mybatis关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析
Posted 编程之艺术
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这篇是我直接用Markdown写的,这其实就是我在看源码过程中记录的一个笔记而已,所以也不会写得多详细。我觉得源码分析类的文章是最难写的,只能挑出个执行流程,还有关键部分代码。
目录
关于一级缓存关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析认识一些类及接口mybatis流程图关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析二级缓存配置详解
关于一级缓存
关于一级缓存不需要我们配置,默认就是开启的,一级缓存的作用域是一次SqlSession的生命周期,请不要与客户端发送请求的Session联系到一起,这是mybatis的SqlSession。
关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析
从源码角度分析,如何配置启用二级缓存,以及如何设置二级缓存和二级缓存的作用域为什么是全局的。
认识一些类及接口
在看源码之前,先来理解一些重要类和接口的定义
=============================================================================================
名称 意义
=============================================================================================
Configuration 管理 mysql-config.xml 全局配置关系类
=============================================================================================
SqlSessionFactory Session 管理工厂接口
=============================================================================================
Session SqlSession 是一个面向用户(程序员)的接口。SqlSession 中提 供了很多操作数据库的方法
=============================================================================================
Executor 执行器是一个接口(基本执行器、缓存执行器) 作用:SqlSession 内部通过执行器操作数据库
=============================================================================================
MappedStatement 底层封装对象,作用:对操作数据库存储封装,包括 sql 语句、输入输出参数
=============================================================================================
StatementHandler 具体操作数据库相关的 handler 接口
=============================================================================================
ResultSetHandler 具体操作数据库返回结果的 handler 接口
=============================================================================================
mybatis流程图
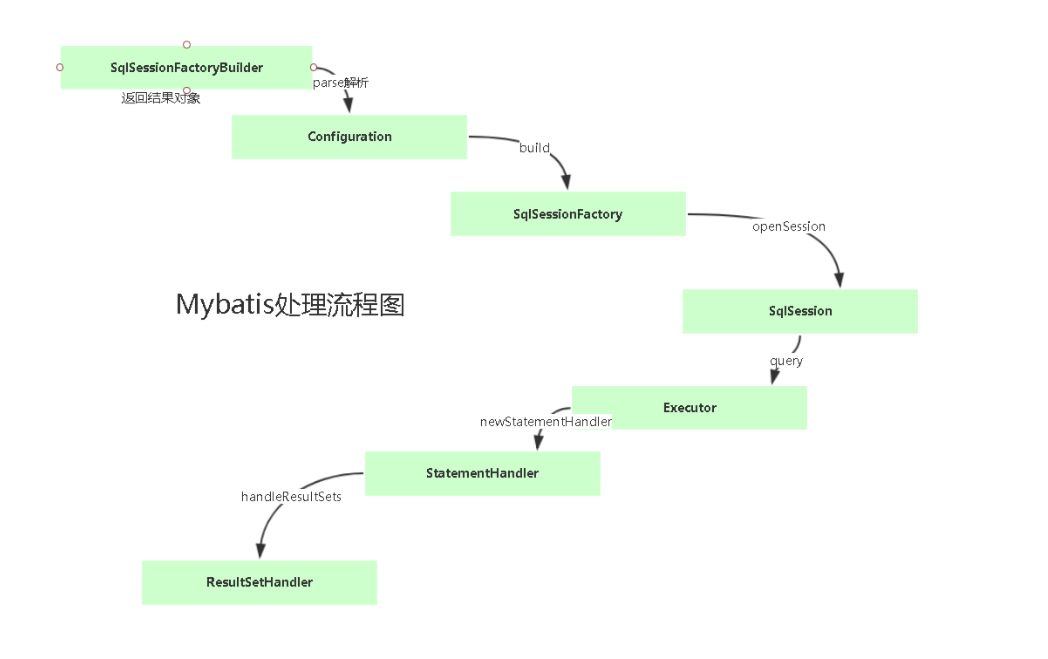
【不是我画的】
关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析
从源码中找出在哪配置开启的二级缓存
我是直接看spring整合mybatis的源码,所以多了一个创建SqlSessionFactoryBean类的步骤(换行+'>':表示方法调用流程)
SqlSessionFactoryBean:
//设置配置文件的路径
setConfigLocation(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResource("classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml"));
//获取SqlSessionFactory,FactoryBean的getObject方法
getObject()
>afterPropertiesSet()
>buildSqlSessionFactory()
>{
new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), (String)null, this.configurationProperties);
}
xml配置文件构造者,此对象负责读取和解析xml配置文件信息
XMLConfigBuilder:
//获取Configuration对象
getConfiguration()
//解析xml配置文件
parse()
//根据根节点解析
>parseConfiguration(XNode root)
>{
//获取settings节点的配置信息
Properties settings = this.settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
this.settingsElement(settings);
}
//根据从配置文件中读取到的属性配置设置是否启动二级缓存
>settingsElement(Properties props)
>{
//默认就是开启二级缓存了
this.configuration.setCacheEnabled(this.booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
}
查看二级缓存的作用域(有效范围)
SqlSessionFactoryBean:
getObject()
>afterPropertiesSet()
>buildSqlSessionFactory()方法
{
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
//this.sqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:
build(Configuration config)
>{
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
默认使用SqlSessionFactory的实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory。当调用SqlSessionFactory的openSession方法获取一个SqlSession时,其调用链如下:
DefaultSqlSessionFactory:
openSession()
>this.openSessionFromDataSource(this.configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), (TransactionIsolationLevel)null, false);
>{
Transaction tx = null;
DefaultSqlSession sqlSession;
try {
//从配置文件中获取环境
Environment environment = this.configuration.getEnvironment();
//创建事务
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = this.getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//构造执行器
Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//根据配置文件、执行器、事务是否自动提交 构造SqlSession
var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception var12) {
this.closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + var12, var12);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return sqlSession;
}
在DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSessionFromDataSource方法中调用了Configuration的newExecutor方法,所以执行器是由Configuration创建的。Configuration保存在SqlSessionFactory实例中,Configuration也是单例的。
Configuration:
>newExecutor方法:
{
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? this.defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Object executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//判断是否启用二级缓存
if (this.cacheEnabled) {
//包装一层,创建二级缓存执行器
executor = new CachingExecutor((Executor)executor);
}
//调用拦截器,责任连模式
Executor executor = (Executor)this.interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
}
二级缓存作用域分析
因为每次openSession方法调用openSessionFromDataSource方法都是创建一个新的执行器,然后再根据创建的执行器创建SqlSession的,所以缓存执行器CachingExecutor是属于这个SqlSession的,所以此SqlSession执行的查询结果只会缓存在此SqlSession的缓存执行器中,下次此SqlSession同样的sql语句同样的参数就只从这个缓存执行器获取结果?一级缓存是这样的, 但是这里CachingExecutor的作用是实现二级缓存,而二级缓存的作用域是全局的,为什么?继续看。。。
Configuration实例是单例的,而所有的MappedStatement都是保存在Configuration实例中的:
Configuration:
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements;
每次执行查询都是从Configuration实例中的mappedStatements获取MappedStatement
> 调用SqlSession实例的query方法,将MappedStatement传递进去
>SqlSession的query方法
{
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
//从MappedStatement获取Cache实例
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
this.ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
//【private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();】
// 从缓存中获取
List<E> list = (List)this.tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
//调用委托的执行器(SimpleExecutor、ReuseExecutor、BatchExecutor)的query方法
list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//写入缓存
this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
return this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
}
cache是在Mapper配置文件中注入的
MappedStatement:
private Cache cache;
Mapper文件:
<!--配置本Mapper的namespace下的二级缓存-->
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="100000" readOnly="true" size="1024"/>
注解方式是使用@CacheNamespace配置的吧?我没用过。
二级缓存配置详解
eviction:代表的是缓存回收策略,目前MyBatis提供以下策略。
LRU:最近最少使用的,移除最长时间不用的对象
FIFO:先进先出,按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除他们
SOFT:软引用,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象
WEAK:弱引用,更积极的移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。flushInterval:刷新间隔时间,单位为毫秒,如果不配置它,那么当SQL被执行的时候才会去刷新缓存。
size:引用数目,一个正整数,代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,不宜设置过大。设置过大会导致内存溢出。
readOnly:只读,意味着缓存数据只能读取而不能修改,这样设置的好处是我们可以快速读取缓存,缺点是我们没有办法修改缓存,他的默认值是false,不允许我们修改。
以上是关于mybatis关于二级缓存的配置及源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章