Codeforces Round #751 (Div. 2)
Posted zhy-cx
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Codeforces Round #751 (Div. 2)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Codeforces Round #751 (Div. 2)
A. Two Subsequences
思路分析:
- x实际上就是字符串里最小的字符。
- 剩下的便是y。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
char ch = \'z\';
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (s[i] < ch)
{
pos = i;
ch = s[i];
}
}
cout << ch << \' \';
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (i != pos)
{
cout << s[i];
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B. Divine Array
思路分析:
- 这题我想复杂了,实际上不需要像我这么麻烦(比赛时的代码太复杂了,就不放了),因为不管怎么样,进行\\(1000\\)轮后都不会再进行改变。
- 所以我们对于每一个序列都操作1000次,然后储存答案,查询时间就是O(1),当然,算法主体时间是O(1000 * \\(n^2\\))。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000;
vector<int> v[maxn];
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
v[0].push_back(x);
}
int i;
for (i = 1;; i++)
{
int flag = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int t = count(v[i - 1].begin(), v[i - 1].end(), v[i - 1][j]);
v[i].push_back(t);
if (v[i][j] != v[i - 1][j])
{
flag = 1;
}
}
if (!flag)
{
break;
}
}
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (b >= i)
cout << v[i][a - 1] << endl;
else
cout << v[b][a - 1] << endl;
}
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
v[j].clear();
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Array Elimination
思路分析:
- 这题一开始没想法,最后猜了一下按位做,然后推了一下,发现确实有道理就写上了。
- 首先,对于每一位,看有多少个\\(1\\),如果有\\(n\\)个\\(1\\)的话,那么只要选择\\(n\\)的因子个当前位为\\(1\\)的数即可(假如是\\(3\\),那么只能选\\(1\\)或者\\(3\\),如果是\\(4\\),那么只能选\\(1\\),\\(2\\),\\(4\\),对于其他的数也是这样的,推一下就可以知道),那么我们对于每一位都是这样的操作的话,那么我们只需要求每一位\\(1\\)的个数的gcd的因子即可。
- 证明如下:
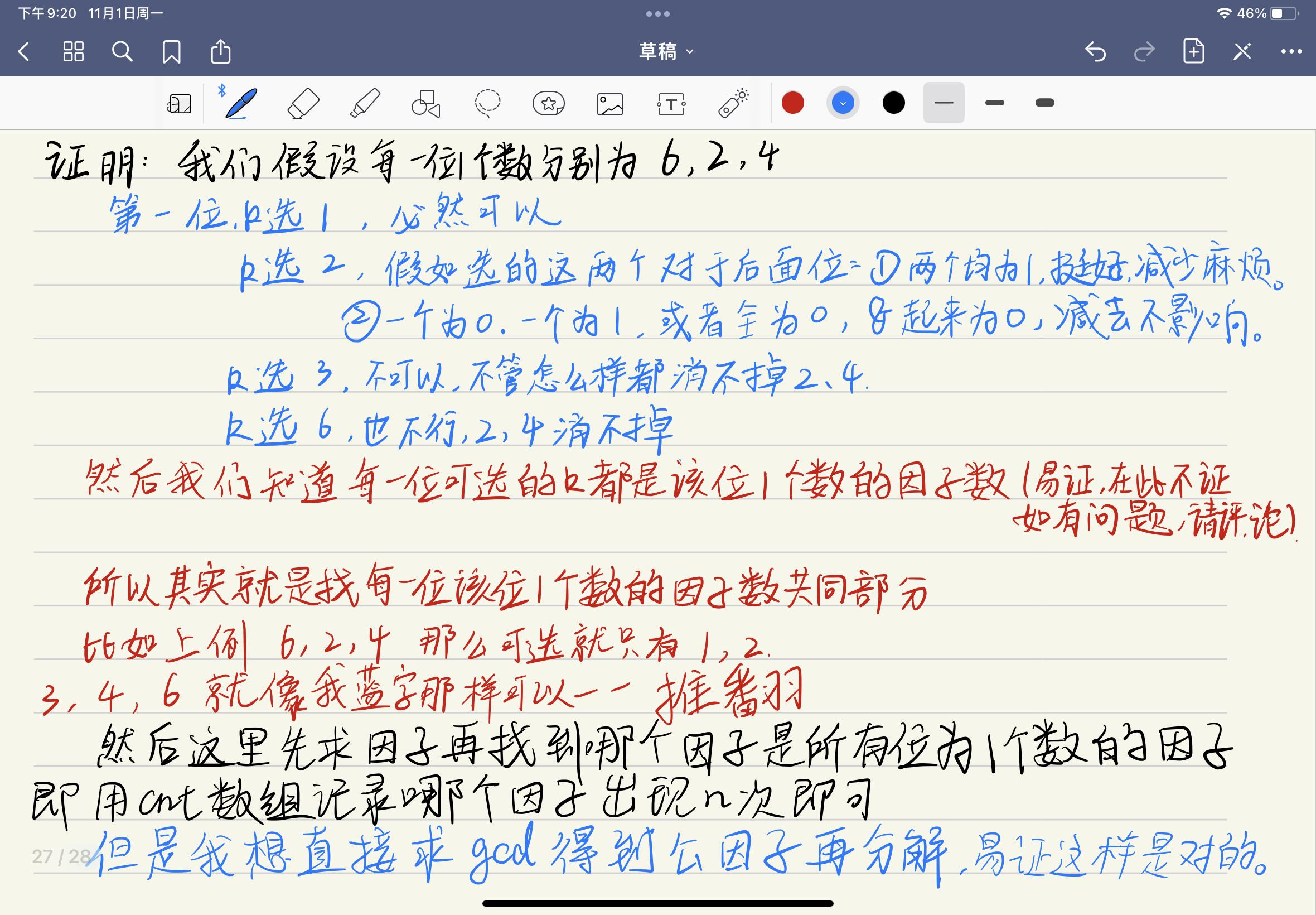
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int a[maxn];
int cnt[30];
int main()
{
int t = read();
while (t--)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 29; i++)
{
cnt[i] = 0;
}
int n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
a[i] = read();
}
for (int j = 29; j >= 0; j--)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if ((a[i] >> j) & 1)
{
cnt[j]++;
}
}
}
int gcd = 0;
for (int j = 30; j >= 0; j--)
{
gcd = __gcd(gcd, cnt[j]);
}
if (gcd == 0)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
else
{
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 1; i <= gcd; i++)
{
if (gcd % i == 0)
{
ans.push_back(i);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
{
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
}
}
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
D. Frog Traveler
思路分析:
- 这题没想到可以用BFS,因为我们要求最小步数,所以在每一轮中保证了步数是一致的,并且我们可以知道,不可能往后退。
- 所以是线性的,每个位置只走一遍,具体看代码注释。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 10;
int a[maxn], b[maxn];
//题目给的
int minh, n;
//我们把上一轮最大高度记录一下
int pre[maxn];
//记录当前位置的前面一个位置
int dis[maxn];
//记录步数
int ans[maxn];
//记录当前位置前面位置的答案
int bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
q.push(n);
minh = n;
dis[n] = 0;
//初始化
while (!q.empty())
{
int h = q.front();
q.pop();
if (h == 0)
return dis[h];
//如果出现了0,那么直接return即可
for (int x = a[h]; x > 0; x--)
{
int now = h - x, temp = 0;
//now是指跳了x高的高度,temp用来储存跳完之后的高度
if (now >= minh)
{
break;
}
if (now > 0)
{
temp = now, now += b[now];
//now变成跳完之后掉下来的高度
}
else
now = 0;
if (dis[now] > dis[h] + 1)//如果当前高度之前没有枚举到
{
dis[now] = dis[h] + 1;
pre[now] = h;
//掉下来的高度的前驱为h
ans[now] = temp;
//掉下来的高度的前面位置的高度
q.push(now);
}
}
minh = min(minh, h - a[h]);
//更新最低高度
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> b[i];
}
minh = n;
cout << bfs() << endl;
stack<int> s;
int x = 0;
while (pre[x] != -1)
{
s.push(x);
x = pre[x];
//找前驱
}
while (!s.empty())
{
int now = s.top();
cout << ans[now] << \' \';
s.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #436 E. Fire(背包dp+输出路径)
题意:失火了,有n个物品,每个物品有价值pi,必须在时间di前(小于di)被救,否则就要被烧毁。救某个物
品需要时间ti,问最多救回多少价值的物品,并输出救物品的顺序。
Examples
Input
3
3 7 4
2 6 5
3 7 6
Output
11
2
2 3
Input
2
5 6 1
3 3 5
Output
1
1
1
思路:有点像一个背包,dp数组记录的是当前时间所能获得的最大价值,转移方程dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-t[i].ti]+t[i].w)
path[i][j]表示到i号物品j时间的状态时救的物品编号(这里是从0开始)
emmmmm 具体的在代码中加以注释。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2010;
struct node{
int ti,en,w,op;
}t[110];
int dp[maxn],path[110][maxn],a[110];
bool cmp(node x,node y){
if(x.en!=y.en)return x.en<y.en;
else return x.ti<y.ti;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>t[i].ti>>t[i].en>>t[i].w;
t[i].op=i+1;
//op为每个物品的标号,题目要求从1开始
}
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
memset(path,-1,sizeof(path));//开始全部置为-1
sort(t,t+n,cmp);
int ma=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
ma=max(ma,t[i].en);
if(i!=0){
for(int j=0;j<t[i].ti;j++)path[i][j]=path[i-1][j];
//时间小于所需的营救时间,那么就不救,等于上一状态
}
for(int j=t[i].en-1;j>=t[i].ti;j--){
if(dp[j]<dp[j-t[i].ti]+t[i].w){
dp[j]=dp[j-t[i].ti]+t[i].w;
path[i][j]=i;
//如果救,那么就更新dp数组以及path数组为该物品
}
else if(i>0){
path[i][j]=path[i-1][j];
//如果不救,那么还是等于上一状态
}
}
}
int sum=0,temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<=ma;i++){
if(dp[i]>sum){
sum=dp[i];
temp=i;
//取出最大价值以及在最大价值的情况下,救完最后一个物品的时间
}
}
int k=n-1,c=0;
while(temp>0){
a[c++]=t[path[k][temp]].op;
temp-=t[path[k][temp]].ti;
k--;
k=path[k][temp];
//反着记录下路径
}
cout<<sum<<endl<<c<<endl;
for(int i=c-1;i>=0;i--){
if(i!=c-1)cout<<‘ ‘;
cout<<a[i];
//倒叙输出
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
以上是关于Codeforces Round #751 (Div. 2)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章