonzero, then the result is NaN.
If
the absolute value of the first argument is greater than 1 and the second argument is positive infinity, or
the absolute value of the first argument is less than 1 and the second argument is negative infinity,
then the result is positive infinity.
If
the absolute value of the first argument is greater than 1 and the second argument is negative infinity, or
the absolute value of the first argument is less than 1 and the second argument is positive infinity,
then the result is positive zero.
If the absolute value of the first argument equals 1 and the second argument is infinite, then the result is NaN.
If
the first argument is positive zero and the second argument is greater than zero, or
the first argument is positive infinity and the second argument is less than zero,
then the result is positive zero.
If
the first argument is positive zero and the second argument is less than zero, or
the first argument is positive infinity and the second argument is greater than zero,
then the result is positive infinity.
If
the first argument is negative zero and the second argument is greater than zero but not a finite odd integer, or
the first argument is negative infinity and the second argument is less than zero but not a finite odd integer,
then the result is positive zero.
If
the first argument is negative zero and the second argument is a positive finite odd integer, or
the first argument is negative infinity and the second argument is a negative finite odd integer,
then the result is negative zero.
If
the first argument is negative zero and the second argument is less than zero but not a finite odd integer, or
the first argument is negative infinity and the second argument is greater than zero but not a finite odd integer,
then the result is positive infinity.
If
the first argument is negative zero and the second argument is a negative finite odd integer, or
the first argument is negative infinity and the second argument is a positive finite odd integer,
then the result is negative infinity.
If the first argument is finite and less than zero
if the second argument is a finite even integer, the result is equal to the result of raising the absolute value of the first argument to the power of the second argument
if the second argument is a finite odd integer, the result is equal to the negative of the result of raising the absolute value of the first argument to the power of the second argument
if the second argument is finite and not an integer, then the result is NaN.
If both arguments are integers, then the result is exactly equal to the mathematical result of raising the first argument to the power of the second argument if that result can in fact be represented exactly as a double value.
(In the foregoing descriptions, a floating-point value is considered to be an integer if and only if it is finite and a fixed point of the method ceil or, equivalently, a fixed point of the method floor. A value is a fixed point of a one-argument method if and only if the result of applying the method to the value is equal to the value.)
A result must be within 1 ulp of the correctly rounded result. Results must be semi-monotonic.
Parameters:
a - the base.
b - the exponent.
Returns:
the value ab.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
round
public static int round(float a)Returns the closest int to the argument. The result is rounded to an integer by adding 1/2, taking the floor of the result, and casting the result to type int. In other words, the result is equal to the value of the expression:
(int)Math.floor(a + 0.5f)Special cases:
If the argument is NaN, the result is 0.
If the argument is negative infinity or any value less than or equal to the value of Integer.MIN_VALUE, the result is equal to the value of Integer.MIN_VALUE.
If the argument is positive infinity or any value greater than or equal to the value of Integer.MAX_VALUE, the result is equal to the value of Integer.MAX_VALUE.
Parameters:
a - a floating-point value to be rounded to an integer.
Returns:
the value of the argument rounded to the nearest int value.
See Also:
Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE 参考技术C 分数太少了,建议你去看JDK
Java Math类(java.lang包)
Math类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法,其所有方法都是静态方法,所以使用该类中的方法时,可以直接使用类名.方法名,如: Math.round();
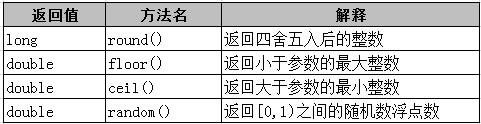

运行结果:

以上是关于Java中Math方法举例的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
在javascript中math.random()的用法问题?有没有简单一点的说明?谢谢!