FastAPI 学习之路请求体有多个参数如何处理?
Posted 北漂的雷子
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FastAPI 学习之路请求体有多个参数如何处理?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
系列文章:
FastAPI 学习之路(一)fastapi--高性能web开发框架
请求体有多个参数如何处理?
别的不多说,我们先写一个需求,然后演示下如何展示。
需求:写一个接口,传递以下参数,书本的名称,描述,价格,打折。
接口返回返回最后的价格
我们去看下代码如何实现
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None @app.put("/items") def update_item(item: Optional[Item]): result={} if item.tax is not None: total=item.price*item.tax result[\'price\'] = total result[\'name\']=item.name return result result[\'price\'] = item.price result[\'name\'] = item.name return result
那么我们测试下,最后是否实现了这个功能,当我们输入所有的参数的时候。
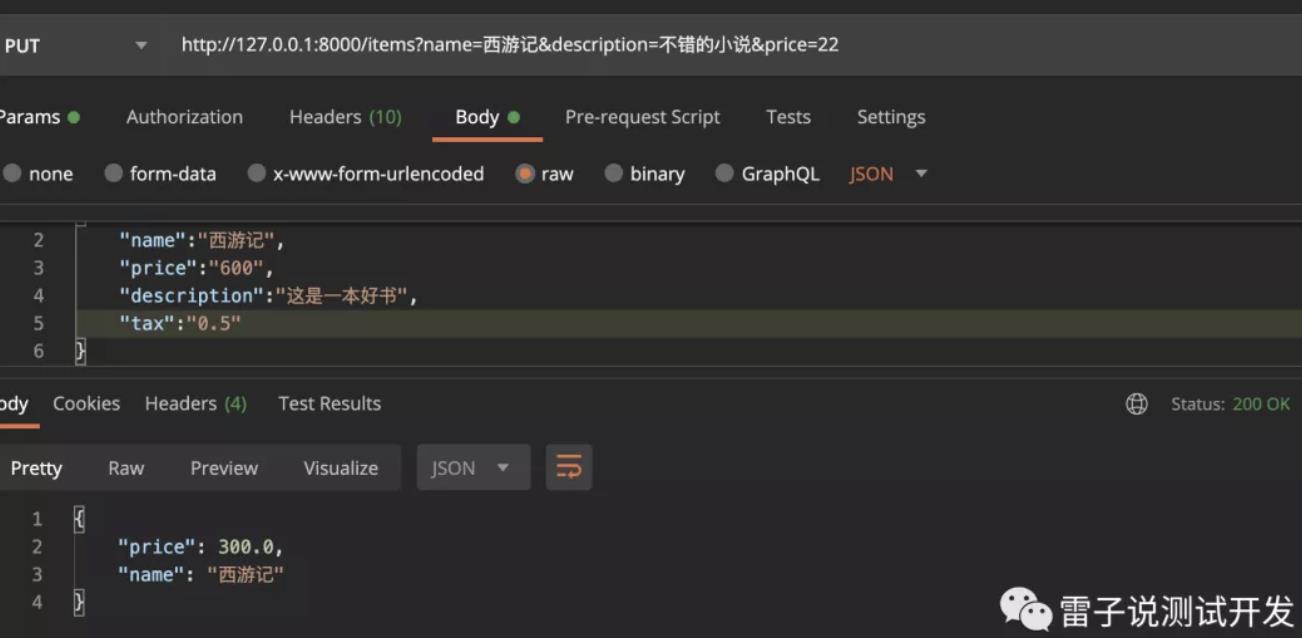
最后是在我们实际的打折上返回的。
那么我们看下,我们不增加打折如何返回
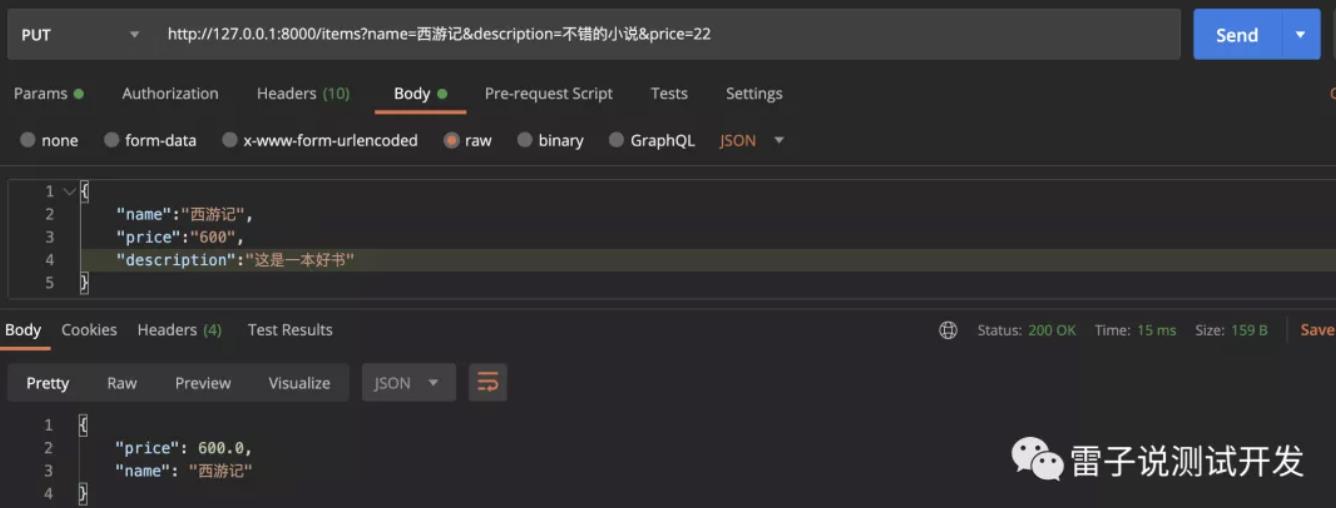
没有打折就原价返回了名称和价格。
如果默认给了None或者其他内容,这个参数就是可以选择增加或者不增加。但是没有给默认值的时候,就是必须传递的,否则会返回对应的错误,我们可以看下。假如我们不传递价格。
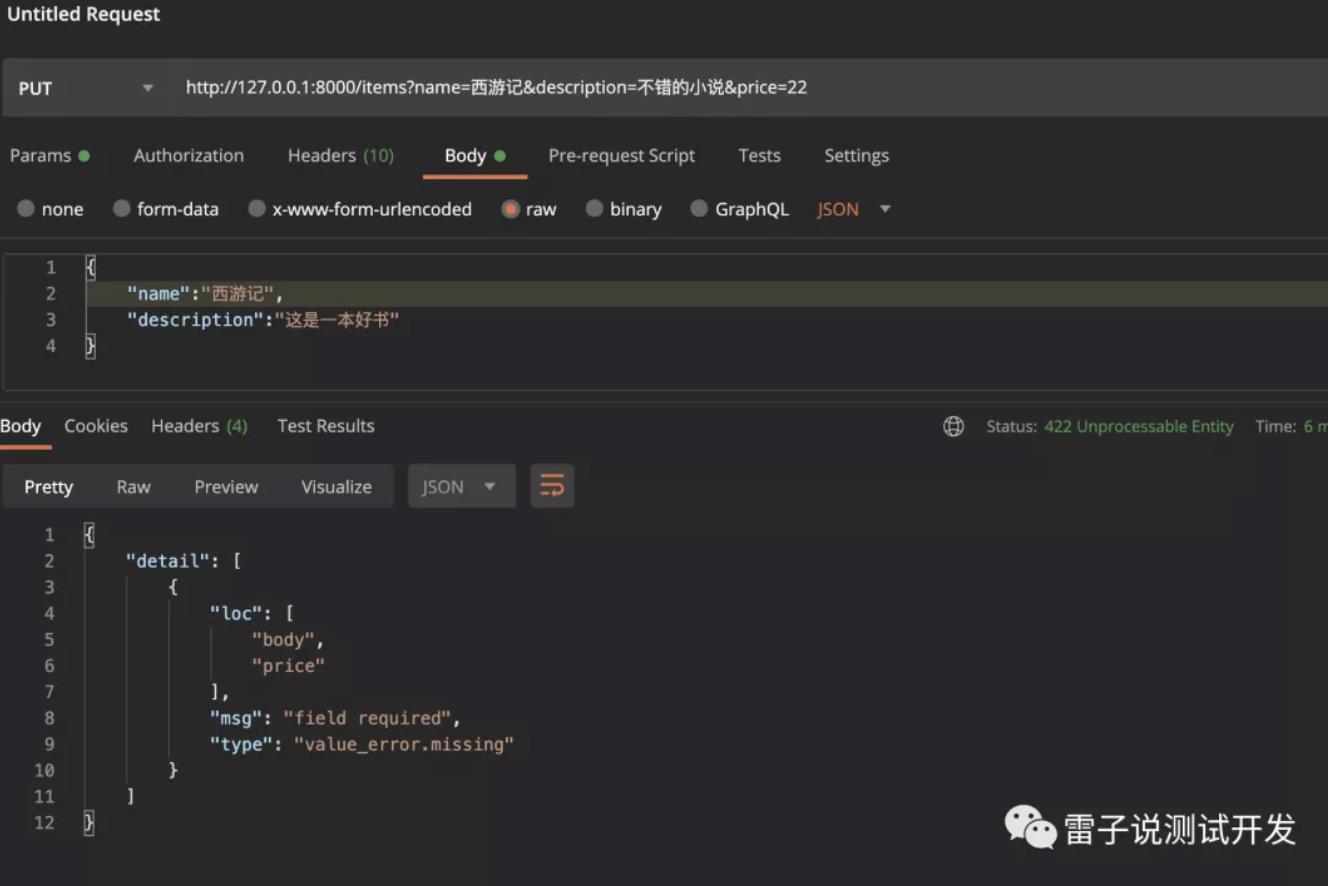
我们可以看到没有默认值的参数就是一个必须的。不然接口会返回对应的错误。
除了声明以上单个的,我们还可以声明多个请求体参数,比如我们可以在之前的需求,增加一个返回,要求返回作者,和作者的朝代。如何实现呢。
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None class User(BaseModel): username: str year: str @app.put("/items") async def update_item(item: Optional[Item],user:User): result={} if item.tax is not None: total=item.price*item.tax result[\'price\'] = total result[\'name\']=item.name result[\'user\']=user return result result[\'price\'] = item.price result[\'name\'] = item.name result[\'user\']=user return result
那么我们看下接口的请求
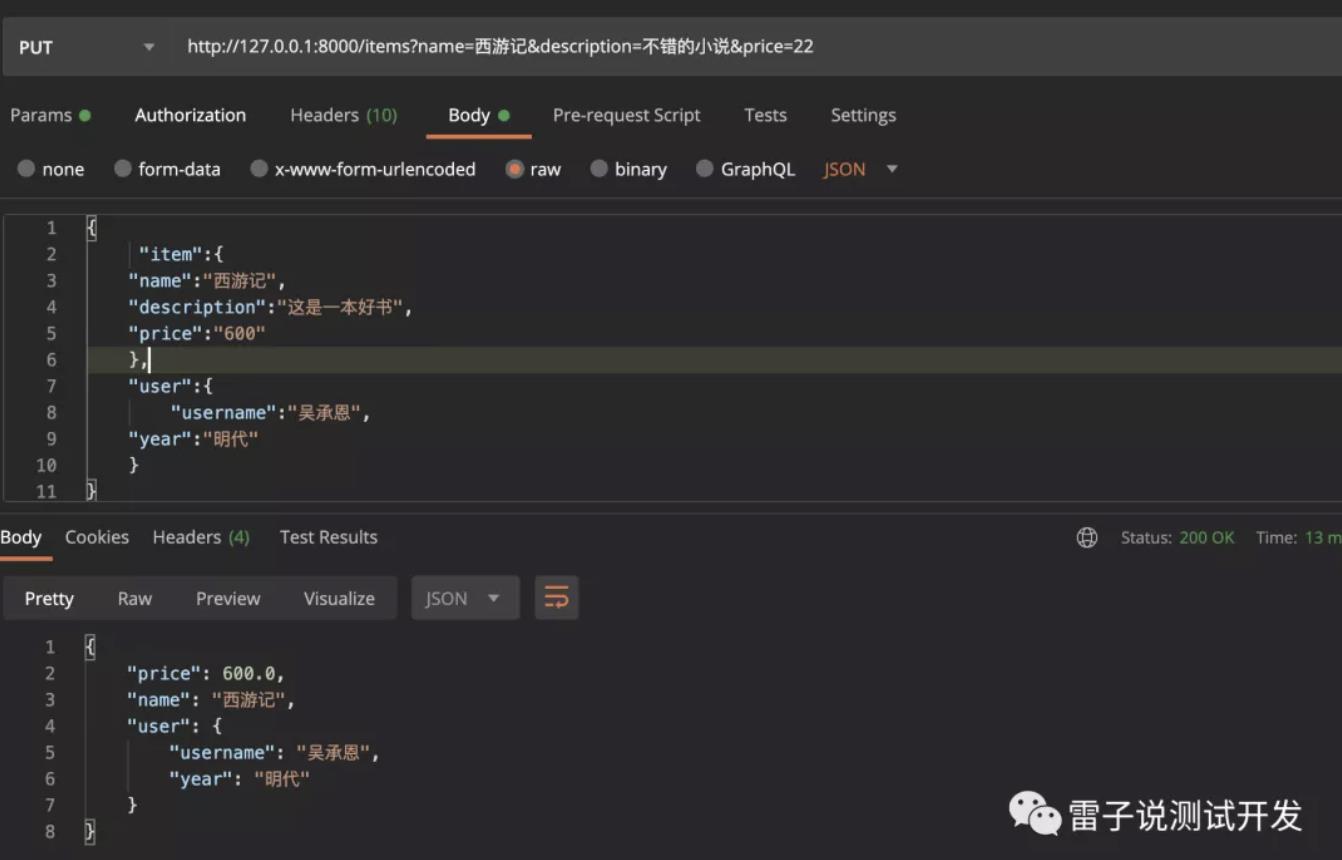
当我们增加打折。看下返回结果
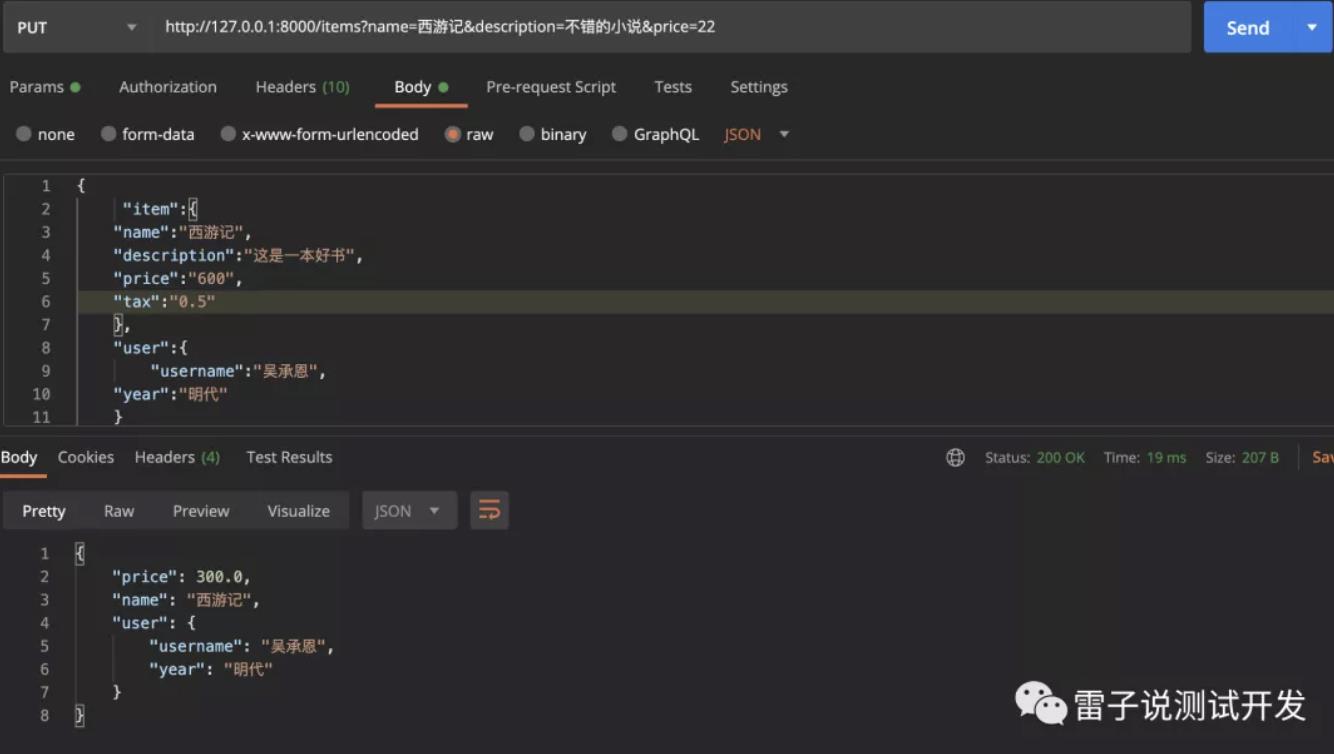
我们可以看下接口的返回。
FastAPI 将自动对请求中的数据进行转换,因此 item 参数将接收指定的内容,user 参数也是如此。
我们要想在增加一个键,在哪里出售,但是要作为请求体的另一个键进行处理,如何 实现呢
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI,Body from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None class User(BaseModel): username: str year: str @app.put("/items") async def update_item(item: Optional[Item],user:User,sell:str=Body(...)): result={} if item.tax is not None: total=item.price*item.tax result[\'price\'] = total result[\'name\']=item.name result[\'user\']=user result[\'sell\']=sell return result result[\'price\'] = item.price result[\'name\'] = item.name result[\'user\']=user result[\'sell\'] = sell return result
我们可以看到如下
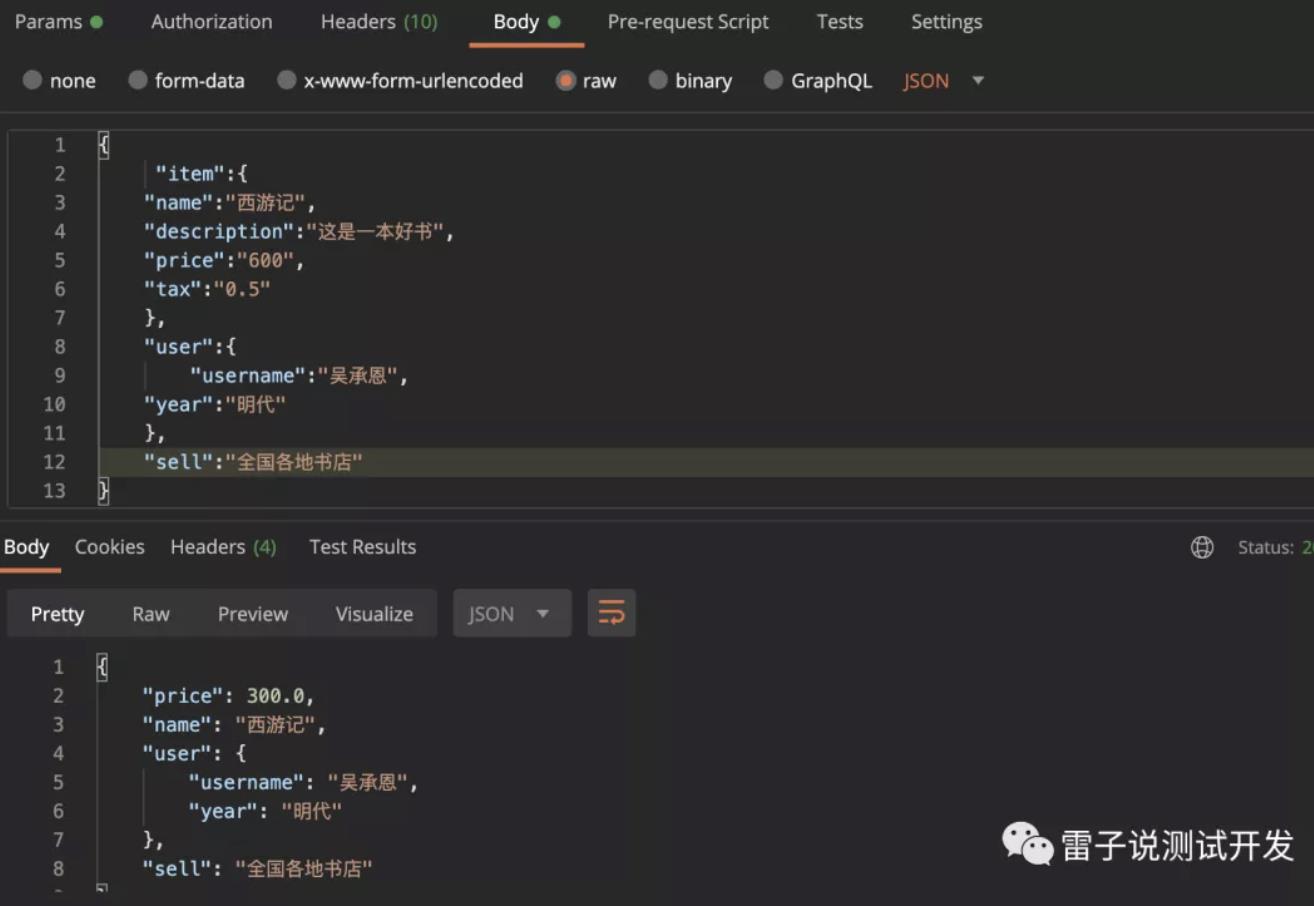
假如我们把参数放在查询内,返回错误
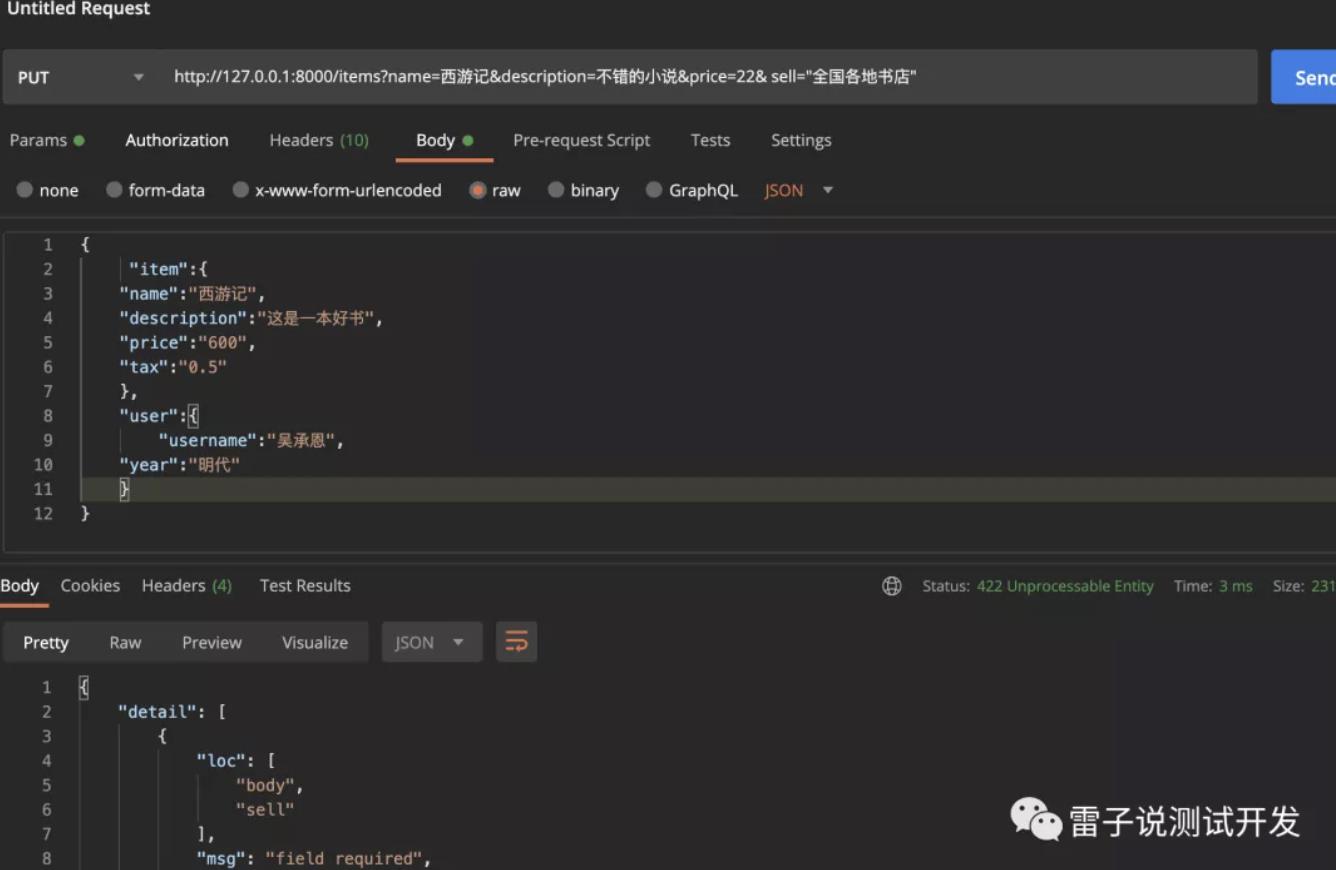
参数必须放在body内请求。
文章首发在公众号,欢迎关注。

FastAPI学习-7.POST请求body-多个参数
前言
既然我们已经知道了如何使用 Path 和 Query,下面让我们来了解一下请求体声明的更高级用法。
混合使用 Path、Query 和请求体参数
你可以随意地混合使用 Path、Query 和请求体参数声明,FastAPI 会知道该如何处理。
还可以通过将默认值设置为 None 来将请求体参数声明为可选参数:
from typing import Optional
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
price: float
tax: Optional[float] = None
@app.put("/items/item_id")
async def update_item(
*,
item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get", ge=0, le=1000),
q: Optional[str] = None,
item: Optional[Item] = None,
):
results = "item_id": item_id
if q:
results.update("q": q)
if item:
results.update("item": item)
return results
请注意,在这种情况下,将从请求体获取的 item 是可选的。因为它的默认值为 None。
多个请求体参数
在上面的示例中,路径操作将期望一个具有 Item 的属性的 JSON 请求体,就像:
"name": "Foo",
"description": "The pretender",
"price": 42.0,
"tax": 3.2
但是你也可以声明多个请求体参数,例如 item 和 user:
from typing import Optional
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
price: float
tax: Optional[float] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
full_name: Optional[str] = None
@app.put("/items/item_id")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, user: User):
results = "item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user
return results
在这种情况下,FastAPI 将注意到该函数中有多个请求体参数(两个 Pydantic 模型参数)。
因此,它将使用参数名称作为请求体中的键(字段名称),并期望一个类似于以下内容的请求体:
"item":
"name": "Foo",
"description": "The pretender",
"price": 42.0,
"tax": 3.2
,
"user":
"username": "dave",
"full_name": "Dave Grohl"
注意,即使 item 的声明方式与之前相同,但现在它被期望通过 item 键内嵌在请求体中。
FastAPI 将自动对请求中的数据进行转换,因此 item 参数将接收指定的内容,user 参数也是如此。
它将执行对复合数据的校验,并且像现在这样为 OpenAPI 模式和自动化文档对其进行记录。
请求体中的单一值
与使用 Query 和 Path 为查询参数和路径参数定义额外数据的方式相同,FastAPI 提供了一个同等的 Body。
例如,为了扩展先前的模型,你可能决定除了 item 和 user 之外,还想在同一请求体中具有另一个键 importance。
如果你就按原样声明它,因为它是一个单一值,FastAPI 将假定它是一个查询参数。
但是你可以使用 Body 指示 FastAPI 将其作为请求体的另一个键进行处理。
from typing import Optional
from fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
price: float
tax: Optional[float] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
full_name: Optional[str] = None
@app.put("/items/item_id")
async def update_item(
item_id: int, item: Item, user: User, importance: int = Body(...)
):
results = "item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user, "importance": importance
return results
在这种情况下,FastAPI 将期望像这样的请求体:
"item":
"name": "Foo",
"description": "The pretender",
"price": 42.0,
"tax": 3.2
,
"user":
"username": "dave",
"full_name": "Dave Grohl"
,
"importance": 5
同样的,它将转换数据类型,校验,生成文档等。
多个请求体参数和查询参数
当然,除了请求体参数外,你还可以在任何需要的时候声明额外的查询参数。
由于默认情况下单一值被解释为查询参数,因此你不必显式地添加 Query,你可以仅执行以下操作:
q: str = None
如:
from typing import Optional
from fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
price: float
tax: Optional[float] = None
class User(BaseModel):
username: str
full_name: Optional[str] = None
@app.put("/items/item_id")
async def update_item(
*,
item_id: int,
item: Item,
user: User,
importance: int = Body(..., gt=0),
q: Optional[str] = None
):
results = "item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user, "importance": importance
if q:
results.update("q": q)
return results
Body 同样具有与 Query、Path 以及其他后面将看到的类完全相同的额外校验和元数据参数。
嵌入单个请求体参数
假设你只有一个来自 Pydantic 模型 Item 的请求体参数 item。
默认情况下,FastAPI 将直接期望这样的请求体。
但是,如果你希望它期望一个拥有 item 键并在值中包含模型内容的 JSON,就像在声明额外的请求体参数时所做的那样,则可以使用一个特殊的 Body 参数 embed:
item: Item = Body(..., embed=True)
比如:
from typing import Optional
from fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
price: float
tax: Optional[float] = None
@app.put("/items/item_id")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item = Body(..., embed=True)):
results = "item_id": item_id, "item": item
return results
在这种情况下,FastAPI 将期望像这样的请求体:
"item":
"name": "Foo",
"description": "The pretender",
"price": 42.0,
"tax": 3.2
而不是
"name": "Foo",
"description": "The pretender",
"price": 42.0,
"tax": 3.2
总结
你可以添加多个请求体参数到路径操作函数中,即使一个请求只能有一个请求体。
但是 FastAPI 会处理它,在函数中为你提供正确的数据,并在路径操作中校验并记录正确的模式。
你还可以声明将作为请求体的一部分所接收的单一值。
你还可以指示 FastAPI 在仅声明了一个请求体参数的情况下,将原本的请求体嵌入到一个键中。
以上是关于FastAPI 学习之路请求体有多个参数如何处理?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章