一个极具意义的 Python 前端开发工具
Posted Python编程时光
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了一个极具意义的 Python 前端开发工具相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Python作为胶水语言,真的是无所不能。这不,最近又出现一个基于Python3,目标是替代javascript的前端开发工具—Brython.
好用吗?咱今天来试试用它写一个计算器有多简单:
不过,我们首先要知道它作为Python的客户端Web编程工具,和JS有什么区别呢?
1.特点
1.可轻易地在页面中内嵌Python终端进行测试
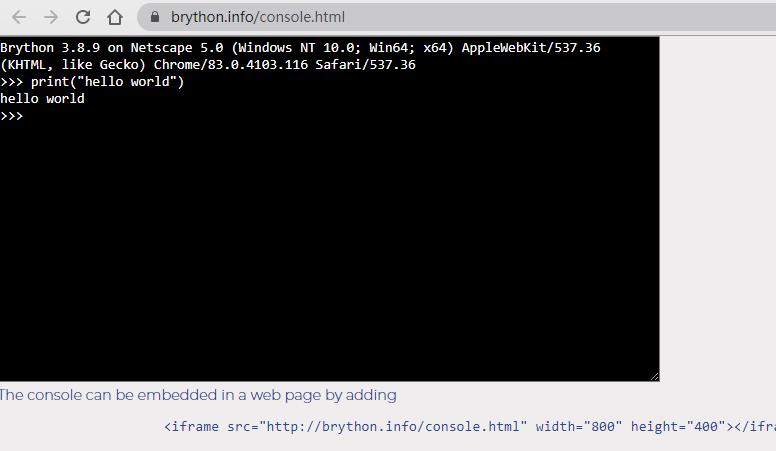
2.运行速度接近于CPyhon
3.写法方便,社区强大,可进行敏捷开发
我个人觉得相同的功能,用Python写起来可能会比JS快。
4.和JS一样,你不用安装任何东西就可以开始编写
下面就用Brython做一些简单的实验吧。
2.实验
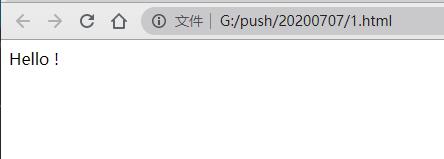
1.在页面上显示 Hello !:
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><script type="text/javascript"src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/brython@3.8.9/brython.min.js"></script></head><body onload="brython()"><script type="text/python">from browser import documentdocument <= "Hello !"</script></body></html>
将这份代码保存为index.html,双击在浏览器中打开,即可看到Hello !字样:
原理:
代码的head中,引入了一个Brython引擎附带的 brython.min.js 模块,用于使用Python控制页面。
而在<script type="text/python"> 和</script>之间就是相应的Python代码。
可以看到,需要在document中显示文本,直接输入:
document <= "你所需要显示的文本"
即可,后续你将会看到用Brython使用标准化的DOM语法和页面交互的例子。
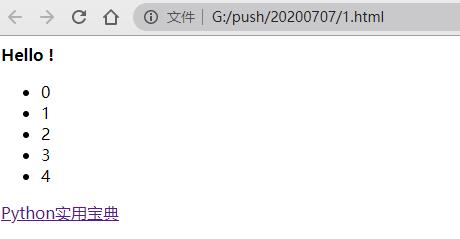
2.用HTML标签来做文本格式化:
如加粗文本:
from browser import document, htmldocument <= html.B("Hello !")
部分加粗、部分不加粗:
from browser import document, htmldocument <= html.B("Hello, ") + "world !"
i 标签:
document <= html.UL(html.LI(i) for i in range(5))超链接:
document <= html.A("Python实用宝典", href="https://pythondict.com")以上例子如下:
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><script type="text/javascript"src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/brython@3.8.9/brython.min.js"></script></head><body onload="brython()"><script type="text/python">from browser import document, htmldocument <= html.B("Hello !")document <= html.UL(html.LI(i) for i in range(5))document <= html.A("Python实用宝典", href="https://pythondict.com")</script></body></html>
效果:
3.写一个简单的计算器
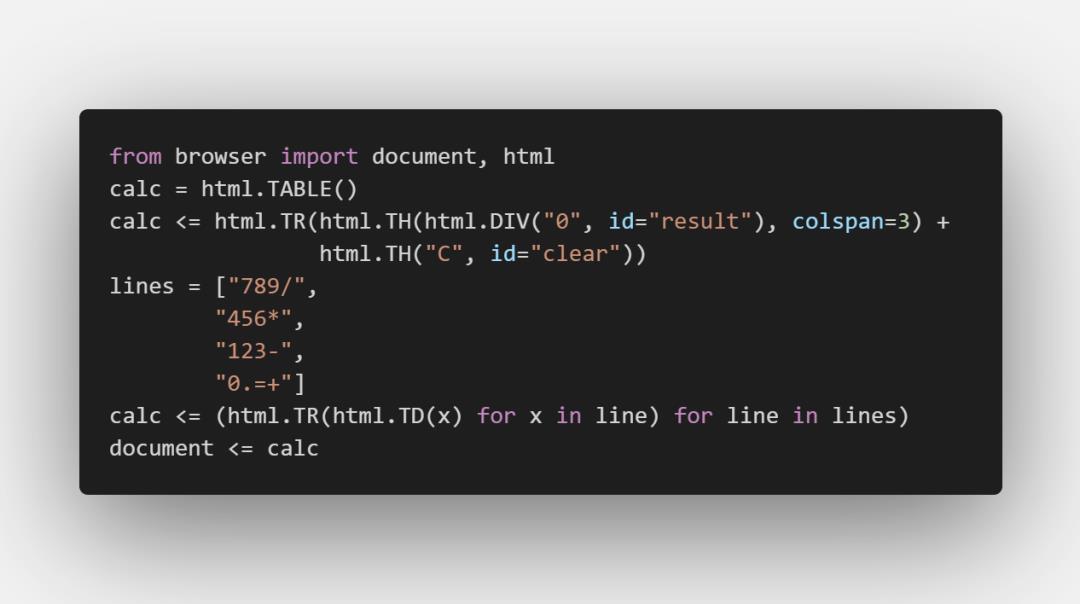
先写好简单的图形架构,用th和tr标签即可:
from browser import document, htmlcalc = html.TABLE()calc <= html.TR(html.TH(html.DIV("0", id="result"), colspan=3) +html.TH("C", id="clear"))lines = ["789/","456*","123-","0.=+"]calc <= (html.TR(html.TD(x) for x in line) for line in lines)document <= calc
图片版代码:
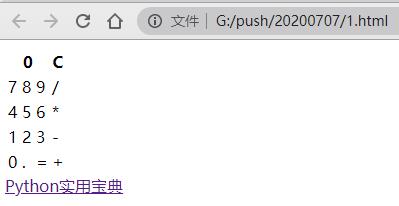
然后加上一些css就可以把这个简单的图形架构变漂亮了:
<style>*{font-family: sans-serif;font-weight: normal;font-size: 1.1em;}td{background-color: #ccc;padding: 10px 30px 10px 30px;border-radius: 0.2em;text-align: center;cursor: default;}#result{border-color: #000;border-width: 1px;border-style: solid;padding: 10px 30px 10px 30px;text-align: right;}</style>
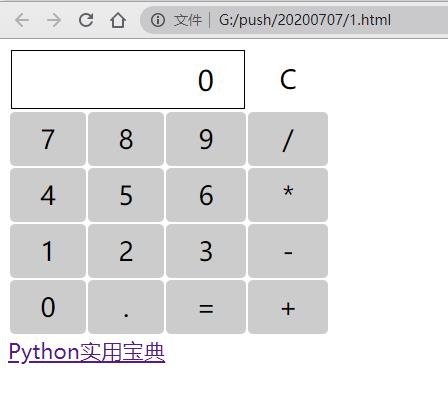
最后只需要做运算符的事件触发器即可,从下面这行代码:
calc <= (html.TR(html.TD(x) for x in line) for line in lines)可以看出,所有的按钮都被创建为td标签,因此我们要获得所有这些按钮是否被点击,仅需要:
for button in document.select("td"):button.bind("click", action)
意思是,按钮被点击后便执行 action 操作,action操作定义如下:
def action(event):"""Handles the "click" event on a button of the calculator."""# The element the user clicked on is the attribute "target" of the# event objectelement = event.target# The text printed on the button is the element's "text" attributevalue = element.textif value not in "=C":# update the result zoneif result.text in ["0", "error"]:result.text = valueelse:result.text = result.text + valueelif value == "C":# resetresult.text = "0"elif value == "=":# execute the formula in result zonetry:result.text = eval(result.text)except:result.text = "error"
图片版代码:
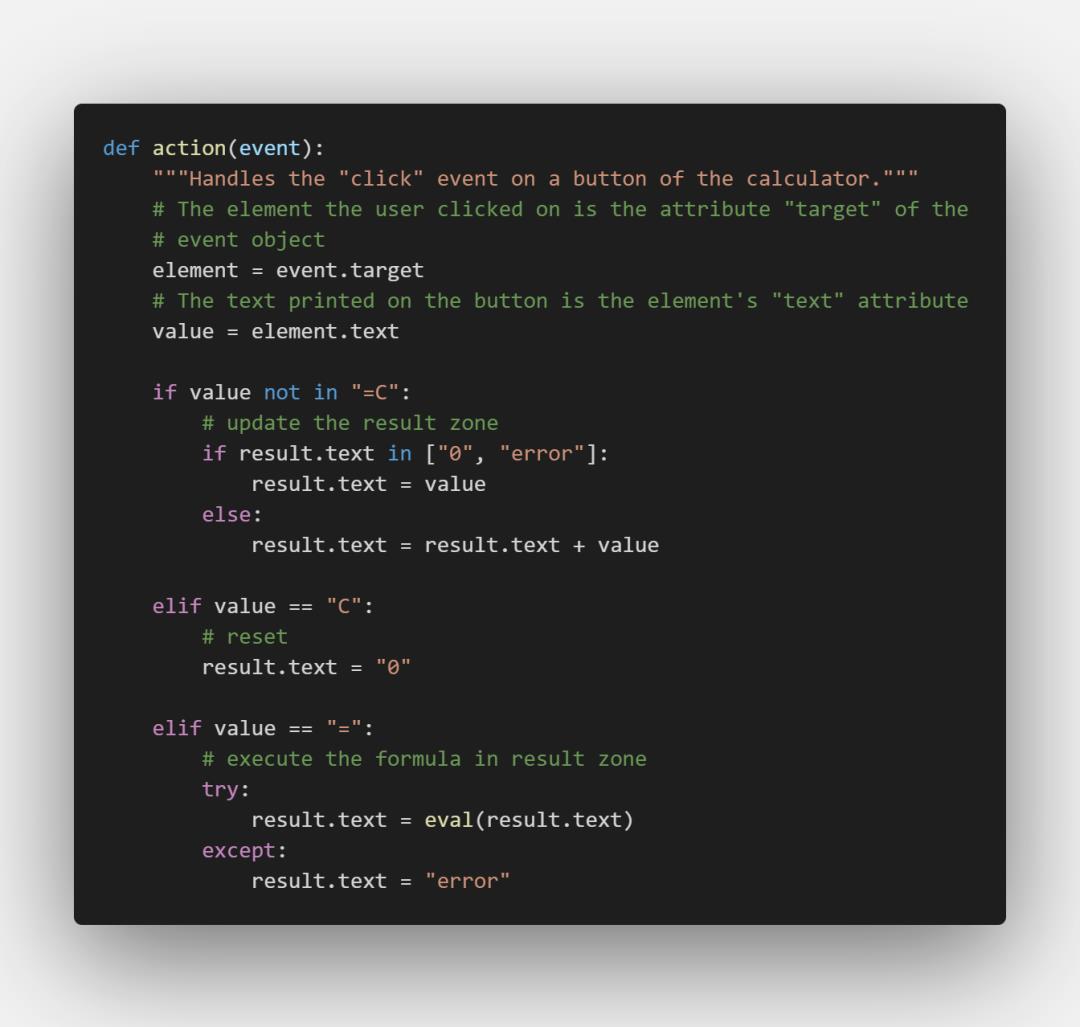
如果不是=号或C号,则进行字符串拼接。
如果是C号,则清空result。
如果是=号,则需要计算出结果,直接对字符串用eval()函数即可完成目的。
以上就是全部核心代码的讲解了。
推荐阅读
长按下图 ➡ 关注博主
(按左边关注 Python, 按右边关注 Goalng)
以上是关于一个极具意义的 Python 前端开发工具的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章