源码分析:JDK1.8 ConcurrentHashMap
Posted 掘客DIGGKR
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了源码分析:JDK1.8 ConcurrentHashMap相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ConcurrentHashMap是conccurrent家族中的一个类,由于它可以高效地支持并发操作,以及被广泛使用,经典的开源框架Spring的底层数据结构就是使用ConcurrentHashMap实现的。与同是线程安全的老大哥HashTable相比,它已经更胜一筹,因此它的锁更加细化,而不是像HashTable一样为几乎每个方法都添加了synchronized锁,这样的锁无疑会影响到性能。
本文的分析的源码是JDK1.8的版本,与JDK1.7的版本有很大的差异。实现线程安全的思想也已经完全变了,它摒弃了Segment(分段锁)的概念,而是启用了一种全新的方式实现,利用CAS算法。它沿用了与它同时期的HashMap版本的思想,底层依然由“数组”+链表+红黑树的方式思想,但是为了做到并发,又增加了很多辅助的类,例如TreeBin,Traverser等对象内部类。
1. 原理解析
利用 CAS + synchronized 来保证并发更新的安全,底层使用数组+链表+红黑树来实现
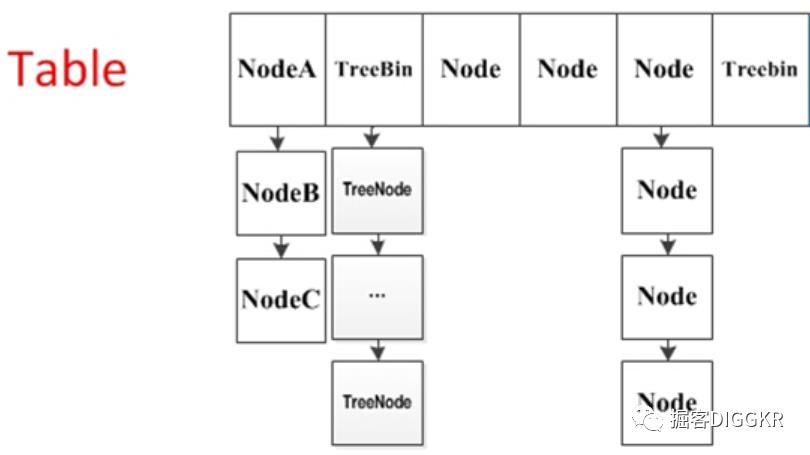
1.1. 重要成员变量
table:默认为null,初始化发生在第一次插入操作,默认大小为16的数组,用来存储Node节点数据,扩容时大小总是2的幂次方。
nextTable:默认为null,扩容时新生成的数组,其大小为原数组的两倍。
sizeCtl:默认为0,用来控制table的初始化和扩容操作,具体应用在后续会体现出来。
-1 代表table正在初始化;-N 表示有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作;其余情况:1、如果table未初始化,表示table需要初始化的大小。2、如果table初始化完成,表示table的容量,默认是table大小的0.75倍,居然用这个公式算0.75(n - (n >>> 2))。Node:保存key,value及key的hash值的数据结构,其中value和next都用volatile修饰,保证并发的可见性。
class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;volatile V val;volatile Node<K,V> next;//... 省略部分代码}
ForwardingNode:一个特殊的Node节点,hash值为-1,其中存储nextTable的引用。只有table发生扩容的时候,ForwardingNode才会发挥作用,作为一个占位符放在table中表示当前节点为null或则已经被移动。
final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {super(MOVED, null, null, null);this.nextTable = tab;}}
1.2. 实例初始化
实例化ConcurrentHashMap时倘若声明了table的容量,在初始化时会根据参数调整table大小,确保table的大小总是2的幂次方。默认的table大小为16。table的初始化操作回延缓到第一put操作再进行,并且初始化只会执行一次。
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {//如果一个线程发现sizeCtl<0,意味着另外的线程执行CAS操作成功,//当前线程只需要让出cpu时间片if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spinelse if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {try {if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];table = tab = nt;sc = n - (n >>> 2); //0.75*capacity}} finally {sizeCtl = sc;}break;}}return tab;}
1.3. put操作
1.3.1 put过程描述
假设table已经初始化完成,put操作采用CAS+synchronized实现并发插入或更新操作:
当前bucket为空时,使用CAS操作,将Node放入对应的bucket中。
出现hash冲突,则采用synchronized关键字。倘若当前hash对应的节点是链表的头节点,遍历链表,若找到对应的node节点,则修改node节点的val,否则在链表末尾添加node节点;倘若当前节点是红黑树的根节点,在树结构上遍历元素,更新或增加节点。
倘若当前map正在扩容f.hash == MOVED, 则跟其他线程一起进行扩容。
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();int hash = spread(key.hashCode());int binCount = 0;for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)tab = initTable(); // lazy Initializationelse if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { // 当前bucket为空if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))break; // no lock when adding to empty bin}else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) // 当前Map在扩容,先协助扩容,在更新值。tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);else { // hash冲突V oldVal = null;synchronized (f) {if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { // 链表头节点if (fh >= 0) {binCount = 1;for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {K ek;if (e.hash == hash && // 节点已经存在,修改链表节点的值((ek = e.key) == key ||(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {oldVal = e.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)e.val = value;break;}Node<K,V> pred = e;if ((e = e.next) == null) { // 节点不存在,添加到链表末尾pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,value, null);break;}}}else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { // 红黑树根节点Node<K,V> p;binCount = 2;if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,value)) != null) {oldVal = p.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)p.val = value;}}}}if (binCount != 0) {if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) //链表节点超过了8,链表转为红黑树treeifyBin(tab, i);if (oldVal != null)return oldVal;break;}}}addCount(1L, binCount); // 统计节点个数,检查是否需要resizereturn null;}
1.3.2 hash算法
与HashMap类似
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hashstatic final int spread(int h) {return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;}
1.3.3 定位索引
int index = (n - 1) & hash // n为bucket的个数1.3.4 获取table对应的索引元素f
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);}
采用Unsafe.getObjectVolatie()来获取,而不是直接用table[index]的原因跟ConcurrentHashMap的弱一致性有关。在java内存模型中,我们已经知道每个线程都有一个工作内存,里面存储着table的副本,虽然table是volatile修饰的,但不能保证线程每次都拿到table中的最新元素,Unsafe.getObjectVolatile可以直接获取指定内存的数据,保证了每次拿到数据都是最新的。
1.4. table 扩容
什么时候会触发扩容?
如果新增节点之后,所在的链表的元素个数大于等于8,则会调用treeifyBin把链表转换为红黑树。在转换结构时,若tab的长度小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY,默认值为64,则会将数组长度扩大到原来的两倍,并触发transfer,重新调整节点位置。(只有当tab.length >= 64, ConcurrentHashMap才会使用红黑树。)
新增节点后,addCount统计tab中的节点个数大于阈值(sizeCtl),会触发transfer,重新调整节点位置。
1.4.1 addCount
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {CounterCell[] as; long b, s;// 利用CAS更新baseCountif ((as = counterCells) != null ||!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {CounterCell a; long v; int m;boolean uncontended = true;if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||!(uncontended =U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {fullAddCount(x, uncontended); // 多线程修改baseCount时,竞争失败的线程会执行fullAddCount(x, uncontended),把x的值插入到counterCell类中return;}if (check <= 1)return;s = sumCount();}if (check >= 0) {Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {int rs = resizeStamp(n);if (sc < 0) {if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||transferIndex <= 0) // 其他线程在初始化,break;break;if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) // 其他线程正在扩容,协助扩容transfer(tab, nt);}else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))transfer(tab, null); // 仅当前线程在扩容s = sumCount();}}}
1.4.2 treeify
private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {Node<K,V> b; int n, sc;if (tab != null) {if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)//如果table.length<64 就扩大一倍 返回tryPresize(n << 1);else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {synchronized (b) {if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;//构造了一个TreeBin对象 把所有Node节点包装成TreeNode放进去for (Node<K,V> e = b; e != null; e = e.next) {TreeNode<K,V> p =new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,null, null);//这里只是利用了TreeNode封装 而没有利用TreeNode的next域和parent域if ((p.prev = tl) == null)hd = p;elsetl.next = p;tl = p;}//在原来index的位置 用TreeBin替换掉原来的Node对象setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd));}}}}}
1.4.3 transfer
当table的元素数量达到容量阈值sizeCtl,需要对table进行扩容:
构建一个nextTable,大小为table两倍。
把table的数据复制到nextTable中。
在扩容过程中,依然支持并发更新操作;也支持并发插入。
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {int n = tab.length, stride;if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide rangeif (nextTab == null) { // initiatingtry {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1]; // 构建一个nextTable,大小为table两倍nextTab = nt;} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOMEsizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return;}nextTable = nextTab;transferIndex = n;}int nextn = nextTab.length;ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);boolean advance = true;boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab//通过for自循环处理每个槽位中的链表元素,默认advace为真,通过CAS设置transferIndex属性值,并初始化i和bound值,i指当前处理的槽位序号,bound指需要处理的槽位边界,先处理槽位15的节点;for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {Node<K,V> f; int fh;while (advance) { // 遍历table中的每一个节点int nextIndex, nextBound;if (--i >= bound || finishing)advance = false;else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {i = -1;advance = false;}else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?nextIndex - stride : 0))) {bound = nextBound;i = nextIndex - 1;advance = false;}}if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {int sc;if (finishing) { // //如果所有的节点都已经完成复制工作 就把nextTable赋值给table 清空临时对象nextTablenextTable = null;table = nextTab;sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1); //扩容阈值设置为原来容量的1.5倍 依然相当于现在容量的0.75倍return;}// 利用CAS方法更新这个扩容阈值,在这里面sizectl值减一,说明新加入一个线程参与到扩容操作if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)return;finishing = advance = true;i = n; // recheck before commit}}//如果遍历到的节点为空 则放入ForwardingNode指针else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);//如果遍历到ForwardingNode节点 说明这个点已经被处理过了 直接跳过 这里是控制并发扩容的核心else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)advance = true; // already processedelse {synchronized (f) {if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {Node<K,V> ln, hn;if (fh >= 0) { // 链表节点int runBit = fh & n; // resize后的元素要么在原地,要么移动n位(n为原capacity)Node<K,V> lastRun = f;//以下的部分在完成的工作是构造两个链表 一个是原链表 另一个是原链表的反序排列for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {int b = p.hash & n;if (b != runBit) {runBit = b;lastRun = p;}}if (runBit == 0) {ln = lastRun;hn = null;}else {hn = lastRun;ln = null;}for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;if ((ph & n) == 0)ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);elsehn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);}//在nextTable的i位置上插入一个链表setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);//在nextTable的i+n的位置上插入另一个链表setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);//设置advance为true 返回到上面的while循环中 就可以执行i--操作advance = true;}//对TreeBin对象进行处理 与上面的过程类似else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;int lc = 0, hc = 0;//构造正序和反序两个链表for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {int h = e.hash;TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);if ((h & n) == 0) {if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)lo = p;elseloTail.next = p;loTail = p;++lc;}else {if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)hi = p;elsehiTail.next = p;hiTail = p;++hc;}}// (1)如果lo链表的元素个数小于等于UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD,默认为6,则通过untreeify方法把树节点链表转化成普通节点链表;//(2)否则判断hi链表中的元素个数是否等于0:如果等于0,表示lo链表中包含了所有原始节点,//则设置原始红黑树给ln,否则根据lo链表重新构造红黑树。ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);setTabAt(tab, i, fwd); // tab[i]已经处理完了advance = true;}}}}}}
如何在扩容时,并发地复制与插入?
遍历整个table,当前节点为空,则采用CAS的方式在当前位置放入fwd
当前节点已经为fwd(with hash field “MOVED”),则已经有有线程处理完了了,直接跳过 ,这里是控制并发扩容的核心
当前节点为链表节点或红黑树,重新计算链表节点的hash值,移动到nextTable相应的位置(构建了一个反序链表和顺序链表,分别放置在i和i+n的位置上)。移动完成后,用Unsafe.putObjectVolatile在tab的原位置赋为为fwd, 表示当前节点已经完成扩容。
1.5. get操作
读取操作,不需要同步控制,比较简单
空tab,直接返回null;
计算hash值,找到相应的bucket位置,为node节点直接返回,否则返回null。
public V get(Object key) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;int h = spread(key.hashCode());if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))return e.val;}else if (eh < 0)return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;while ((e = e.next) != null) {if (e.hash == h &&((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))return e.val;}}return null;}
1.6. 统计size
ConcurrentHashMap的元素个数等于baseCounter和数组里每个CounterCell的值之和,这样做的原因是,当多个线程同时执行CAS修改baseCount值,失败的线程会将值放到CounterCell中。所以统计元素个数时,要把baseCount和counterCells数组都考虑。
/*** Base counter value, used mainly when there is no contention,* but also as a fallback during table initialization* races. Updated via CAS.*/private transient volatile long baseCount;/*** Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.*/private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {volatile long value;CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }}/*** Returns the number of mappings. This method should be used* instead of {@link #size} because a ConcurrentHashMap may* contain more mappings than can be represented as an int. The* value returned is an estimate; the actual count may differ if* there are concurrent insertions or removals.*(大致的意思是:返回容器的大小。这个方法应该被用来代替size()方法,因为* ConcurrentHashMap的容量大小可能会大于int的最大值。* 返回的值是一个估计值;如果有并发插入或者删除操作,则实际的数量可能有所不同。)* @return the number of mappings* @since 1.8*/final long sumCount() {CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;long sum = baseCount;if (as != null) {for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {if ((a = as[i]) != null)sum += a.value;}}return sum;}public int size() {long n = sumCount();return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :(int)n);}public long mappingCount() {long n = sumCount();return (n < 0L) ? 0L : n; // ignore transient negative values}
1.7 删除元素
1.7.1 清空map:clear
清空tab的过程:遍历tab中每一个bucket
当前bucket正在扩容,先协助扩容
给当前bucket上锁,删除元素
更新map的size
public void clear() { // 移除所有元素long delta = 0L; // negative number of deletionsinti = 0;Node<K,V>[] tab = table;while (tab != null && i < tab.length) {intfh;Node<K,V> f = tabAt(tab, i);if (f == null) // 为空,直接跳过++i;else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) { //检测到其他线程正对其扩容//则协助其扩容,然后重置计数器,重新挨个删除元素,避免删除了元素,其他线程又新增元素。tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);i = 0; // restart}else{synchronized (f) { // 上锁if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { // 其他线程没有在此期间操作fNode<K,V> p = (fh >= 0 ? f :(finstanceof TreeBin) ?((TreeBin<K,V>)f).first : null);while (p != null) { // 首先删除链、树的末尾元素,避免产生大量垃圾--delta;p = p.next;}setTabAt(tab, i++, null); // 利用CAS无锁置null}}}}if (delta != 0L)addCount(delta, -1); // 无实际意义,参数check<=1,直接return。}
1.7.2 删除元素
/*** Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this map.* This method does nothing if the key is not in the map.** @param key the key that needs to be removed* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null*/public V remove(Object key) {return replaceNode(key, null, null);}/*** Implementation for the four public remove/replace methods:* Replaces node value with v, conditional upon match of cv if* non-null. If resulting value is null, delete.*/final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) {int hash = spread(key.hashCode());for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||(f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null)break; // 桶位为空,跳过else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); // 协助扩容else {V oldVal = null;boolean validated = false;synchronized (f) {if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {if (fh >= 0) {validated = true;for (Node<K,V> e = f, pred = null;;) {K ek;if (e.hash == hash &&((ek = e.key) == key ||(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {V ev = e.val;if (cv == null || cv == ev ||(ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) {oldVal = ev;if (value != null)e.val = value;else if (pred != null) // 非链表头节点,直接删除该节点pred.next = e.next;else // 更新链表头节点setTabAt(tab, i, e.next);}break;}pred = e;if ((e = e.next) == null)break;}}else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {validated = true;TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;TreeNode<K,V> r, p;if ((r = t.root) != null &&(p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) {V pv = p.val;if (cv == null || cv == pv ||(pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) {oldVal = pv;if (value != null)p.val = value;else if (t.removeTreeNode(p)) // 当红黑树太小,会返回truesetTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first));}}}}}if (validated) {if (oldVal != null) {if (value == null)addCount(-1L, -1);return oldVal;}break;}}}return null;}
2. ConcurrentHashMap 在1.7与1.8中的不同
3. ConcurrentHashMap与HashMap的区别
ConcurrentHashMap是HashMap的高并发版本
4. ConcurrentHashMap能完全替代HashTable吗?
hash table虽然性能上不如ConcurrentHashMap,但并不能完全被取代,两者的迭代器的一致性不同的,hash table的迭代器是强一致性的,而concurrenthashmap是弱一致的。ConcurrentHashMap的get,clear,iterator 都是弱一致性的。
下面是大白话的解释:
Hashtable的任何操作都会把整个表锁住,是阻塞的。好处是总能获取最实时的更新,比如说线程A调用putAll写入大量数据,期间线程B调用get,线程B就会被阻塞,直到线程A完成putAll,因此线程B肯定能获取到线程A写入的完整数据。坏处是所有调用都要排队,效率较低。
ConcurrentHashMap 是设计为非阻塞的。在更新时会局部锁住某部分数据,但不会把整个表都锁住。同步读取操作则是完全非阻塞的。好处是在保证合理的同步前提下,效率很高。坏处是严格来说读取操作不能保证反映最近的更新。例如线程A调用putAll写入大量数据,期间线程B调用get,则只能get到目前为止已经顺利插入的部分 数据。
选择哪一个,是在性能与数据一致性之间权衡。ConcurrentHashMap适用于追求性能的场景,大多数线程都只做insert/delete操作,对读取数据的一致性要求较低。
欢迎小伙伴们留言交流~~
以上是关于源码分析:JDK1.8 ConcurrentHashMap的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章