Golang反射原理
Posted 搬砖之友
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Golang反射原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.go汇编1.1 基本语法本文基于go1.13.15
go采用plan9的汇编器完成汇编,有下面几个重要的伪寄存器
FP: Frame pointer: 局部变量访问
PC: Program counter: 程序计数器
SB: Static base pointer: 全局变量访问
SP: Stack pointer: 存储栈顶指针
常用指令如下
_type
size ptrdata hash tflag tflag align fieldalign kind alg *typeAlg gcdata * str nameOff ptrToThis typeOff
Interfacetype
interfacetype
typ _type pkgpath name mhdr []imethod structtype
typ _type
pkgPath name
fields []structfield
structfield
name name
typ *_type
offsetAnon eface
_type *_type data unsafe.Pointer iface
tab *itab data unsafe.Pointer itab
inter *interfacetype _type *_type hash _ [ fun [myInterface
test1(id test2(flag MyStruct
Id Name test1(id
id + m.Id
test2(flag fmt.Println(flag)
3.3.2 MyStruct
type."".MyStruct SRODATA size=144
|--------- size -----| |-------ptrdata-------|
0x0000 18 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
|- hash --||--------| |------- alg ---------|
0x0010 dc a7 2c a3 07 08 08 19 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ..,.............
|------- gcdata ------| |-- str --||ptrToThis|
0x0020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
|------- pkgPath -----| |------- name --------|
0x0030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
|------- typ ---------| |---- offsetAnon -----|
0x0040 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
|------- name --------| |------- typ ---------|
0x0050 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........@.......
|---- offsetAnon -----|
0x0060 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0x0070 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0x0080 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
rel 24+8 t=1 type..alg."".MyStruct+0;定义了使用的<hash,equal>函数对
rel 32+8 t=1 runtime.gcbits.02+0;gc使用
rel 40+4 t=5 type..namedata.*main.MyStruct.+0;结构体名称
rel 44+4 t=5 type.*"".MyStruct+0;*MyStruct类型
rel 56+8 t=1 type."".MyStruct+96;
rel 80+4 t=5 type..importpath."".+0
rel 96+8 t=1 type..namedata.Id.+0
rel 104+8 t=1 type.int64+0
rel 120+8 t=1 type..namedata.Name.+0
rel 128+8 t=1 type.string+0
type..namedata.*main.MyStruct. SRODATA dupok size=17
0x0000 01 00 0e 2a 6d 61 69 6e 2e 4d 79 53 74 72 75 63 ...*main.MyStruc
0x0010 74
type..namedata.Id. SRODATA dupok size=5
0x0000 01 00 02 49 64 ...Id
type..namedata.Name. SRODATA dupok size=7
0x0000 01 00 04 4e 61 6d 65 ...Name
3.3.3 myInterface
go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface SRODATA dupok size=40
|--------- inter -----| |--------- _type -----|
0x0000 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
|- hash --| |-- 对齐 --| | fun[0] | | fun[1] |
0x0010 58 6c 00 8b 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 Xl..............
0x0020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........
rel 0+8 t=1 type."".myInterface+0
rel 8+8 t=1 type.*"".MyStruct+0
rel 24+8 t=1 "".(*MyStruct).test1+0
rel 32+8 t=1 "".(*MyStruct).test2+0
3.3.4 类型转换
runtime/iface.go中给出了许多进行类型转换的接口,go编译器只在必要时(如强制类型转换)才调用下面接口
convT2E
convT2I
convT16
convTstring
convTslice
...
4.1以空接口为桥梁
Type和Value4.1.1 Type、rtype和emptyInterface
1)Type
是一个接口,提供了许多用于访问类型元信息的方法
Type
Align()
FieldAlign()
Method(
MethodByName(
NumMethod()
Name()
PkgPath()
Size()
String()
Kind() Kind
Implements(u Type)
AssignableTo(u Type)
ConvertibleTo(u Type)
Comparable()
Bits()
ChanDir() ChanDir
IsVariadic()
Elem() Type
Field(i
FieldByIndex(index []
FieldByName(name
FieldByNameFunc(match
In(i
Key() Type
Len()
NumField()
NumIn()
NumOut()
Out(i
common() *rtype
uncommon() *uncommonType
2)rtype
结构类,是Type的实现,其元素和runtime下的_type完全一致,目的是为了反射期间对运行时类型变量进行成功转型
3)emptyInterface
emptyInterface
typ *rtype
word unsafe.Pointer
此接口和runtime下的eface完全一致,目的是为了反射期间可以将eface成功转型
4)TypeOf函数
这里会用到unsafe.Pointer来完成成功的指针转型操作,零拷贝
Type
eface := *(*emptyInterface)(unsafe.Pointer(&i))
toType(eface.typ)
Type
t ==
t
调用此方法经过下面步骤
转型为eface
转型为emptyInterface
取出实际类型rtype
得到rtype后,后续就可以通过调用Type提供的方法来反射获取类型的元信息
5)反射期和运行期的类型对比
| 反射(reflect包下) | 运行时(runtime包下) |
|---|---|
| rtype | _type |
| emptyInterface | eface |
| xxxType | xxxtype |
xxx包括map、chan、interface、uncommon、array、func、ptr、slice、struct
4.1.2 Value
1)Value
Value
typ *rtype
ptr unsafe.Pointer
flag
Value结构体很简单,由类型、原变量指针和标志位组成,其定义了许多方法,如
直接修改原变量值的方法
SetLen(n
SetCap(n
SetMapIndex(key, val Value)
Index(i FieldByName(name CanAddr()
v.flag&flagAddr != CanSet()
v.flag&(flagAddr|flagRO) == flagAddr
.......
2)Header
“Go 语言里的引用类型有如下几个:切片、映射、通道、接口和函数类型。当声明上述类型的变量时,创建的变量被称作标头(header)值。从技术细节上说,字符串也是一种引用类型。
每个引用类型创建的标头值是包含一个指向底层数据结构的指针。每个引用类型还包含一组独特的字段,用于管理底层数据结构。因为标头值是为复制而设计的,所以永远不需要共享一个引用类型的值。”
——《go语言实战》
go语言中提供了StringHeader和SliceHeader来反射修改属性,其余引用类型使用Value内置的方法进行操作
3)ValueOf方法
Value
i ==
Value
escapes(i)
unpackEface(i)
Value
e := (*emptyInterface)(unsafe.Pointer(&i))
don\'t read e.word until we know whether it is really a pointer or not.
t := e.typ
t ==
Value
f := flag(t.Kind())
ifaceIndir(t)
f |= flagIndir
Valuet, e.word, f
经历如下步骤
将变量转型为eface
将eface转型为emptyInterface
将实际类型、原变量指针(如果传入的是指针,如果传入的变量,获取到的是副本的指针),flag三者作为参数构建Value
4.2.1 接口为nil
buf *bytes.Buffer
out io.Writer = buf
out !=
out.Write([] myStruct = MyStruct
Id: Name:
val := reflect.ValueOf(myInter)
fmt.Println(val)
在myStruct传入的值为
MyStruct变量
会触发runtime.convT2E
(e eface)
raceenabled
raceReadObjectPC(t, elem, getcallerpc(), funcPC(convT2E))
msanenabled
msanread(elem, t.size)
x := mallocgc(t.size, t, e._type = t
e.data = x
myInter myInterface
myInter = &MyStruct
Id: Name:
reflect.ValueOf(myInter)
"".main STEXT size=114 args=0x0 locals=0x30
0x0000 00000 (test1.go:26) TEXT "".main(SB), ABIInternal, $48-0
//判断是否要扩展栈
0x0000 00000 (test1.go:26) MOVQ (TLS), CX
0x0009 00009 (test1.go:26) CMPQ SP, 16(CX)
0x000d 00013 (test1.go:26) JLS 107
//移动SP指针,分配出48字节的栈空间
0x000f 00015 (test1.go:26) SUBQ $48, SP
//存储调用点到栈底8字节
0x0013 00019 (test1.go:26) MOVQ BP, 40(SP)
//BP中存储栈底地址
0x0018 00024 (test1.go:26) LEAQ 40(SP), BP
//一些初始化动作
0x001d 00029 (test1.go:26) FUNCDATA $0, gclocals·33cdeccccebe80329f1fdbee7f5874cb(SB)
0x001d 00029 (test1.go:26) FUNCDATA $1, gclocals·33cdeccccebe80329f1fdbee7f5874cb(SB)
0x001d 00029 (test1.go:26) FUNCDATA $2, gclocals·bfec7e55b3f043d1941c093912808913(SB)
0x001d 00029 (test1.go:30) PCDATA $0, $1
0x001d 00029 (test1.go:30) PCDATA $1, $0
//将type."".MyStruct的指针传入AX
0x001d 00029 (test1.go:30) LEAQ type."".MyStruct(SB), AX
0x0024 00036 (test1.go:30) PCDATA $0, $0
//将type."".MyStruct的指针移入栈顶
0x0024 00036 (test1.go:30) MOVQ AX, (SP)
//传入栈顶的type."".MyStruct的指针,调用newobject,其会在堆上申请一块大小相当的内存,
//并返回一个*MyStruct,放入SP的8~15字节
0x0028 00040 (test1.go:30) CALL runtime.newobject(SB)
0x002d 00045 (test1.go:30) PCDATA $0, $1
//将*MyStruct传入AX
0x002d 00045 (test1.go:30) MOVQ 8(SP), AX
//将1赋给*MyStruct指向的堆中的Id字段
0x0032 00050 (test1.go:29) MOVQ $1, (AX)
//将2赋给*MyStruct指向的堆中的StringHeader的Len
0x0039 00057 (test1.go:30) MOVQ $2, 16(AX)
0x0041 00065 (test1.go:30) PCDATA $0, $2
//将go.string."sj"的地址传入CX
0x0041 00065 (test1.go:30) LEAQ go.string."sj"(SB), CX
0x0048 00072 (test1.go:30) PCDATA $0, $1
//将&"sj"赋给*MyStruct指向的堆中的StringHeader的Data
0x0048 00072 (test1.go:30) MOVQ CX, 8(AX)
//--------------至此,MyStruct对象构造完成------------------//
0x004c 00076 (test1.go:32) PCDATA $0, $2
//将go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface+8也即type.*"".MyStruct的地址传入CX
//这里是经过编译器优化的,如果开启-N禁止优化,此处指令应为
//LEAQ go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface(SB), CX
0x004c 00076 (test1.go:32) MOVQ go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface+8(SB), CX
0x0053 00083 (test1.go:32) PCDATA $0, $1
//将type.*"".MyStruct的地址移到栈顶
//如果开启-N禁止优化,此处传入*go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface
0x0053 00083 (test1.go:32) MOVQ CX, (SP)
/*
若没有ValueOf调用,则栈顶会传入*go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface(无关-N),
至此就完成了类型转换,但是,这里调用了ValueOf,其需要转换为eface,所以需要传入
*type.*"".MyStruct,所以开启了编译器优化后会直接传入此地址而不是先传itab再后移8字节传入
*type.*"".MyStruct
*/
0x0057 00087 (test1.go:32) PCDATA $0, $0
//将*MyStruct移到SP的8~15字节
0x0057 00087 (test1.go:32) MOVQ AX, 8(SP)
//传入type.*"".MyStruct的地址调用ValueOf
//如果将指针改为变量,则会触发convT2E
//如果禁用编译器优化,栈顶传入的仍为type.*"".MyStruct
0x005c 00092 (test1.go:32) CALL reflect.ValueOf(SB)
/*
func ValueOf(i interface) Value
if i == nil
return Value
return unpackEface(i)
**/
//刷新BP,存储栈底地址
0x0061 00097 (test1.go:33) MOVQ 40(SP), BP
//移动SP指针只鸢尾,栈的内存被回收
0x0066 00102 (test1.go:33) ADDQ $48, SP
0x006a 00106 (test1.go:33) RET
0x006b 00107 (test1.go:33) NOP
0x006b 00107 (test1.go:26) PCDATA $1, $-1
0x006b 00107 (test1.go:26) PCDATA $0, $-1
//扩展栈
0x006b 00107 (test1.go:26) CALL runtime.morestack_noctxt(SB)
0x0070 00112 (test1.go:26) JMP 0
0x0000 65 48 8b 0c 25 00 00 00 00 48 3b 61 10 76 5c 48 eH..%....H;a.v\\H
0x0010 83 ec 30 48 89 6c 24 28 48 8d 6c 24 28 48 8d 05 ..0H.l$(H.l$(H..
0x0020 00 00 00 00 48 89 04 24 e8 00 00 00 00 48 8b 44 ....H..$.....H.D
0x0030 24 08 48 c7 00 01 00 00 00 48 c7 40 10 02 00 00 $.H......H.@....
0x0040 00 48 8d 0d 00 00 00 00 48 89 48 08 48 8b 0d 00 .H......H.H.H...
0x0050 00 00 00 48 89 0c 24 48 89 44 24 08 e8 00 00 00 ...H..$H.D$.....
0x0060 00 48 8b 6c 24 28 48 83 c4 30 c3 e8 00 00 00 00 .H.l$(H..0......
0x0070 eb 8e ..
rel 5+4 t=16 TLS+0
rel 32+4 t=15 type."".MyStruct+0
rel 41+4 t=8 runtime.newobject+0
rel 68+4 t=15 go.string."sj"+0
rel 79+4 t=15 go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface+8
rel 93+4 t=8 reflect.ValueOf+0
rel 108+4 t=8 runtime.morestack_noctxt+0
内存分布如下所示
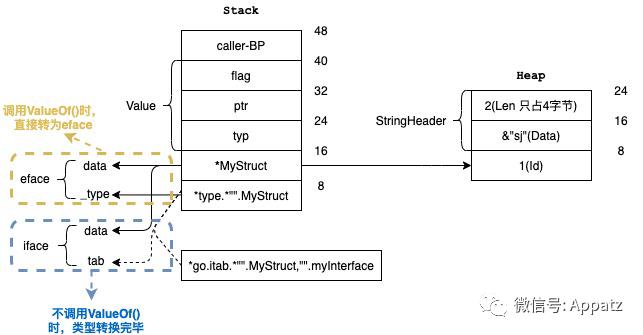
通过研究go的接口和反射,发现下面两条原则
想要实现反射需要有入口获取元信息,接口就是这个入口,元信息在编译后就已生成
指针和变量触发的拷贝决定了是否是对同一个对象进行的操作
A Quick Guide to Go\'s Assembler
从栈上理解 Go语言函数调用 - luozhiyun - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
[译]Go 和 interface 探究 (xargin.com)
深入研究 Go interface 底层实现 (halfrost.com)
Go 语言接口的原理 | Go 语言设计与实现 (draveness.me)
深度解密Go语言之关于 interface 的 10 个问题
Go 语言反射的实现原理 | Go 语言设计与实现 (draveness.me)
深度解密Go语言之反射 | qcrao
有点不安全却又一亮的 Go unsafe.Pointer - SegmentFault 思否
《Go语言实战》
func main()
var myInter myInterface
myInter = &MyStruct
Id: 1,
Name: "sj",
//convI2I
var subInterface subInterface
subInterface = myInter
fmt.Println(subInterface)
//convT2E
var emptyInterface interface
val := reflect.ValueOf(myInter)
emptyInterface = val
fmt.Println(emptyInterface)
//convI2I
0x0050 00080 (test1.go:36) LEAQ type."".subInterface(SB), CX
0x0057 00087 (test1.go:36) PCDATA $0, $1
0x0057 00087 (test1.go:36) MOVQ CX, (SP)
0x005b 00091 (test1.go:36) PCDATA $0, $2
0x005b 00091 (test1.go:36) LEAQ go.itab.*"".MyStruct,"".myInterface(SB), CX
0x0062 00098 (test1.go:36) PCDATA $0, $1
0x0062 00098 (test1.go:36) MOVQ CX, 8(SP)
0x0067 00103 (test1.go:36) PCDATA $0, $0
0x0067 00103 (test1.go:36) MOVQ AX, 16(SP)
//这里显式调用了convI2I将iface类型转换为iface类型
0x006c 00108 (test1.go:36) CALL runtime.convI2I(SB)
/*
//未触发堆上内存分配,直接将itab和data进行复制
func convI2I(inter *interfacetype, i iface) (r iface)
tab := i.tab
if tab == nil
return
if tab.inter == inter
r.tab = tab
r.data = i.data
return
//根据两个接口间的方法集合判断两个集合的交集是否等于目标接口的集合(方法签名)
r.tab = getitab(inter, tab._type, false)
r.data = i.data
return
**/
//convT2E
0x020f 00527 (test1.go:40) LEAQ type.reflect.Value(SB), AX
0x0216 00534 (test1.go:40) PCDATA $0, $0
0x0216 00534 (test1.go:40) MOVQ AX, (SP)
0x021a 00538 (test1.go:40) PCDATA $0, $1
0x021a 00538 (test1.go:40) PCDATA $1, $0
0x021a 00538 (test1.go:40) LEAQ ""..autotmp_5+216(SP), AX
0x0222 00546 (test1.go:40) PCDATA $0, $0
0x0222 00546 (test1.go:40) MOVQ AX, 8(SP)
0x0227 00551 (test1.go:40) CALL runtime.convT2E(SB)
/*
//触发了在堆上申请内存并拷贝的动作
func convT2E(t *_type, elem unsafe.Pointer) (e eface)
if raceenabled
raceReadObjectPC(t, elem, getcallerpc(), funcPC(convT2E))
if msanenabled
msanread(elem, t.size)
x := mallocgc(t.size, t, true)
typedmemmove(t, x, elem)
e._type = t
e.data = x
return
**/

golang 反射原理
本文章主要讲解一下reflect包中TypeOf和ValueOf两个函数的工作原理。
TypeOf
在 Go语言中通过调用 reflect.TypeOf 函数,我们可以从一个任何非接口类型的值创建一个 reflect.Type 值。reflect.Type 值表示着此非接口值的类型。通过此值,我们可以得到很多此非接口类型的信息。当然,我们也可以将一个接口值传递给一个 reflect.TypeOf 函数调用,但是此调用将返回一个表示着此接口值的动态类型的 reflect.Type 值。
实际上,reflect.TypeOf 函数的唯一参数的类型为 interface{},reflect.TypeOf 函数将总是返回一个表示着此唯一接口参数值的动态类型的 reflect.Type 值。
TypeOf 的源码如下
type eface struct{
_type *_type
data unsafe.Pointer
}
type emptyInterface struct{
typ *rtype
word unsafe.Pointer
}
func TypeOf (i interface()) Type{
eface := *(* emptyInterface)(unsafe.Pointer(&i)) //&i 是eface 类型
return toType(eface.typ)
}这里是反射的一些简单应用
package main
import "fmt"
import "reflect"
type Eggo struct{
name string
}
func (e Eggo) A(){
fmt.Println(e.name)
}
func main() {
a := Eggo{name:"eggo"}
t:=reflect.TypeOf(a)
fmt.Println(t.NumMethod(),t.Kind(),t)
}输出如下:1 struct main.Eggo。t.Kind()会返回golang原始类型,原始类型string,struct等等
package main
import "fmt"
import "reflect"
import "encoding/json"
type Stu struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int
HIgh bool
sex string
Class *Class `json:"class"`
}
type Class struct {
Name string
Grade int
}
type Eggo struct{
Name string
}
func (e Eggo) A(){
fmt.Println(e.Name)
}
func main() {
/*
stu := Stu{
Name: "张三",
Age: 18,
HIgh: true,
sex: "男",
}
//指针变量
cla := new(Class)
cla.Name = "1班"
cla.Grade = 3
stu.Class=cla
//Marshal失败时err!=nil
jsonStu, err := json.Marshal(stu)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("生成json字符串错误")
}
//jsonStu是[]byte类型,转化成string类型便于查看
fmt.Println(string(jsonStu))*/
a := Eggo{Name:"eggo"}
b := &Eggo{}
bdata, err:= json.Marshal(a)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("生成json字符串错误")
}
t:=reflect.TypeOf(a)
fmt.Println(string(bdata))
aa := reflect.New(t).Interface()
fmt.Println("...........",t,aa,b)
json.Unmarshal(bdata, aa)
fmt.Println("reflect-get-name",(aa).(*Eggo).Name)
}输出如下:
{"Name":"eggo"}
........... main.Eggo &{} &{}
reflect-get-name eggo。
根据反射解析json。cellnet使用的就是这种方式编码和解码
以上是关于Golang反射原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章