数组的五个迭代方法
Posted 打遍天下吴敌手
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数组的五个迭代方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
ECMAScript 为数组定义了 5 个迭代方法:
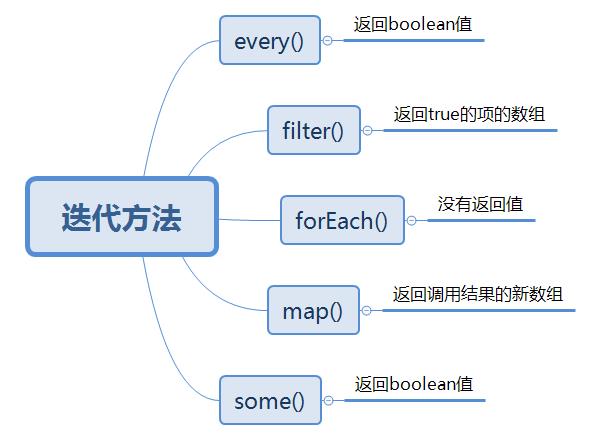
每个方法都会接收两个参数:运行的函数以及作为函数运行上下文的作用域对象。其中运行的函数接收 3 个参数:数组元素、元素索引和数组本身。这些方法都不改变调用它们的数组。
对比区别
在这些方法中, every() 和 some() 是最相似的,都是从数组中搜索符合某个条件的元素。虽相似但还是有区别的,如下
<script> let arr = [4,5,1,7,6,8,66,9,88]; let everyResult = arr.every((item,index,array) => item > 7); let someResult = arr.some((item,index,array) => item > 7);
console.log(everyResult);//false console.log(someResult) //true </script>
- 对于 every(),数组里的每一项都必须满足函数才会返回 true,否则返回 false.
- 对于 some(),数组里只要一项传入函数并满足函数就会返回 true.
接下来我们再来看看 filter() ,这个方法基于给定的函数来决定某一项是否应该包含在它返回的数组中。比如,要返回所有数值都大于 2 的数组,如下:
<script> let arr = [4,5,1,7,6,8,66,9,88]; let filterResult = arr.filter((item,index,array) => item > 7); console.log(filterResult);//[8,66,9,88] </script>
这个方法比较适合从数组中筛选满足给定条件的元素。
我们再来看看 map() ,这个方法也会返回一个数组。但是它返回的数组是对原始数组中同样位置的元素运行传入函数而返回的结果,如下:
<script> let arr = [4,5,1,7,66,88]; let mapResult1 = arr.map((item,index,array) => item > 7); let mapResult2 = arr.map((item,index,array) => item * 2); console.log(mapResult1);//[false,false,false,false,true,true] console.log(mapResult2);//[8,10,2,14,132,176] </script>
这个方法非常适合创建一个与原始数组元素一一对应的新数组。
最后,我们来看一下 forEach() ,这个方法只会对每一项运行传入的函数,没有返回值。本质上,就相当于使用 for 循环遍历数组,如下:
<script> let arr = [4,5,1,7,66,88]; arr.forEach((item,index,array) => { //执行某些操作 }); </script>
好了,数组的五个迭代方法介绍完毕(*^▽^*)
测试题目:两个有序数组,找出最大的五个数字组成一个新的数组
注意点:
1.输入两行的方法
2.两行输入的数量和小于5的情况
1 //评测题目: 两个有序数组,找出最大的五个数字组成一个新的数组 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 vector<int> getTop5(vector<int>& data1, vector<int>& data2, int& up) 9 int i=data1.size()-1; 10 int j=data2.size()-1; 11 vector<int> res; 12 for(int k=0; k<up;k++) 13 if( i<0 || j<0 ) break; 14 if(data1[i] >= data2[j] ) 15 res.push_back( data1[i] ); 16 i--; 17 18 else 19 res.push_back( data2[j] ); 20 j--; 21 22 23 24 if(res.size()<up) //注意有可能不够5个。 25 if(i == -1 ) 26 for(int m=j; res.size()<up && m>=0; m-- ) 27 res.push_back( data2[m] ); 28 29 30 31 if(j == -1) 32 for(int n=i; res.size()<up && n>=0; n-- ) 33 res.push_back( data1[n] ); 34 35 36 37 38 return res; 39 40 41 int main() 42 43 int up = 5; 44 vector<int> data1; 45 vector<int> data2; 46 string str; 47 bool sign1=0; //代表data1已经读入 48 bool sign2=0; //代表data2已经读入 49 while( getline(cin, str) ) 50 if(!sign1 ) 51 istringstream temp1(str); 52 int cur1; 53 while(temp1>>cur1) 54 data1.push_back(cur1); 55 56 sign1 = 1; 57 58 else if(!sign2 ) 59 istringstream temp2(str); 60 int cur2; 61 while(temp2>>cur2) 62 data2.push_back(cur2); 63 64 sign2 = 1; 65 66 67 if(sign1&&sign2) 68 69 vector<int> res = getTop5(data1, data2, up); 70 if(res.size()<up) cout<<"nums are not enough\n"; 71 else 72 for(int i=0; i<up; i++) 73 cout<<res[i]<<" "; 74 75 cout<<endl; 76 77 78 sign1 = 0; 79 sign2 = 0; 80 data1.clear(); 81 data2.clear(); 82 83 84 85 86
以上是关于数组的五个迭代方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章