购物车的程序设计
Posted 亿杯奶茶
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了购物车的程序设计相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
购物车程序的面向对象设计
一、前期调查:
调查京东商城中的购物车,体验从搜索商品、加入购物车、操作购物车、下单全过程:
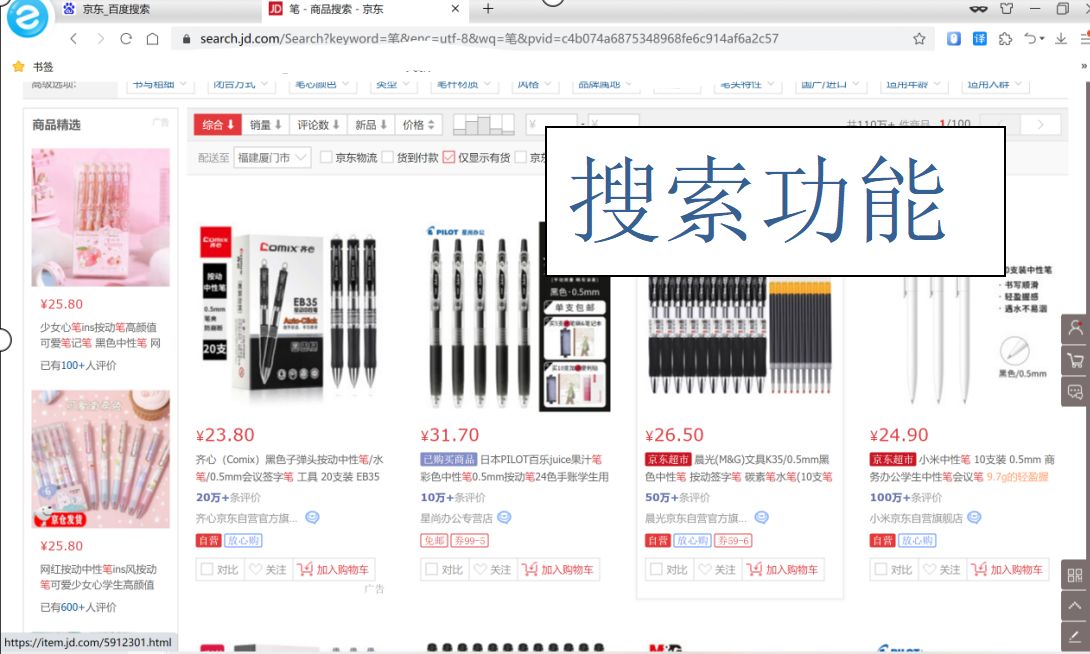
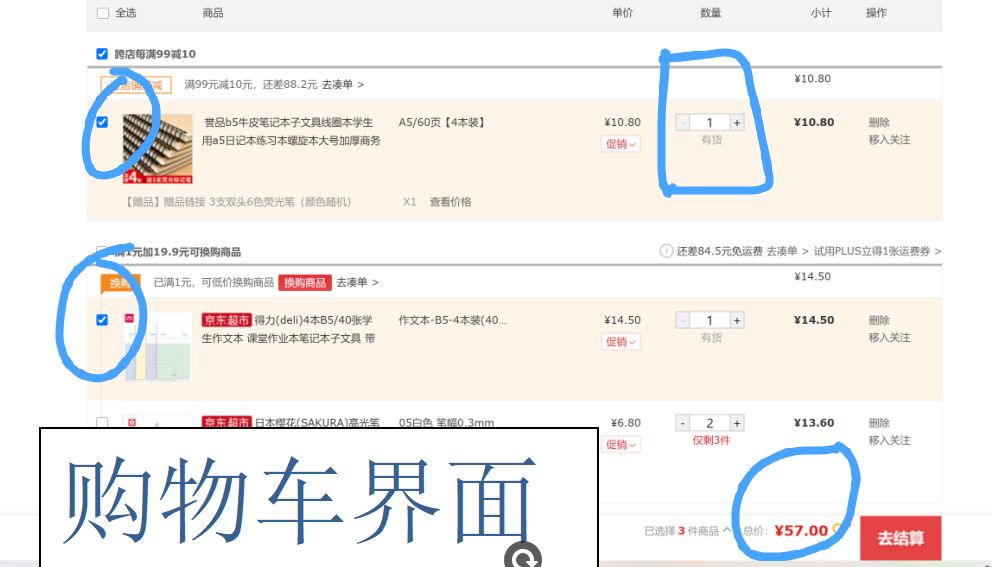
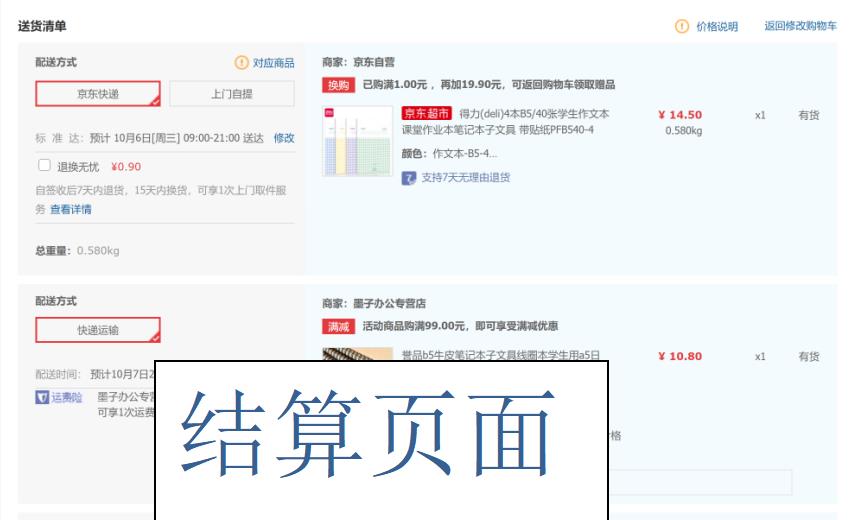
二、功能设计:
系统功能结构图
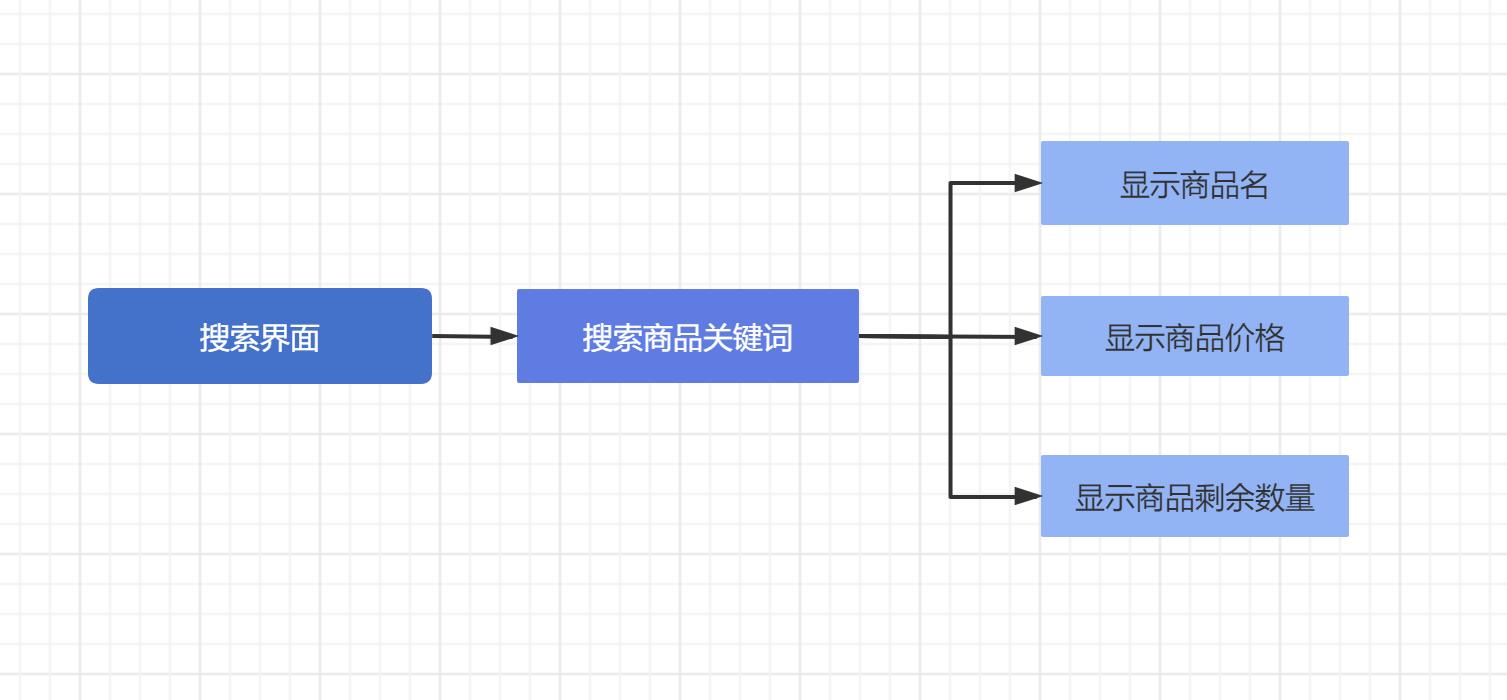
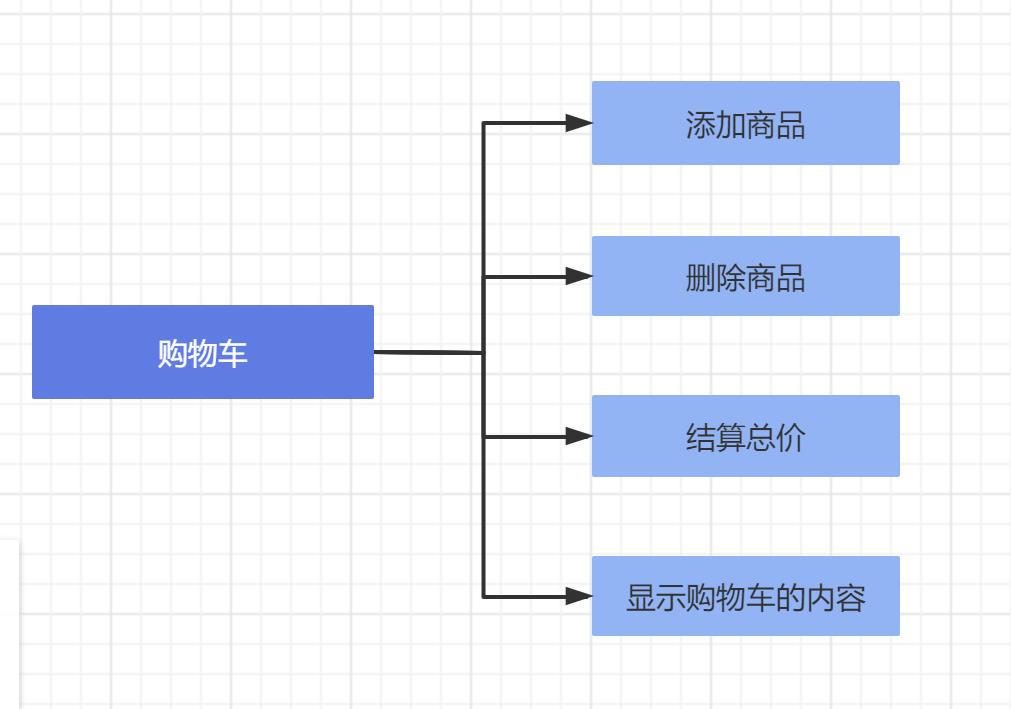
分三大类:操作页面,购物车与商品区
预实现功能:可显示购物车中,所有商品名、商品价格;可显示商品名,价格,数量;可实现选定商品及数量后得到总价。
三、UML类图:
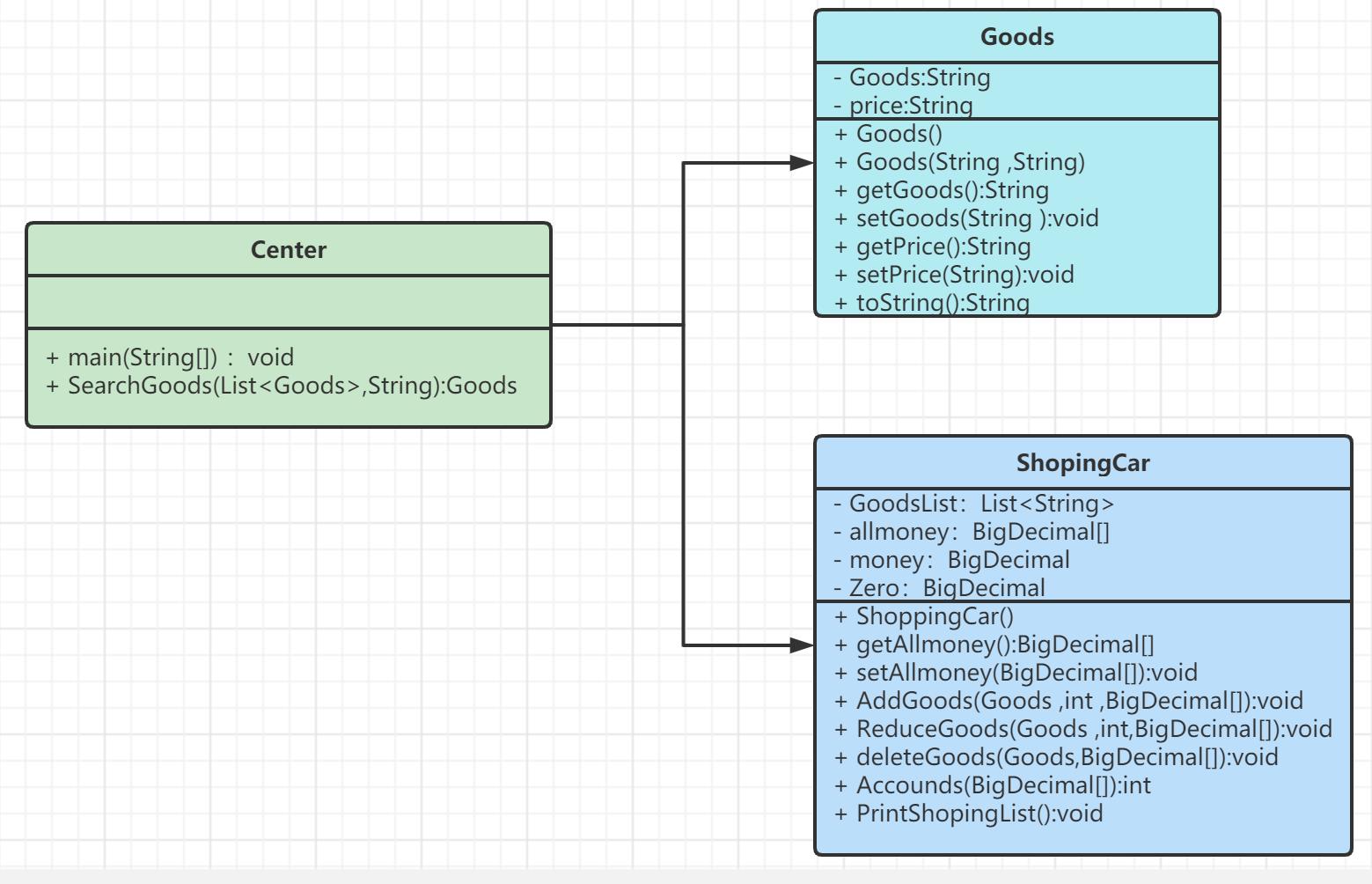
四、主要代码:
Center:
public class Center {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
List<Goods> Goodslist= new ArrayList<>();
BigDecimal[] carbet = new BigDecimal[100];
while(in.hasNextLine()) {
String goodsname = in.nextLine();
String goodsprice = in.nextLine();
if(goodsname.equals("end")) {
break;
}
Goods goods = new Goods(goodsname,goodsprice);
Goodslist.add(goods);
}
ShopingCar car = new ShopingCar();
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.printf("\\t1.Check Goods\\n");
System.out.printf("\\t2.Add ShopingCar\\n");
System.out.printf("\\t3.Check ShopingCar\\n");
System.out.printf("\\t4.Clean ShopingCar\\n");
System.out.printf("\\t5.Reduce ShopingCar\\n");
System.out.printf("\\t6.Accounds ShopingCar\\n");
System.out.printf("\\t7.Exit\\n");
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
while (in.hasNextLine()) {
String s = in.nextLine();
switch (s) {
case "1":
for (Goods goods : Goodslist) {
System.out.println(goods.toString());
}
break;
case "2":
for (Goods goods : Goodslist) {
System.out.println(goods.toString());
}
System.out.println("Please input Goods Name and Goods Count:");
String s1 = in.nextLine();
String s0 = in.nextLine();
int c = Integer.parseInt(s0);
car.AddGoods(SearchGoods(Goodslist,s1), c,carbet);//有点问题
car.PrintShopingList();
System.out.println("Add ShopingCar Sucsessful");
break;
case "3":
car.PrintShopingList();
break;
case "4":
car.PrintShopingList();
System.out.println("Please input Goods Name :");
String s2 = in.nextLine();
car.deleteGoods(SearchGoods(Goodslist,s2),carbet);
System.out.println("Delete ShopingCar Sucsessful");
car.PrintShopingList();
break;
case "5":
car.PrintShopingList();
System.out.println("Please input Goods Name and Goods Count:");
String s3 = in.nextLine();
String s4 = in.nextLine();
int a = Integer.parseInt(s4);
car.ReduceGoods(SearchGoods(Goodslist,s3),a,carbet);
car.PrintShopingList();
break;
case "6":
car.Accounds(carbet);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Exit");
System.exit(0);
break;
}
}
in.close();
}
public static Goods SearchGoods(List<Goods> Goodslist,String s) {
Goods goods2 = new Goods();
for(int j = 0;j<Goodslist.size();j++) {
goods2 = (Goods) Goodslist.get(j);
if(s.equals(goods2.getGoods())) {
break;
}
}
return goods2;
}
}
Shopping:
class ShopingCar {
private static List<String> GoodsList = new ArrayList<String>();//加入购物车的商品名
private static BigDecimal[] allmoney = new BigDecimal[100];
private static BigDecimal money = new BigDecimal(0);//初始化
//private static int count;
private final BigDecimal Zero = new BigDecimal(0);
public static BigDecimal[] getAllmoney() {
return allmoney;
}
public static void setAllmoney(BigDecimal[] allmoney) {
ShopingCar.allmoney = allmoney;
}
public ShopingCar() {
super();
}
public void AddGoods(Goods Goods,int count,BigDecimal[] allmoney){
BigDecimal price = new BigDecimal(Goods.getPrice());
BigDecimal count1 = new BigDecimal(count);
if(GoodsList.isEmpty()) {
GoodsList.add(Goods.getGoods());//若购物车为空,则直接添加
allmoney[0] = price.multiply(count1);//相应数组的位置为该商品的价格总和
}else {
int i = GoodsList.indexOf(Goods.getGoods());
allmoney[i] = allmoney[i].add(price.multiply(count1));
}
}
public void ReduceGoods(Goods Goods,int count,BigDecimal[] allmoney) {
BigDecimal price = new BigDecimal(Goods.getPrice());
BigDecimal count1 = new BigDecimal(count);
int i = GoodsList.indexOf(Goods.getGoods());
if(i<0) {
System.out.println("ShopingCar Haven\'t This Goods!");//前面没找到商品
}else {
if(count1.compareTo(allmoney[i].divide(price)) == -1) {//要删减的数量小于原来购物车商品的数量
allmoney[i] = allmoney[i].subtract(price.multiply(count1));//减少相应商品总价
}else {
System.out.println("Now Clean Your ShopingCar!");
GoodsList.remove(i);
allmoney[i] = Zero;
}
}
}
public void deleteGoods(Goods Goods,BigDecimal[] allmoney) {
int i = GoodsList.indexOf(Goods.getGoods());
if(i<0) {
System.out.println("ShopingCar Haven\'t This Goods!");//前面没找到商品
}else {
GoodsList.remove(i);
allmoney[i] = Zero;
}
}
public void Accounds(BigDecimal[] allmoney) {//计算总价,遍历整个商品价格,计算总价
for (int i = 0; i < allmoney.length; i++) {
money = money.add(allmoney[i]);
}
// return money;
System.out.println(money);
// BigDecimal[] allmoney
}
public void PrintShopingList() {
for(int i = 0;i<GoodsList.size();i++) {
System.out.println("Goods: "+GoodsList.get(i)+" ALlPrice: "+allmoney[i]);
}
}
}
Goods:
public class Goods {
private String Goods;//商品名
private String price;//单价
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String Goods,String price) {
super();
this.Goods = Goods;
this.price = price;
}
public String getGoods() {
return Goods;
}
public void setGoods(String goods) {
this.Goods = goods;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods [Goods=" + Goods + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
五、系统描述
1、商品区可完成所有商品名及其价格的展示
2、购物车界面输入所选商品及其数量后可以得到商品及其总价。
以上是关于购物车的程序设计的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章