干货 | Elasticsearch Nested 数组大小求解,一网打尽!
Posted 铭毅天下Elasticsearch
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了干货 | Elasticsearch Nested 数组大小求解,一网打尽!相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
2、数据模型如何查询所有 objectList (Nested 类型)里面的 lossStatus="ENABLE" 且 objectList 的数组大小大于2的数据?
——问题来源:死磕Elasticsearch 知识星球
索引导入和样例数据批量写入如下所示。
PUT appweb
"mappings":
"properties":
"name":
"type": "text"
,
"orderTime":
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"objectList":
"type": "nested",
"properties":
"addTime":
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"customerPersonId":
"type": "long"
,
"lossStatus":
"type": "text"
POST appweb/_bulk
"index":"_id":1
"name":"111","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":101,"lossStatus":"ENABLE","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":102,"lossStatus":"ENABLE"]
"index":"_id":2
"name":"222","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":201,"lossStatus":"2222","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":202,"lossStatus":"2222","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":203,"lossStatus":"3333"]
"index":"_id":3
"name":"111","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":101,"lossStatus":"ENABLE"]
"index":"_id":4
"name":"111","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":101,"lossStatus":"ENABLE","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":102,"lossStatus":"ENABLE","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":103,"lossStatus":"ENABLE"]
开搞,方案逐步展开讨论。
3、问题拆解涉及三个核心知识点:
这个在检索的时候要注意指定 path,否则会报错。
问题转化为:检索条件1、检索条件2的组合实现。
3.1 检索条件 1 实现POST appweb/_search
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"match_phrase":
"objectList.lossStatus": "ENABLE"
]
中规中矩的 Nested 语法,无需过多解释。唯一强调的是:path的用法。
如果 Nested 语法不熟悉,可以参考官方文档:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.0/query-dsl-nested-query.html
3.2 检索条件 2 实现本质是获取 objectList 的数组大小大于 2 的数据。再进一步缩小范围是:获取 objectList 数组的大小。
问题转化为如何获取 Nested 嵌套类型数组大小?
这里的确没有非常现成的实现,我总结了如下几种方案。
方案1:function_score 检索实现
该方案包含了:3.1 小节 检索条件 1 的实现,完整实现如下。
POST appweb/_search
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"match_phrase":
"objectList.lossStatus": "ENABLE"
,
"function_score":
"query":
"match_all":
,
"functions": [
"script_score":
"script":
"source": "params._source.containsKey(\'objectList\') && params._source[\'objectList\'] != null && params._source.objectList.size() > 2 ? 2 : 0"
],
"min_score": 1
]
注意在 script_score 下做了多条件判断:
params._source.containsKey(\'objectList\')
params._source[\'objectList\'] != null
params._source.objectList.size() > 2
官方语法参考:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.0/query-dsl-function-score-query.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/8.0/painless-score-context.html
方案2:funciton_score 检索实现2
POST appweb/_search
"query":
"function_score":
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"exists":
"field": "objectList.customerPersonId"
,
"score_mode": "sum"
,
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"match_phrase":
"objectList.lossStatus": "ENABLE"
]
,
"functions": [
"script_score":
"script":
"source": "_score >= 3 ? 1 : 0"
],
"boost_mode": "replace"
,
"min_score": 1
该方式本质是曲线救国,借助:sum 求和累加评分实现。
实现条件是:存在字段“objectList.customerPersonId”,评分就高。该方式不太容易想到,“可遇而不可求”。
方案3:runtime_field 运行时字段实现
POST appweb/_search
"runtime_mappings":
"objectList_tmp":
"type": "keyword",
"script": """
int genre = params[\'_source\'][\'objectList\'].size();
emit(genre.toString());
"""
,
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"match_phrase":
"objectList.lossStatus": "ENABLE"
,
"range":
"objectList_tmp":
"gte": 3
]
这是我整合了聚合 + runtime_field 实现的结果,召回结果达到预期且令人满意。
最后发现聚合部分是多余的,删除之。
解读如下:
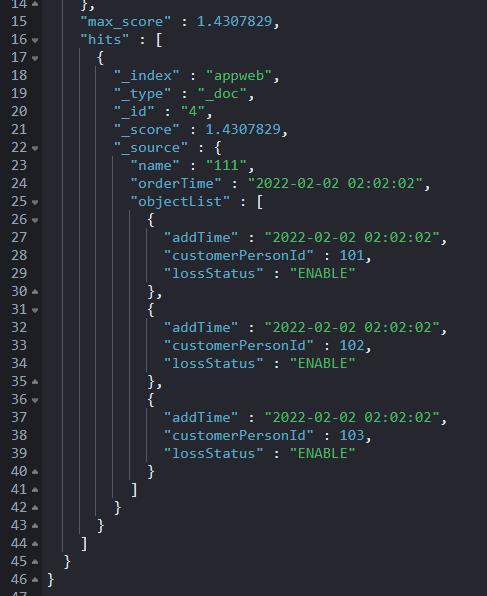
综合对比看,它比下面的方案4更简洁,如果线上环境想不修改数据的前提下使用,推荐此方案。
方案4:聚合实现
GET appweb/_search
"size": 0,
"query":
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"match_phrase":
"objectList.lossStatus": "ENABLE"
,
"aggs":
"counts_aggs":
"terms":
"script": "params[\'_source\'][\'objectList\'].size()"
,
"aggs":
"top_hits_aggs":
"top_hits":
"size": 10
对比方案 3,方案 4相对鸡肋和繁冗、复杂。
也更进一步体会:runtime_field 的妙处。
4、换个思路?轻装上阵!什么思路?之前文章有过解读——空间换时间。
具体实现如下:
4.1 步骤1:预处理新增字段 nested_size。PUT _ingest/pipeline/add_nested_size_pipeline
"processors": [
"script":
"lang": "painless",
"source": "ctx.nested_size = ctx.objectList.size();"
]
创建索引同时指定步骤 1 的 pipeline 预处理管道。
PUT appweb_ext
"settings":
"index":
"default_pipeline": "add_nested_size_pipeline"
,
"mappings":
"properties":
"name":
"type": "text"
,
"orderTime":
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"objectList":
"type": "nested",
"properties":
"addTime":
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"customerPersonId":
"type": "long"
,
"lossStatus":
"type": "text"
POST appweb_ext/_bulk
"index":"_id":1
"name":"111","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":101,"lossStatus":"ENABLE","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":102,"lossStatus":"ENABLE"]
"index":"_id":2
"name":"222","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":201,"lossStatus":"2222","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":202,"lossStatus":"2222","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":203,"lossStatus":"3333"]
"index":"_id":3
"name":"111","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":101,"lossStatus":"ENABLE"]
"index":"_id":4
"name":"111","orderTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","objectList":["addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":101,"lossStatus":"ENABLE","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":102,"lossStatus":"ENABLE","addTime":"2022-02-02 02:02:02","customerPersonId":103,"lossStatus":"ENABLE"]
bool 组合条件,一个 nested 检索 + 一个 range query,轻松搞定!
POST appweb_ext/_search
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "objectList",
"query":
"match_phrase":
"objectList.lossStatus": "ENABLE"
,
"range":
"nested_size":
"gt": 2
]
此方案是我极力推广的方案,需要我们多结合业务实际,多在数据写入前的设计阶段、数据建模阶段做“文章”。而不是快速导入数据,后面丢给复杂的检索脚本实现。
一般项目实战阶段,很多人会说,“工期要紧,我管不了那么多”。项目后期复盘会发现,“看似快了,实则慢了”,最终感叹:“预处理的工作不要省也不能省”!
5、小结看似简单的几个方案,我从入手到梳理完毕耗时大于 6 个小时+。主要是painless 脚本没有固定的章法可循,需要摸索和反复验证。
意外收获是方案3,基于方案 4 的创新方案,比较灵活好用。
但,我更推荐空间换时间的方案。能预处理搞定的事情,就不要留到检索阶段实现。
欢迎留言说下您的方案和思考!
6、参考https://stackoverflow.com/questions/64447956
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54022283
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57144172
https://t.zsxq.com/FAQ7mUN
https://www.ru-rocker.com/2020/11/03/filtering-nested-array-objects-in-elasticsearch-document-with-painless-scripting/
https://medium.com/@felipegirotti/elasticsearch-filter-field-array-more-than-zero-8d52d067d3a0
更短时间更快习得更多干货!
和全球近 1600+ Elastic 爱好者一起精进!

干货 | Elasticsearch Nested类型深入详解
Elasticsearch 最少必要知识实战教程直播回放
0、概要
在Elasticsearch实战场景中,我们或多或少会遇到嵌套文档的组合形式,反映在ES中称为父子文档。
父子文档的实现,至少包含以下两种方式:
1)父子文档
父子文档在5.X版本中通过parent-child父子type实现,即:1个索引对应多个type;
6.X+版本已经不再支持一个索引多个type,6.X+的父子索引的实现改成Join。
2)Nested嵌套类型
本文通过一个例子将Nested类型适合解决的问题、应用场景、使用方法串起来,
文中所有的DSL都在Elasticsearch6.X+验证通过。
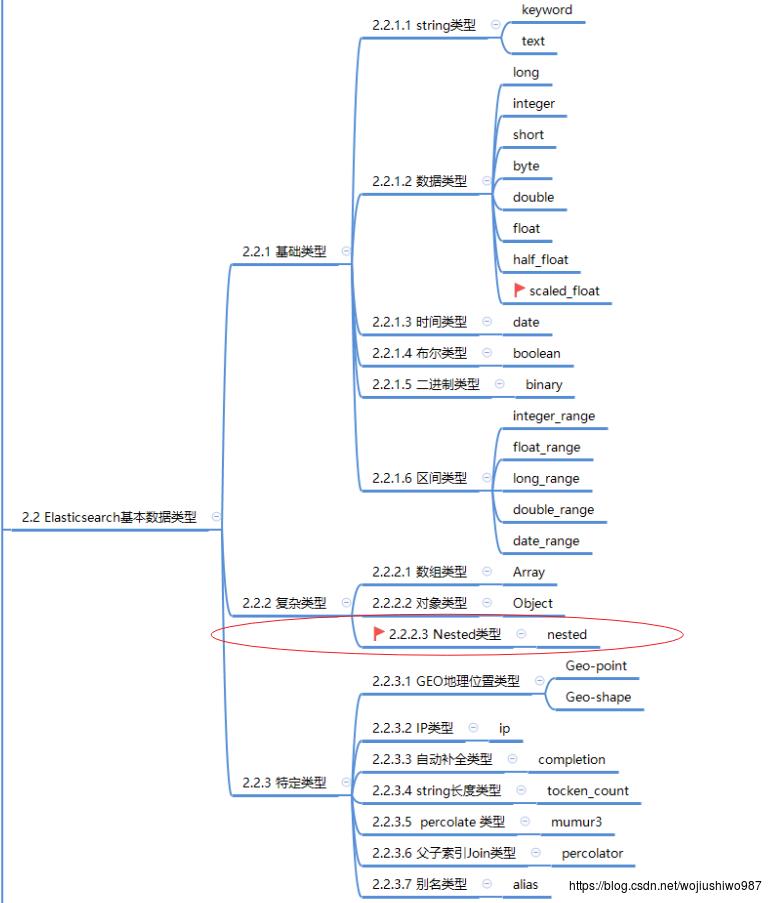
1、Elasticsearch 数据类型全景概览
2、从一个例子说起吧

2.1 问题背景
在elasticsearch中,我们可以将密切相关的实体存储在单个文档中。 例如,我们可以通过传递一系列评论来存储博客文章及其所有评论。
举例:
"title": "Invest Money",
"body": "Please start investing money as soon...",
"tags": ["money", "invest"],
"published_on": "18 Oct 2017",
"comments": [
"name": "William",
"age": 34,
"rating": 8,
"comment": "Nice article..",
"commented_on": "30 Nov 2017"
,
"name": "John",
"age": 38,
"rating": 9,
"comment": "I started investing after reading this.",
"commented_on": "25 Nov 2017"
,
"name": "Smith",
"age": 33,
"rating": 7,
"comment": "Very good post",
"commented_on": "20 Nov 2017"
]
如上所示,所以我们有一个文档描述了一个帖子和一个包含帖子上所有评论的内部对象评论。
但是Elasticsearch搜索中的内部对象并不像我们期望的那样工作。
2.2 问题出现
现在假设我们想查找用户name:john,age:34评论过的所有博客帖子。 让我们再看一下上面的示例文档,找到评论过的用户。
| name | age |
|---|---|
| William | 34 |
| John | 38 |
| Smith | 33 |
从列表中我们可以清楚地看到,没有34岁的用户John。
为简单起见,我们在elasticsearch索引中只有1个文档。
让我们通过查询索引来验证它:
GET /blog/_search?pretty
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"match":
"comments.name": "John"
,
"match":
"comments.age": 34
]
我们的示例文档作为回复返回。 很惊讶,这是为什么呢?
2.3 原因分析
这就是为什么我说:
elasticsearch中的内部对象无法按预期工作
这里的问题是elasticsearch(lucene)使用的库没有内部对象的概念,因此内部对象被扁平化为一个简单的字段名称和值列表。
我们的文档内部存储为:
"title": [ invest, money ],
"body": [ as, investing, money, please, soon, start ],
"tags": [ invest, money ],
"published_on": [ 18 Oct 2017 ]
"comments.name": [ smith, john, william ],
"comments.comment": [ after, article, good, i, investing, nice, post, reading, started, this, very ],
"comments.age": [ 33, 34, 38 ],
"comments.rating": [ 7, 8, 9 ],
"comments.commented_on": [ 20 Nov 2017, 25 Nov 2017, 30 Nov 2017 ]
如上,您可以清楚地看到,comments.name和comments.age之间的关系已丢失。
这就是为什么我们的文档匹配john和34的查询。
2.4 如何解决呢?
要解决这个问题,我们只需要对elasticsearch的映射进行一些小改动。
如果您查看索引的映射,您会发现comments字段的类型是object。
我们需要更新它的类型为nested。
我们可以通过运行以下查询来简单地更新索引的映射:
PUT /blog_new
"mappings":
"blog":
"properties":
"title":
"type": "text"
,
"body":
"type": "text"
,
"tags":
"type": "keyword"
,
"published_on":
"type": "keyword"
,
"comments":
"type": "nested",
"properties":
"name":
"type": "text"
,
"comment":
"type": "text"
,
"age":
"type": "short"
,
"rating":
"type": "short"
,
"commented_on":
"type": "text"
将映射更改为Nested类型后,我们可以查询索引的方式略有变化。 我们需要使用Nested查询。
下面给出了Nested查询示例:
GET /blog_new/_search?pretty
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "comments",
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"match":
"comments.name": "john"
,
"match":
"comments.age": 34
]
]
由于用户name:john,age:34没有匹配,上面的查询将不返回任何文档。
再次感到惊讶? 只需一个小小的改变即可解决问题。
这可能是我们理解的一个较小的变化,但是在elasticsearch存储我们的文档的方式上有很多变化。
在内部,嵌套对象将数组中的每个对象索引为单独的隐藏文档,这意味着可以独立于其他对象查询每个嵌套对象。
下面给出了更改映射后样本文档的内部表示:
"comments.name": [ john ],
"comments.comment": [ after i investing started reading this ],
"comments.age": [ 38 ],
"comments.rating": [ 9 ],
"comments.date": [ 25 Nov 2017 ]
,
"comments.name": [ william ],
"comments.comment": [ article, nice ],
"comments.age": [ 34 ],
"comments.rating": [ 8 ],
"comments.date": [ 30 Nov 2017 ]
,
"comments.name": [ smith ],
"comments.comment": [ good, post, very],
"comments.age": [ 33 ],
"comments.rating": [ 7 ],
"comments.date": [ 20 Nov 2017 ]
,
"title": [ invest, money ],
"body": [ as, investing, money, please, soon, start ],
"tags": [ invest, money ],
"published_on": [ 18 Oct 2017 ]
如您所见,每个内部对象都在内部存储为单独的隐藏文档。 这保持了他们的领域之间的关系。
3、Nested类型的作用?
从上一小节,可以清晰的看出nested类型的特别之处。
nested类型是对象数据类型的专用版本,它允许对象数组以可以彼此独立查询的方式进行索引。
4、Nested类型的适用场景
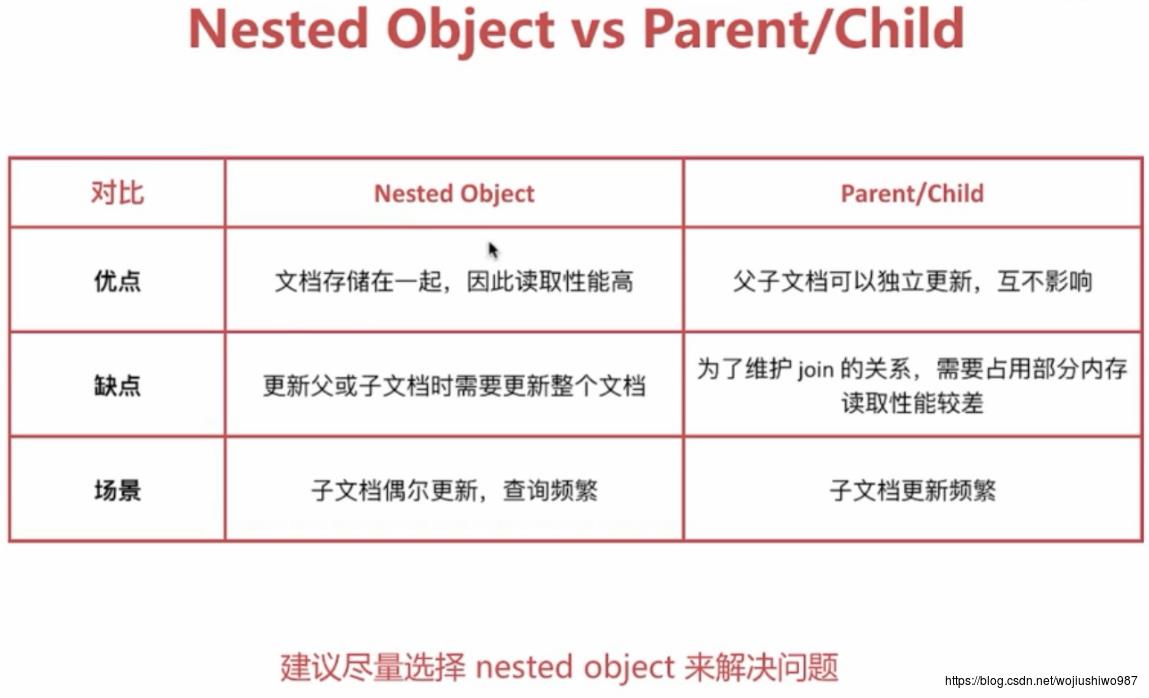
——图片来自:rockybean教程
5、Nested类型的增、删、改、查、聚合操作详解
还是以第2节的blog_new索引示例,Nested类型的增、删、改、查操作。
5.1 Nested类型——增
新增blog和评论
POST blog_new/blog/2
"title": "Hero",
"body": "Hero test body...",
"tags": ["Heros", "happy"],
"published_on": "6 Oct 2018",
"comments": [
"name": "steve",
"age": 24,
"rating": 18,
"comment": "Nice article..",
"commented_on": "3 Nov 2018"
]
5.2 Nested类型——删
序号为1的评论原来有三条,现在删除John的评论数据,删除后评论数为2条。
POST blog_new/blog/1/_update
"script":
"lang": "painless",
"source": "ctx._source.comments.removeIf(it -> it.name == 'John');"
5.3 Nested类型——改
将steve评论内容中的age值调整为25,同时调整了评论内容。
POST blog_new/blog/2/_update
"script":
"source": "for(e in ctx._source.comments)if (e.name == 'steve') e.age = 25; e.comment= 'very very good article...';"
5.4 Nested类型——查
如前所述,查询评论字段中评论姓名=William并且评论age=34的blog信息。
GET /blog_new/_search?pretty
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"nested":
"path": "comments",
"query":
"bool":
"must": [
"match":
"comments.name": "William"
,
"match":
"comments.age": 34
]
]
5.5 Nested类型——聚合
认知前提:nested聚合隶属于聚合分类中的Bucket聚合分类。
聚合blog_new 中评论者年龄最小的值。
GET blog_new/_search
"size": 0,
"aggs":
"comm_aggs":
"nested":
"path": "comments"
,
"aggs":
"min_age":
"min":
"field": "comments.age"
6、小结
如果您在索引中使用内部对象并做查询操作,请验证内部对象的类型是否为nested类型。 否则查询可能会返回无效的结果文档。
更新认知是非常痛苦的,不确定的问题只有亲手实践才能检验真知。
参考:
[1]http://t.cn/Evwh0uW
[2]官网6.x+:http://t.cn/Ehltakr

打造Elasticsearch基础、进阶、实战第一公众号!
以上是关于干货 | Elasticsearch Nested 数组大小求解,一网打尽!的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章