Jdk7中HashMap源码分析
Posted bilifuture
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Jdk7中HashMap源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
今天加班没事把hashMap源码整理下:
首先hashMap使用数组+链表的形式实现的,初始容量为16,默认扩容阈值为0.75f.
先看HashMap的成员变量,构造方法:
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
//初始容量16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
//最大容量2的30次方,而且容量必须是2的次幂
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//默认加载因子,当达到0.75的时候扩容
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//空的表,初始化的时候会赋值
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
//表的大小
transient int size;
//计数器
transient int modCount;
//加载因子
final float loadFactor;
//下次扩容的临界值,size>=threshold就会扩容
int threshold
//哈希因子,在创建表之后会初始化这个因子,目的是让生成的hash产生碰撞几率减小
transient int hashSeed = 0;
构造方法一共有4个如下:
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
HashMap内部维护了一个静态内部类,作为HashMap的元素抽象Entry<K,V>
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
}
可以看出来如果元素之间形成链表的话一定单向链表,因为Entry<K,V>中只定义了 Entry<K,V> next;指针.
整体的结构示意图应该是下面这样:
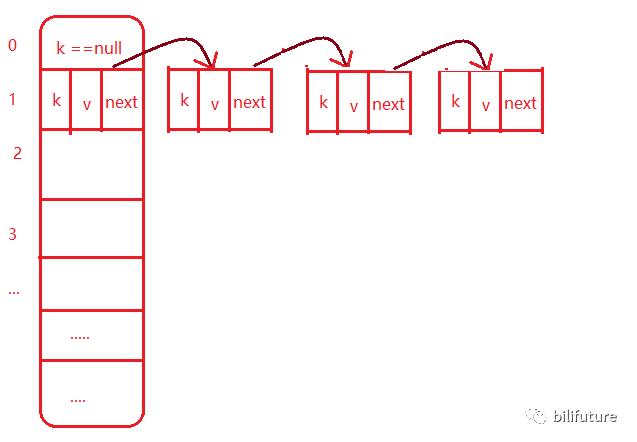
分析Map.list.set.数组这种容器类型源码,不外乎CRUD,
一 增加 put方法
里边用到的方法:
如果key是null放在数组首位也就是table[0]的位置
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
计算hash值.
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
根据hash值和数组长度进行按位于运算,得到的是一定小于数组长度
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
忘记写了,这个方法是留给子类实现的,可以扩展,我记得在linkedHashMap中实现这个方法
e.recordAccess(this);
//添加新的Entry元素
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
//就是把数据放在table[i]的位置上
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
//如果容量达到了要扩展的阈值,会调用这个方法来扩容
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
在HashMap几乎都是把全局变量赋值位方法中的局部变量来进行一系列操作完成之后再赋值回全局变量.
二. 删除
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {//如果数组大小为0,直接返回null
return null;
}
//计算key的hash值,null的话是0
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);//根据hash计算位置
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];//把当前位置元素取出来
Entry<K,V> e = prev;
while (e != null) {//table[i]位置不是0的时候进循环
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key)==key||(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {//如果当前位置的就是要删除的元素,长度减一,计数器加一,
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
//如果删除的是这个位置链表的第一个元素,把下一个补上来
table[i] = next;
else
//不是的话,把删除元素的上一个的next指向删除元素的next
prev.next = next;
e.recordRemoval(this);//留给子类扩展
return e;
}
prev = e;//如果上面的if没有成立,赋值后进下一次循环
e = next;//如果上面的if没有成立,赋值后进下一次循环
}
return e;
}
删除就是把元素从位置上移去如果没有形成链,那把null补上来.
三. 修改
修改实际调用的还是put方法,如果key相同,则会替换
四. 查询
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();//这里肯定是从table[0]去拿
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
//Key不是null的时候查询调用这个方法
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {//长度为0 返回null
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);//计算key的hash
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
//根据位置定位数组的位置,然后如果存在链,循环遍历这个链表
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;//找到之后返回
}
return null;
}
总结了一下Java中hash的定义:
Object类:
public native int hashCode();//根据jvm实现不同,
String类:
//只要String内容相容,得到的hash值肯定相容
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
Integer类:
//也就是这个包装类对应的值是多少,返回就是多少
public int hashCode() {
return value;
}
int,char...这种基础类:
不需要hashCode,作为key放入hashMap的时候会先装箱,计算的是包装类的hashCode.
以上是关于Jdk7中HashMap源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章