从babel编译结果分析class的实现原理
Posted 过鹿人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从babel编译结果分析class的实现原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
示例:
class A { // 属性表达式 prop1 = 1; // get方法 get value() { console.log(\'Getting the current value!\'); return this.prop1; } // set方法 set value(newValue) { console.log(\'Setting the current value!\'); this.prop1 = newValue; } // 箭头函数表达式 arrowFunc = (...args) => { console.log(args); } // constructor constructor(b = 2) { this.prop2 = b; } // 普通函数表达式 Func() { console.log("Func"); } // 静态属性 static prop3 = 3; // 静态普通函数 static staticFunc() { console.log("staticFunc", this); } // 静态箭头函数 static staticArrowFunc = () => { console.log("staticArrowFunc", this); } } const a = new A(3);
使用babel编译成es5的代码,编译结果会生成几个内部函数:
// 类的调用检查,如果调用A不使用new,则会报错 function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) { if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) { throw new TypeError("Cannot call a class as a function"); } } // 属性描述符默认配置为不可枚举 function _defineProperties(target, props) { for (var i = 0; i < props.length; i++) { var descriptor = props[i]; descriptor.enumerable = descriptor.enumerable || false; descriptor.configurable = true; if ("value" in descriptor) descriptor.writable = true; Object.defineProperty(target, descriptor.key, descriptor); } } // 定义原型上的普通函数、静态普通函数、get和set方法
function _createClass(Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) { if (protoProps) _defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps); if (staticProps) _defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps); return Constructor; } // 定义属性到obj上,重新赋值使用defineProperty,第一次赋值直接添加属性 function _defineProperty(obj, key, value) { if (key in obj) { Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { value: value, enumerable: true, configurable: true, writable: true }); } else { obj[key] = value; } return obj; }
类的编译结果:
// A是一个立即执行函数 返回结果是个函数 函数名就是类名 var A = /*#__PURE__*/ (function () { // constructor function A() { // 转化constructor中的默认参数 var b = arguments.length > 0 && arguments[0] !== undefined ? arguments[0] : 2; // 检查类是否使用new执行 _classCallCheck(this, A); // 属性表达式定义到类实例上 _defineProperty(this, "prop1", 1); // 箭头函数表达式定义到类实例上 _defineProperty(this, "arrowFunc", function () { // 这个for循环是转换...args,遍历arguments,将每一项赋值给args对象 for ( var _len = arguments.length, args = new Array(_len), _key = 0; _key < _len; _key++ ) { args[_key] = arguments[_key]; } console.log(args); }); this.prop2 = b; } _createClass( A, [ {// get和set方法 key: "value", get: function get() { console.log("Getting the current value!"); return this.prop1; }, set: function set(newValue) { console.log("Setting the current value!"); this.prop1 = newValue; } }, {// 普通函数表达式 key: "Func", value: function Func() { console.log("Func"); } } ], [ {// 静态普通函数 key: "staticFunc", value: function staticFunc() { console.log("staticFunc", this); } } ] ); return A; })(); // 静态属性定义到类上 _defineProperty(A, "prop3", 3); // 静态箭头函数定义到类上 _defineProperty(A, "staticArrowFunc", function () { console.log("staticArrowFunc", A); }); var a = new A(3);
下图可描述整个编译结果:
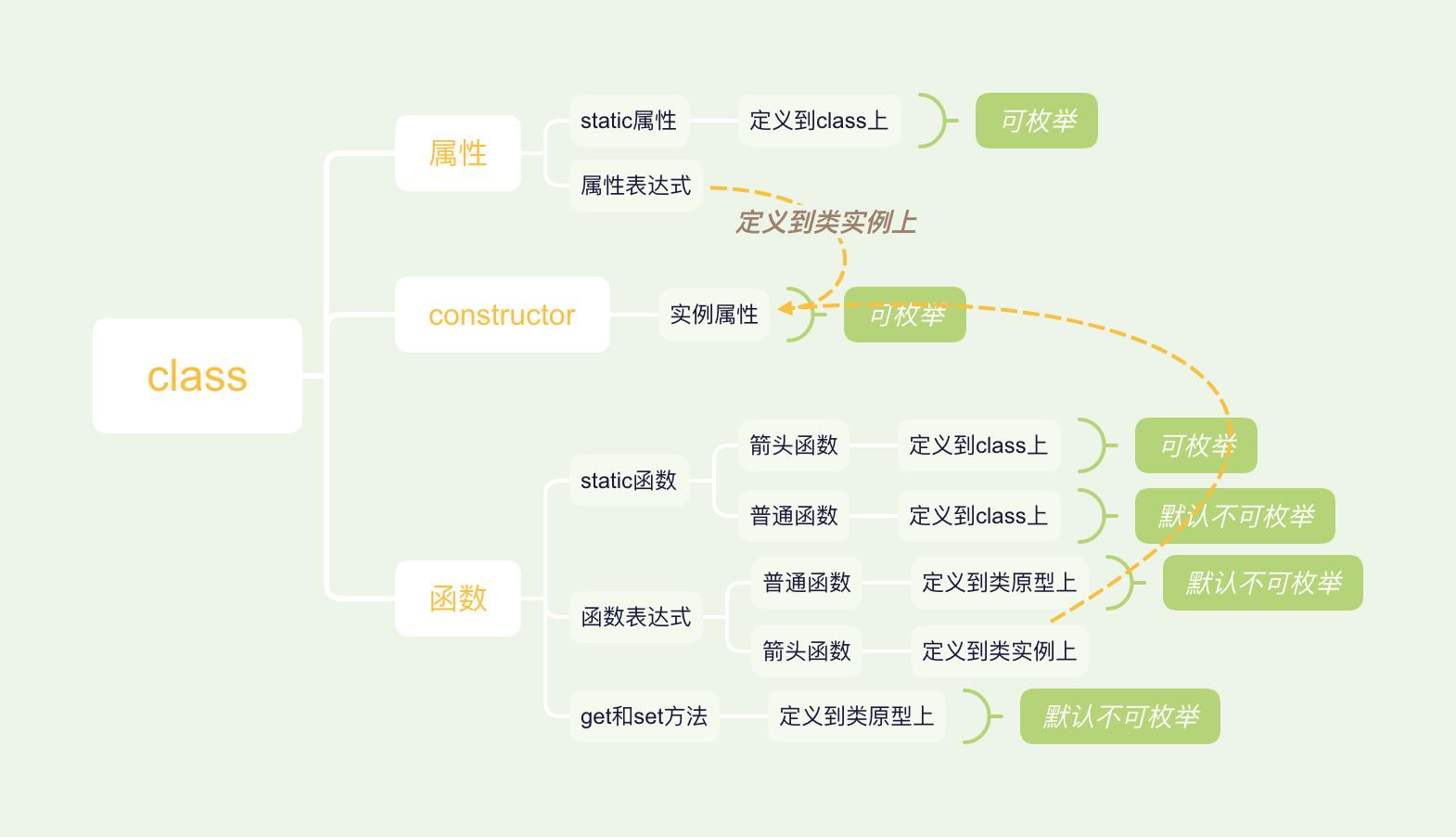
需要注意的是:
- 类原型上的方法、类的静态方法、类的get和set方法默认是不可枚举的
- 类实例上的方法和属性、类的静态箭头函数是可枚举的
之后再出一章class继承的相关内容
以上是关于从babel编译结果分析class的实现原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章