MySQL子查询原理分析
Posted 360云计算
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL子查询原理分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
( INT ( ) NOT NULL, INT ( ) DEFAULT NULL, INT ( ) DEFAULT NULL,),( )) ENGINE = INNODB;( INT ( ) NOT NULL, INT ( ) DEFAULT NULL, INT ( ) DEFAULT NULL,),( )) ENGINE = INNODB;( INT ( ) NOT NULL, INT ( ) DEFAULT NULL, INT ( ) DEFAULT NULL,),( )) ENGINE = INNODB; i int; i= insert into t1 values(i, i, i); i=i+ end i int; i= insert into t2 values(i, i, i); i=i+ end i int; i= insert into t3 values(i, i=i+ end explain select from t1 where t1_a = (select t2_a from t2 limit 1);
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+-------+---------+--------+------+-------------+
|id |select_type |table |type |possible_keys |key |key_len |ref |rows |Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+-------+---------+--------+------+-------------+
|1 |PRIMARY |t1 |ref |idx_a |idx_a |5 |const |1 |Using where |
|2 |SUBQUERY |t2 |index |<null> |idx_a |5 |<null> |1000 |Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+-------+---------+--------+------+-------------+
| | | | | |
| SUBQUERY | | | | |
explain select from t3 where t3_a in (select t2_a from t2);
+----+--------------+-------------+--------+---------------+------------+---------+--------------+------+-------------+
|id |select_type |table |type |possible_keys |key |key_len |ref |rows |Extra |
+----+--------------+-------------+--------+---------------+------------+---------+--------------+------+-------------+
|1 |SIMPLE |t3 |ALL |idx_a |<null> |<null> |<null> |1000 |Using where |
|1 |SIMPLE |<subquery2> |eq_ref |<auto_key> |<auto_key> |5 |test.t3.t3_a |1 |<null> |
|2 |MATERIALIZED |t2 |index |idx_a |idx_a |5 |<null> |1000 |Using index |
+----+--------------+-------------+--------+---------------+------------+---------+--------------+------+-------------+
t3 left join t2 on t3.type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+--------+---------+--------------+------+--------+
| 1 |SIMPLE | t3 | ALL | <SIMPLE | t2 | ref | idx_a | idx_a | 5 | test.t3.t3_a | 1 | <t3 where t3_a (select t2_a t2 where t2.type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------------+
| 1 |SIMPLE | t3 | ref | idx_a | idx_a | 5 | const | 1 | <SIMPLE | t2 | ref | idx_a | idx_a | 5 | const | 4 | Using index; FirstMatch(t3) |
+----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+-------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------------+
FROM outer_tables
expr (FROM inner_tables FROM outer_tables
(oe1, oe2, (ie1, ie2, FROM inner_tables inner_expr ... subquery_where)
(inner_expr ... subquery_where outer_expr=inner_expr)
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | (select from t2 t2.t2_a>=and t2.t2_a=t3.t3_a) or t3_b > | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| SUBQUERY | | | | | | | where; Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+------+---------------+--------+---------+--------------+------+--------------------------+
需要注意的是,如果 IN 子查询不满足转换为 semi-join 的条件,又不能转换为物化表或者转换为物化表的成本太大,那么它就会被转换为 EXISTS 查询。或者转换为物化表的成本太大,那么它就会被转换为 EXISTS 查询。
05
总结
1. 如果IN子查询符合转换为 semi-join 的条件,查询优化器会优先把该子查询转换为 semi-join,然后再考虑下边执行半连接的策略中哪个成本最低,
1)Table pullout
2)DuplicateWeedout
3)LooseScan
4)FirstMatch
选择成本最低的那种执行策略来执行子查询。
2. 如果IN子查询不符合转换为 semi-join 的条件,那么查询优化器会从下边两种策略中找出一种成本更低的方式执行子查询:
1)先将子查询物化之后再执行查询
2)执行 IN to EXISTS 转换
MySQL 原理分析之 Trace 分析 order by 的索引原理
一、背景
昨天早上,交流群有一位同学提出了一个问题。看下图:
我不是大佬,而且当时我自己的想法也只是猜测,所以并没有回复那位同学,只是接下来自己做了一个测试验证一下。
他只简单了说了一句话,就是同样的sql,一个没加 order by 就全表扫描,一个加了 order by 就走索引了。
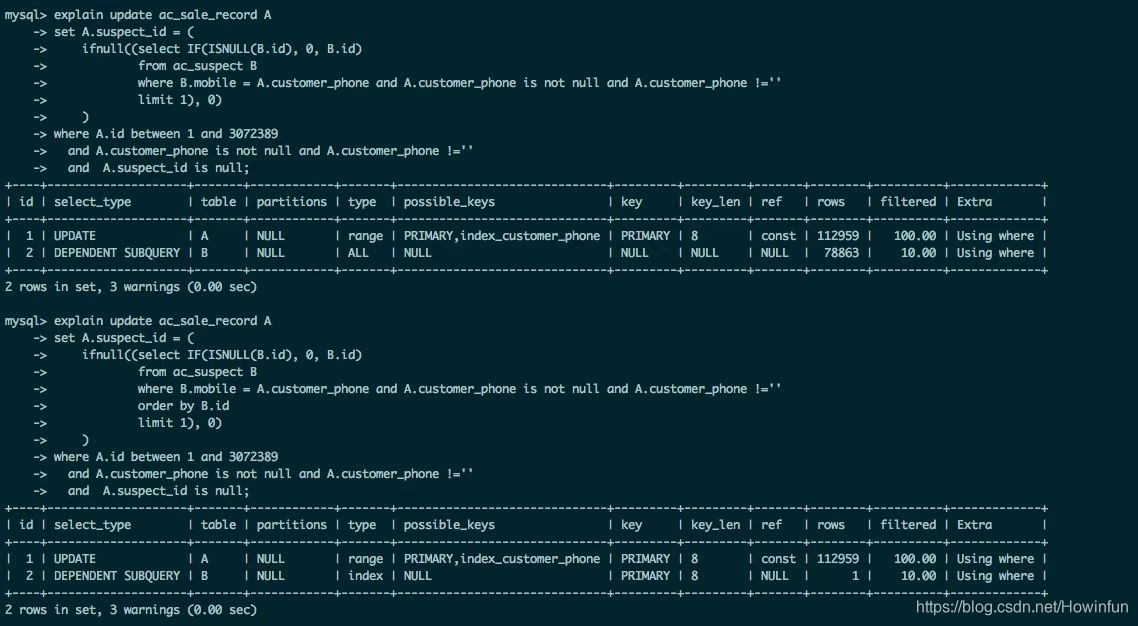
我们可以仔细点看一下他提供的图(主要分析子查询即可,就是关于表 B 的查询,因为只有表 B 的查询前后不一致),我们可以先得出两个前提:
1、首先可以肯定的是,where 条件中的 mobile 字段是没有索引的。因为没有 order by 时,是全表扫描,如果 mobile 字段有索引,查询优化器必定会使用 mobile 字段的索引。
2、其实重点不但在 order by,更重要的是在于 order by 后面跟着的字段是 表B 的主键 id。之所以判断 id 为主键,是因为 explain 执行计划里看到使用了 PRIMARY 索引,即主键索引。
二、数据准备和场景重现
创建表 user:
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone` varchar(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=100007 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;准备数据:
看了一下截图,数据量应该在10万左右,我们也准备10万数据,尽量做到一致。
delimiter ;
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `iniData`()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=100000)do
insert into user(name,age,phone) values('测试', i, 15627230000+i);
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call iniData();执行 SQL ,查看执行计划:
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' limit 1;
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;执行结果:
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) ALL (Null) (Null) (Null) (Null) 99927 10 Using where
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) index (Null) PRIMARY 4 1 10 Using where我们可以看到,执行计划和那位同学的基本一致,都是第一条 SQL 全表扫描,第二条 SQL 是走了主键索引。
三、猜想和猜测着总结
只要加 order by 就走索引?
根据上面的执行计划来看,明显这位同学的表达是不对的,更重要的是因为 order by 后跟着的字段是主键 id,所以才走了索引,走了主键索引。
我们可以试试用 age 字段来排序,这时候肯定是没有走索引的,因为我们压根没有为 age 字段没有建立索引。
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by age limit 1;id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) ALL (Null) (Null) (Null) (Null) 99927 10 Using where; Using filesort分析:
首先,我们看到 type 是 ALL,就是全表扫描,而且我们还留意到:Extra的值多了 using filesort,表明 MySQL 有文件排序的操作。
我们可以拿 order by age 和 order by id 的执行计划来对比一下。
1、explain 的 tepe 字段:
首先,type 不一样,一个是 index,表明利用了索引树;一个是 ALL,表明是全表扫描。
2、explain 的 Extra 字段:
第二,也是最重点的,它其实可以说明为何利用了主键索引。就是 Extra 字段。
先说明一下正常的排序,Extra 都会有 Using filesort 来表明使用了文件排序。
而明显 order by id 是没有这个,这是因为,索引树本来就是一个带有顺序的数据结构,大家不了解的可以去看看 B+Tree 的介绍。查询优化器正是利用了索引的顺序性,使得 SQL 的执行计划走主键索引树来去掉原本需要的排序。
之前的大白话 MySQL 学习总结中也提到过查询优化器。SQL 的执行计划能有很多,并且结果是一样的,但是为了提高性能,MySQL 的查询优化器组件会为 SQL 制定一套最优的执行计划。
阶段总结:
查询优化器帮我们制定的最优计划是:充分利用主键索引的顺序性,避免了全表扫描后还是需要排序操作。
当然了,我们不能自己只是根据现象做判断,下面将利用 Trace 来查看优化器追踪的信息,进一步的验证我们的总结是没问题的。
四、通过 Trace 分析来验证
开启和查看 Trace
-- 开启优化器跟踪
set session optimizer_trace='enabled=on';
select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;
-- 查看优化器追踪
select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace;下面我们只看 TRACE 就行了。
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id`,`user`.`name` AS `name`,`user`.`age` AS `age`,`user`.`phone` AS `phone` from `user` where (`user`.`phone` = '15627231000') order by `user`.`id` limit 1"
}
]
}
},
{
"join_optimization": { // 优化工作的主要阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
// .... 省略很多步骤
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": { // 重新考虑索引排序的访问路径
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`user`",
"index_provides_order": true,
"order_direction": "asc",
"index": "PRIMARY", // 排序的字段为主键 id,有主键索引
"plan_changed": true, // 改变执行计划
"access_type": "index"
}
}
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`user`"
}
]
}
]
}
},
{
"join_explain": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
]
}
}
]
}好了,在最后的那里,我们看到了查询优化器帮我们使用了主键索引。
所以,我们上面的猜想是正确的,因为 where 条件后的 phone 字段没有加上索引,所以到 order by id 时,查询优化器发现可以利用主键索引所以来避免排序,所以最后就使用了主键索引。
那么,按照上面的说法,如果 phone 字段加上了索引,那么最后应该就是走 phone 的索引而不是主键索引了。而且,SQL 调优有那么一条建议:建议经常在 where 条件后出现的字段加上索引来提高查询性能。
下面我们来继续验证一下我们的猜想。
五、关于 where 条件字段索引和 order by 字段索引的选择
1、给字段 phone 增加索引:
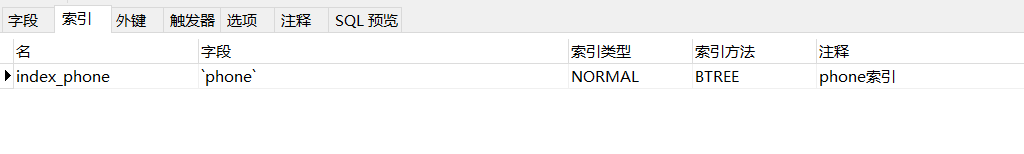
2、执行 SQL :
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;3、结果:
我们可以看到,最后查询优化器判断 phone索引 比 主键索引 更能提高性能,所以使用了 phone 的索引。
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) index index_phone index_phone 36 1 100 Using index condition4、Trace进一步验证:
最后,我们可以看到,查询优化器否定了使用主键索引,不改变之前的执行计划。
-- 开启优化器跟踪
set session optimizer_trace='enabled=on';
select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;
-- 查看优化器追踪
select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace;Trace 分析:
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id`,`user`.`name` AS `name`,`user`.`age` AS `age`,`user`.`phone` AS `phone` from `user` where (`user`.`phone` = '15627231000') order by `user`.`id` limit 1"
}
]
}
},
{
"join_optimization": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
// .... 省略很多步骤
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
],
"table": "`user`",
"best_access_path": {
"considered_access_paths": [
{
"access_type": "ref",
"index": "index_phone",
"rows": 1,
"cost": 1.2,
"chosen": true
},
{
"access_type": "range",
"range_details": {
"used_index": "index_phone" // 使用 phone 的索引
},
"chosen": false,
"cause": "heuristic_index_cheaper"
}
]
},
"condition_filtering_pct": 100,
"rows_for_plan": 1,
"cost_for_plan": 1.2,
"chosen": true
}
]
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": "(`user`.`phone` = '15627231000')",
"attached_conditions_computation": [
],
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"attached": null
}
]
}
},
{
"clause_processing": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"original_clause": "`user`.`id`",
"items": [
{
"item": "`user`.`id`"
}
],
"resulting_clause_is_simple": true,
"resulting_clause": "`user`.`id`"
}
},
{
"added_back_ref_condition": "((`user`.`phone` <=> '15627231000'))"
},
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": { // 重新考虑索引排序的访问路径
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`user`",
"index_provides_order": true,
"order_direction": "asc",
"index": "index_phone",
"plan_changed": false // 不改变执行计划
}
}
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"pushed_index_condition": "(`user`.`phone` <=> '15627231000')",
"table_condition_attached": null
}
]
}
]
}
},
{
"join_explain": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
]
}
}
]
}六、最后总结
到这里,分析就结束了,我们可以得出一个结论,当然了,只是基于上面的实验所得:
1、SQL 带有 order by :
order by 后面的字段有索引:
where 条件后面的所有字段都没索引,则使用 order by 后面的字段的索引。
where 条件后面有字段带有索引,则使用 where 条件对应的字段的索引。
order by 后面的字段没有索引:
- where 条件后面的所有字段都没索引,则全表扫描。
- where 条件后面有字段带有索引,则使用 where 条件后面的字段的索引。
2、SQL 不带 order by:
where 条件后面的所有字段都没索引,则全表扫描。
where 条件后面只要有字段带索引,则使用该字段对应的索引。
最后我们也可以得出一个绝对的结论:查询优化器是真的好使,哈哈哈!
七、题外话
其实上面的实验需要大家对 MySQL 的索引原理有一定的了解,但是不用特别深。
如果大家感兴趣的话,可以关注一下我现在写的 【大白话系列】MySQL 学习总结 这一系列的文章,我会将自己学习 MySQL 后的学习总结分享在这里。
以上是关于MySQL子查询原理分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章