厌倦了Python训练?C++版本PyTorch尝试一下
Posted AIZOO
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了厌倦了Python训练?C++版本PyTorch尝试一下相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
PyTorch的流行给深度学习的发展带来了巨大的便利,然而工业界和嵌入式平台对于深度学习的应用还远远不够,很重要的一个原因就是Python在效率方面不能满足工业界的需求。PyTorch 1.5正式版的发布则是填补了PyTorch在这个方面的空缺。今天的一篇文章就为大家简单介绍一下如何用C++版本的PyTorch来训练。
翻译:zdi
PyTorch 1.5稳定版的一个重要更新就是增加了对于C++前端API的支持。C++API的支持对于要求低延迟,多线程,高并发的系统的很有必要。PyTroch的文档中对此有详细的说明(点击阅读原文即可查看)。本文以一个两层的神经网络为例带大家入门PyTorch的C++用法,后续还会为大家带来更多有关PyTorch的C++使用的教程。

Libtorch C++库的安装
首先介绍一下如何安装,安装其实很简单,只需要从PyTorch官方下载代码,解压编译即可。
wget https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/nightly/cpu/libtorch-shared-with-deps-latest.zipunzip libtorch-shared-with-deps-latest.zip
这里只是针对最新版本的配置,对于不同的硬件条件和深度学习环境,请大家参考https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/cpp_frontend.html查看。
下载完成之后的步骤是编译libtorch。
//build the examplemkdir buildcmake -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=/path/to/libtorch// run the examplecmake --build . --config Release
正常的输出为:
$ cmake -DCMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=~/pytorch/libtorchCMake Warning:No source or binary directory provided. Both will be assumed to be thesame as the current working directory, but note that this warning willbecome a fatal error in future CMake releases.-- The C compiler identification is GNU 7.5.0-- The CXX compiler identification is GNU 7.5.0-- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc-- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- works-- Detecting C compiler ABI info-- Detecting C compiler ABI info - done-- Detecting C compile features-- Detecting C compile features - done-- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++-- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- works-- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info-- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info - done-- Detecting CXX compile features-- Detecting CXX compile features - done-- Looking for pthread.h-- Looking for pthread.h - found-- Looking for pthread_create-- Looking for pthread_create - not found-- Looking for pthread_create in pthreads-- Looking for pthread_create in pthreads - not found-- Looking for pthread_create in pthread-- Looking for pthread_create in pthread - found-- Found Threads: TRUE-- Found Torch: /home/yasasri/pytorch/libtorch/lib/libtorch.so-- Configuring done-- Generating done-- Build files have been written to: /home/yasasri/code/PyTorchCppFrontEnd(base) yasasri@yasasri-MacBookPro:~/code/PyTorchCppFrontEnd$ cmake --build . --config ReleaseScanning dependencies of target TwoLayerNetwork[ 50%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/TwoLayerNetwork.dir/TwoLayerNetwork.cpp.o[100%] Linking CXX executable TwoLayerNetwork[100%] Built target TwoLayerNetwork

张量
PyTorch中最基础的三个模块为:张量,自动求导和网络模块。由于Python是动态语言,因此在Python中声明张量不需要指定变量类型,而C++是一门静态语言,在编码过程中指定变量类型,因此可以更快更安全的执行。因此将PyTorch的Python代码转化为C++代码的第一步就是指定变量类型。现代C++同样支持了 auto 类型的变量类型,编译器会在编译过程中自动为变量分配类型。
假设我们想要构造一个输入输出为随机值的函数
在PyTorch的Python接口中我们的写法为:
# Python
x = torch.randn(N, D_in)
y = torch.randn(N, D_out)
对应的C++写法为:
// C++torch::Tensor x = torch::rand({N, D_in});torch::Tensor y = torch::rand({N, D_out});
在这里我们用作用域运算符::取代了Python中.的用法。

两层的神经网络模型
使用Python在PyTorch中定义模型时,需要继承torch.nn.Module。子类会相应继承父类的方法和属性,在Python中定义一个两层的神经网络的代码为:
# Python
import torch
class TwoLayerNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, D_in, H, D_out):
super(TwoLayerNet, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(D_in, H)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(H, D_out)
def forward(self.x):
h_relu = self.linear1(x).clamp(min=0)
y_pred = self.linear2(h_relu)
return y_pred
C++定义神经网络的方法是使用结构体(struct),值语义(value semantics)和引用语义(reference semantics)的都可以用于创建模型。使用值语义的代码为:
// C++ value semantics
#include <torch/torch.h>
// C++ neural network model defined with value semantics
struct TwoLayerNet : torch::nn::Module {
// constructor with submodules registered in the initializer list
TwoLayerNet(int64_t D_in, int64_t D_out, int64_t H) :
linear1(register_module("linear1", torch::nn::Linear(D_in, H))),
linear2(register_module("linear2", torch::nn::Linear(H, D_out)))
{}
torch::Tensor forward(torch::Tensor x) {
x = torch::relu(linear1->forward(x));
x = linear2->forward(x);
return x;
}
torch::nn::Linear linear1;
torch::nn::Linear linear2;
};
// Usage: access the object using dot . operator
TwoLayerNet model(D_in, D_out, H);
model.to(device);
model.forward(x);
model.parameters();
子类使用register_module() 方法可以调用父类的属性和方法:
/// Registers a submodule with this `Module`.
///
/// This method deals with `ModuleHolder`s.
///
/// Registering a module makes it available to methods such as
/// `modules()`, `clone()` or `to()`.
///
///
st
/// .. code-block:: cpp
///
/// MyModule::MyModule() {
/// submodule_ = register_module("linear", torch::nn::Linear(3, 4));
/// }
/// endrst
template <typename ModuleType>
std::shared_ptr<ModuleType> register_module(
std::string name,
ModuleHolder<ModuleType> module_holder);
使用引用语义定义在C++中定义网络的方法是使用std::shared_ptr。TORCH_MODULE(TwoLayerNet)的宏定义定义了两层的网络结构。PyTorch推荐使用引用语义的方式在C++中定义模型,具体的代码为:
// C++ neural network model defined with reference semantics
struct TwoLayerNetImpl : torch::nn::Module {
// module holders are assigned in the constructor
TwoLayerNetImpl(int64_t D_in, int64_t D_out, int64_t H) :
linear1(D_in, H), linear2(H, D_out) {
register_module("linear1", linear1);
register_module("linear2", linear2);
}
... // forward() method
torch::nn::Linear linear1{nullptr}; //construct an empty holder
torch::nn::Linear linear2{nullptr}; //construct an empty holder
};
TORCH_MODULE(TwoLayerNet);
// Usage: access the object using arrow -> operator
TwoLayerNet model(D_in, D_out, H);
model->to(device);
model->forward(x);
model->parameters();

优化器
Python和C++的优化器代码类似:
# Python SGD optimizerlearning_rate = 1e-4optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, momentum=0.5)# Zero the gradients before running the backward passoptimizer.zero_grad()# Update weightsoptimizer.step()
// C++ SGD optimizer
float_t learning_rate = 1e-4;
torch::optim::SGD optimizer(
model.parameters(),
torch::optim::SGDOptions(learning_rate).momentum(0.5));
// Zero the gradients before running the backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad()
// Update the weights
optimizer.step()

结果对比
在Ubuntu 18.04的机器上,C++的效率大致是Python的两倍,下图为对比结果
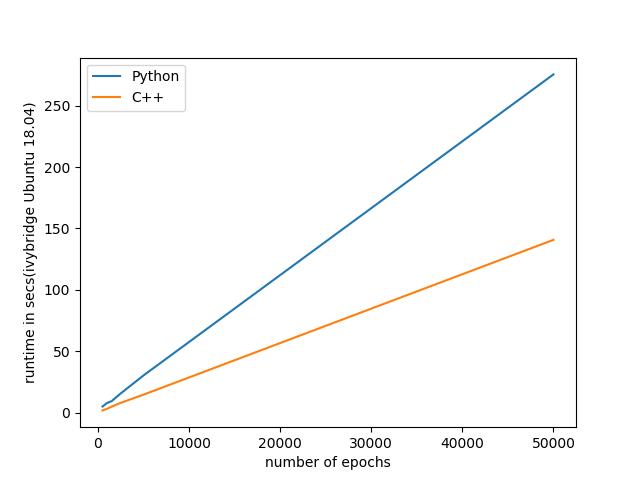
可以看到C++大致能达到两倍以上的加速效果,本文完整的代码链接为:https://github.com/venkatacrc/PyTorchCppFrontEnd。后续我们也将为大家带来更多有关于PyTorch C++用法(MNIST和DCGAN)和TensorRT的用法,敬请期待。

以上是关于厌倦了Python训练?C++版本PyTorch尝试一下的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章