如何用C语言读取txt文件中的数据到结构体数组中
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何用C语言读取txt文件中的数据到结构体数组中相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
struct employee
int eid; //员工号
char name[30]; //姓名,用字符数组存放。姓名的最大长度不超过30个字符
char gender; //性别,取值Male和Female之一
int age; //年龄
double score; //综合得分
char level; //等级,不能直接输入,而是通过计算
emp[NUM];
int ReadFile(const char *filename, struct employee *emp, int len)
FILE *fp;
int i = 0;
fp = fopen("empinfo.txt", "r");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
fscanf(fp, "%d %s %c %d %f", &emp[i].eid, emp[i].name, emp[i].gender, &emp[i].age, &emp[i].score);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
//此处填入代码,实现从文件中读出员工信息
读完以后显示是0,不知道为啥,有人能帮忙解决下么?
1、在vscode里面添加了Python文件和用于读取的文本文件。

2、然后在txt文件写上一些内容用于待会的内容读取,随便写上即可。
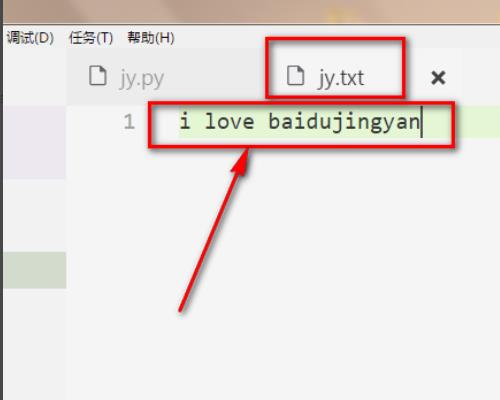
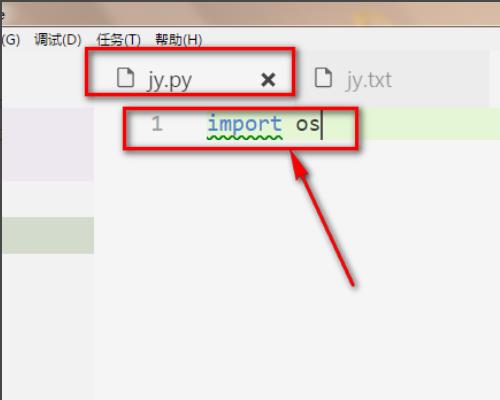
3、此外,我们还必须要导入os文件,这样才可调用os中的一些文件操作方法。
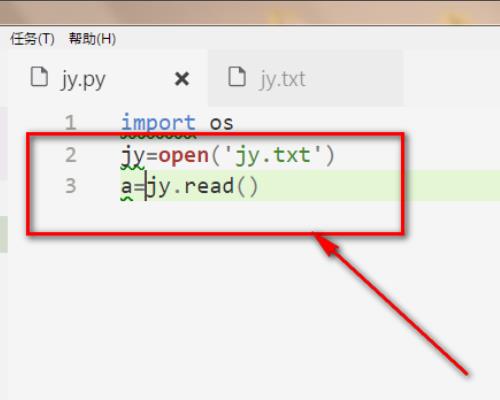
4、然后打开要进行读取内容的文件,并且把读取到的内容数据复制给了变量a。
5、然后把变量a打印即可把内容给展现出来,方便查阅了。

6、接着运行jy.py文件,这样就会开始读取,打印内容。
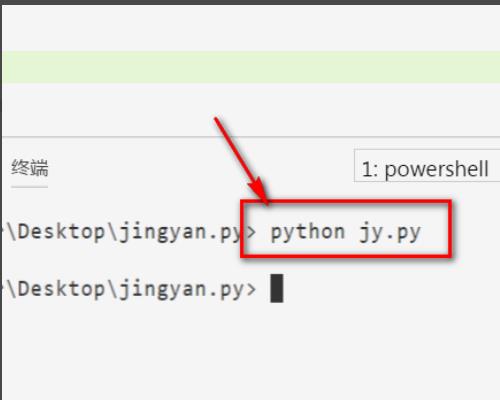
7、可以看到文件的内容真的被读取到了。
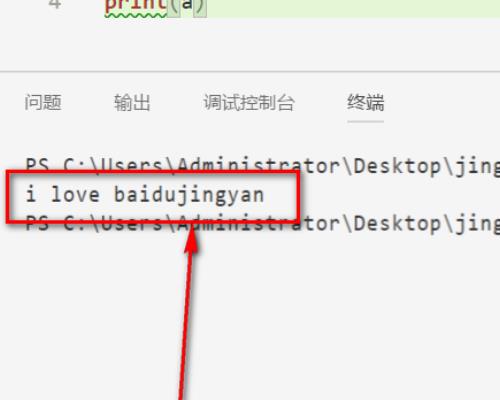
用C语言读取txt文件中的数据到结构体数组中的步骤如下:
1、使用VS新建空工程,我们直接点击确定。
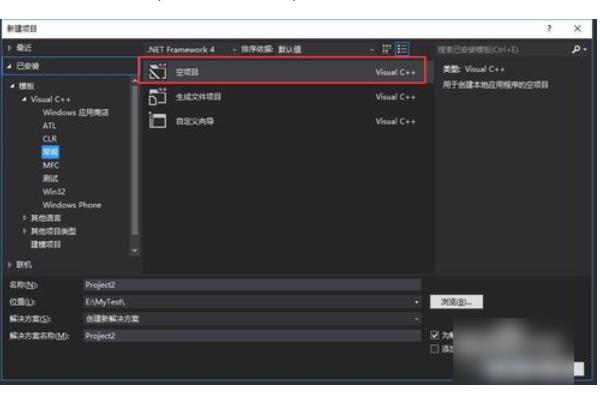
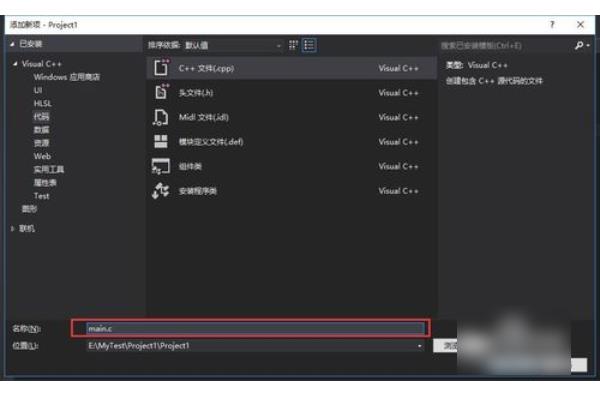
2、然后我们新建c文件,用于C语言编译器。

3、然后我们再这个界面输入main.c文件。
4、参考代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_LINE 1024
void ReadTxt(char* pFilePath)
char buf[MAX_LINE]; /*缓冲区*/
FILE *fp; /*文件指针*/
int len; /*行字符个数*/
if((fp = fopen(pFilePath,"r")) == NULL)
perror("fail to read");
exit (1) ;
while(fgets(buf,MAX_LINE,fp) != NULL)
len = strlen(buf);
buf[len-1] = '\\0'; /*去掉换行符*/
printf("%s %d \\n",buf,len - 1);
return ;
int main()
ReadTxt("D:\\\\test.txt"); //读取TXT文件函数
getchar();
return 0;
5、将上述参考代码,复制到main.c文件内,直接编译即可。
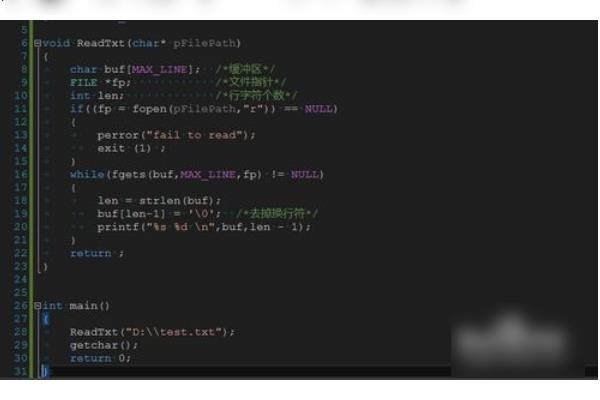
6、编译完成后,运行exe程序,执行后显示console程序。
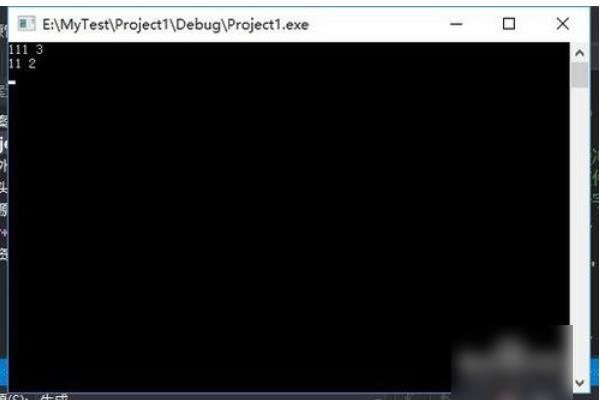
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#defineN10
typedefstruct
charwork_ID[5];
charname[20];
charphone_nu[12];
student;
intmain(intargc,char*argv[])
studentst[N];
FILE*fp;
inti;
intcount;
if(argc!=2)
fprintf(stderr,"usage:argcisnottwo\\n");
exit(1);
if((fp=fopen(argv[1],"rb"))==NULL)
fprintf(stderr,"Can'topenthe%s",argv[1]);
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
if((fscanf(fp,"%s%s%s",st[i].work_ID,st[i].name,st[i].phone_nu))!=3)
break;
count=i;
//display
printf("theturecountis%d\\n",count);
for(i=0;i<count;i++)
printf("%s\\t%s\\t%s\\n",st[i].work_ID,st[i].name,st[i].phone_nu);
return0;

扩展资料
结构体变量作为函数参数和返回值
#include<stdio.h>
structSTUcharname[10];intnum;;
voidf1(structSTUd)//值传递
structSTUa="wwu",2;
d=a;
structSTUf2(structSTUd)//值传递,但有返回值
structSTUb="wwu4",4;
d=b;
returnd;
voidf3(structSTU*d)//指针传递
structSTUc="wwu6",6;
*d=c;
intmain()
structSTUa="wwu1",1,b="wwu3",2043;
structSTUc="wwu5",5;
f1(a);b=f2(b);f3(&c);
printf("%d%d%d\\n",a.num,b.num,c.num);
system("pause");
return0;
//输出:146
参考技术C根据txt文件中数据的格式,可以用fscanf把数据读取到数组中。
下面以一种最基本的情况为例,给出参考代码。
假定结构体格式为
struct testint i;
float f;
;
文本文件约定,第一行为存储结构体总数,从第二行起,每行为一个结构体的数据。每个结构体内数据以空格分隔。
样本文件in.txt如下:
41 2.0
3 4.0
5 6.0
7 8.0
那么代码可以写作:
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
struct test *v = NULL;
int n, i;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("in.txt", "r");//打开文件
if(fp == NULL)return -1; //文件打开失败
fscanf(fp, "%d", &n); //读取结构体数据总数。
if(n <= 0)//数据总数非法
fclose(fp);
return -2;
v = (struct test*)malloc(sizeof(*v) * n); // 分配内存空间。
for(i = 0; i < n; i ++)
if(fscanf(fp, "%d%f", &v[i].i, &v[i].f) != 2) break;//读取数据。
//将读取到的数据输出。
printf("文件中预计有数据%d个,实际读到%d个\\n", n, i);
n = i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i ++)
printf("%d,%f\\n", v[i].i, v[i].f);
fclose(fp);//关闭文件
free(v);//释放内存
return 0;
在以上文本文件及程序下,运行后的结果为:
文件中预计有数据4个,实际读到4个1,2.000000
3,4.000000
5,6.000000
7,8.000000 参考技术D fscanf(fp, "%d %s %c %d %f", &emp[i].eid, emp[i].name, emp[i].gender, &emp[i].age, &emp[i].score);
该语句有两个问题
1、emp[i].gender前要加取址符&。
2、用%f读入double类型数据,应该改为%l
正确f的写法是:
fscanf(fp, "%d %s %c %d %lf", &emp[i].eid, emp[i].name, &emp[i].gender, &emp[i].age, &emp[i].score);
不行,还是0
C语言 怎么把文件中的信息储存到结构体数组中
要把这个文件中的数据保存到结构体数组中
我是这么写的
输出为什么是这个

总体写得不错,问题出在你的
fscanf和fprintf函数参数传递错误了
#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"
struct s
int id;
char name[10];
int co1;
int co2;
int co3;
int co4;
;
int main()
int i=0,count;
struct s st[10];
char fname[10],ch;
FILE *infile,*outfile;
printf("please input data file name:\\n");
scanf("%s",fname);
infile=fopen(fname,"r");
outfile=fopen("output.txt","w");
if(infile==NULL)
printf("\\nFailed to open the file");
exit(1);
fscanf(infile,"%d",&count);
while(i<count)
fscanf(infile,"%d %s %d %d %d %d\\n",&(st[i].id),st[i].name,&(st[i].co1),&(st[i].co2),&(st[i].co3),&(st[i].co4));
fprintf(outfile,"%d %s %d %d %d %d\\n",st[i].id,st[i].name,st[i].co1,st[i].co2,st[i].co3,st[i].co4);
i++;
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
首先,你的name是结构体中的字符数组,fscanf要传入的应该是存储字符的地址,所以直接是数组名name就行
第二,fprintf你要写入文件的数据,应该是真正的数据本身,不是数据的地址,所以应该将变量前的取地址符全去掉就好,
第三,注意加好换行符\\n
结果:
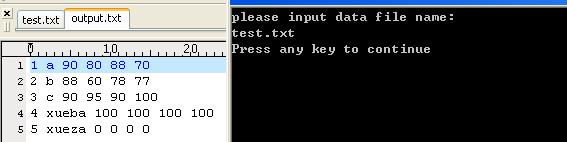
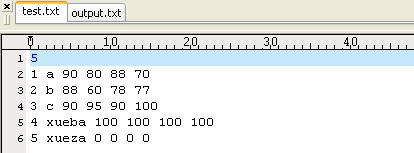
text.txt中内容就是output.txt中的内容
以上是关于如何用C语言读取txt文件中的数据到结构体数组中的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章