基础排序算法之冒泡排序
Posted 放你一码
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基础排序算法之冒泡排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
大家好:
今天分享一下基础排序算法之冒泡排序。
1. 冒泡排序:
原理:比较两个相邻的元素,将较大的元素交换至右端。
思路:依次比较相邻的两个数,将小数放在前面,大数放在后面。即在第一趟:首先比较第1个和第2个数,将小数放前,大数放后。然后比较第2个数和第3个数,将小数放前,大数放后,如此继续,直至比较最后两个数,将小数放前,大数放后。重复第一趟步骤,直至全部排序完成。
实现:
public void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int tem = 0;
int sortBorder= array.length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
int jBorder = sortBorder - i;
for (int j = 0; j < jBorder; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
tem = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = tem;
}
}
}
System.out.println("冒泡排序,花费时间(s):" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - nowTime) / 1000.0 + "s");
}
2. 冒泡排序优化:
如果已经排序好,就不需要再排序了。
比如{2,1,3,5,4,6,8,7,9} 。
循环 倒数第二次已经是 {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},就需要再比较最后一次了。
比较第一次变为 {1,2,3,4,5,6,8,7,9},第二次从 2 开始就不需要比较那么多了,只需要最远比较到上一次交换的位置。
public void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int tem = 0;
//记录最后一次交换的位置
int lastExchangeIndex = 0;
//无序数列的边界,每次比较只需要比到这里为止
int sortBorder= array.length - 1;
boolean isSorted;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
isSorted = true;
for (int j = 0; j < sortBorder; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
tem = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = tem;
//数组无序
isSorted = false;
//把无序数列的边界更新为最后一次交换元素的位置
lastExchangeIndex = j;
}
}
sortBorder = lastExchangeIndex;
if(isSorted) break;
}
System.out.println("冒泡排序,花费时间(s):" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - nowTime) / 1000.0 + "s");
}
3. 冒泡排序升级之鸡尾酒排序:
void cocktailSort(int[] array) {
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int top = array.length - 1;
int bottom = 0;
boolean flag = true;
int i, j;
while (flag) {
flag = false;
//从小到大,升序
for (i = bottom; i < top; i++) {
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
CommonSortAlgorithmUtils.swap(array, i, i + 1);
flag = true;
}
}
top--;
//从大到小,降序
for (j = top; j > bottom; j--) {
if (array[j] < array[j - 1]) {
CommonSortAlgorithmUtils.swap(array, j, j - 1);
flag = true;
}
}
bottom++;
}
System.out.println("冒泡排序之鸡尾酒排序,花费时间(s):" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - nowTime) / 1000.0 + "s");
}
CommonSortAlgorithmUtils.java:
package algorithm;/**
* Created by on 2018/7/24
*/public class CommonSortAlgorithmUtils { //交换方法
static void swap(int[] data, int i, int j) { int tmp=data[i];
data[i]=data[j];
data[j]=tmp;
}
}
耗时对比:
10W 条随机 数据 运行如图:
可以看出优化的优势不明显。鸡尾酒排序时间明显缩短。
50W 条随机 数据 运行如图:
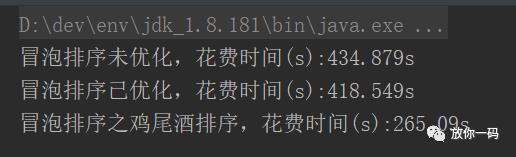
可以看出优化的稍微有优势。鸡尾酒排序时间明显缩短。
100W 条随机 数据 运行如图:
可以看出优化的稍微有优势。鸡尾酒排序时间明显缩短。
总结:
冒泡排序写法比较简单。
冒泡排序的最坏时间复杂度为:O(n2) 。
冒泡排序总的平均时间复杂度为:O(n2) 。
各种排序方法比较:
以上是关于基础排序算法之冒泡排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章