LeetCode剑指Offer刷题总结
Posted GaoYuan206
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode剑指Offer刷题总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题号为LeetCode剑指Offer题库中的题号。网址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problem-list/xb9nqhhg/
合并两个排序链表25
本题思路非常简单,两个链表元素依次比较,压入新链表即可,但有易错点。
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode head = res;
int flag = 0;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
res.next = l1;
res = res.next;
l1 = l1.next;
}
else{
res.next = l2;
res = res.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if(l1==null){
res.next = l2;
}
else if(l2 == null){
res.next = l1;
}
return head.next;
}
为何要写成.next,因为本题给的ListNode不能无参构造,而且试想以下代码:
res.val = l1.val;
res.next = new ListNode(0);
res = res.next;
l1 = l1.next;
//这是我最初写在第一个if中的
这样写的话while执行完毕后,肯定需要写
if(l1==null){ res = l2;}
这样就会发生错误,因为当前res为需要赋新值的那个节点,而且已经被上一个节点连接,当前值为0,只能改变值,如果像上面这一行的话,只是res的引用改变,而实际上需要赋值的那个节点失踪了。
而用.next可以保证,我们操作赋值之后,会停留在赋值完的这个节点,每次如果需要赋值,就连接新节点,不会乱。
树的子结构26
题解如下:
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
return (A!=null && B!=null) && (judge(A,B) || isSubStructure(A.left,B) || isSubStructure(A.right,B));
//注意这里的顺序,(A!=null && B!=null)只是附加条件根节点不为空
}
boolean judge(TreeNode A,TreeNode B){
if(B==null) return true;
if(A==null || A.val!=B.val) return false;
return judge(A.left,B.left) && judge(A.right,B.right);
}
}
算法思想比较容易思考,要仔细体会代码结构。
二叉树的镜像27
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
//if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return root;
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(temp);
return root;
}
这道题的思路也是非常简单,只需要每次交换每个节点的左节点和右节点的指针。
但是该部分需要注意的是,java中的值传递和引用传递相关知识。
此外,还可以利用辅助栈进行BFS。
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode head = root;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>(){{push(head);}}; //这里head改为root会异常,需要Push一个具有final性质的变量
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
root = stack.pop();
if(root.left != null) stack.push(root.left);
if(root.right != null) stack.push(root.right);
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
return head;
}
对于上方的stack初始化,外层的 {} 定义了一个 LinkedList 的匿名内部类。内层的 {} 的定义了一个实例初始化代码块。 这个代码块在初始化内部类时执行。所以这里相当于定义了一个匿名内部类,并使用 add 添加元素来初始化。
这种方式有几个缺点:
- 使用匿名内部类,会有效率上的损失。当然在大多数情况下,这点效率都是可接受的。
- 静态内部类持有所在外部类的引用。如果需要将 List 返回给到其他地方使用,可能造成内存泄漏。
具体可参考这个帖子匿名内部类中局部变量为什么要用final修饰
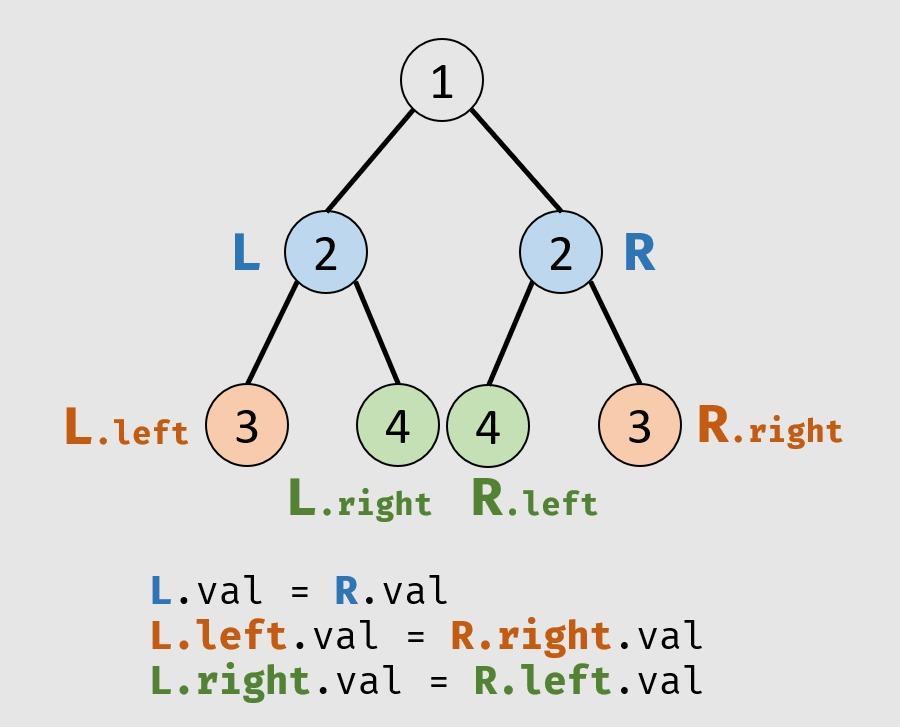
对称的二叉树28
这道题的思路很巧妙,需要注意一下,如果想不到,算法就会很麻烦
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? true : recur(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean recur(TreeNode L,TreeNode R){
if(L==null && R == null) return true;
if(L==null || R==null || L.val != R.val) return false;
return recur(L.left,R.right) && recur(L.right,R.left);
}
}
顺时针打印矩阵29
可将矩阵每一层外围看作一次遍历,思想还是很简单的,可以看一下实现,空间复杂度低。
class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
return new int[0];
int len = matrix.length;
int count = 0;
int len2 = matrix[0].length;
int[] ans = new int[len*len2];
int top = 0,left =0;
int right = len2-1, bottom = len-1;
while(left<=right && top <= bottom){
for(int i = top,j = left ; j <= right ; j++){
ans[count++]=matrix[i][j];
}
for(int i = top+1,j = right ; i <= bottom ; i++){
ans[count++]=matrix[i][j];
}
if(top<bottom && left<right){
for(int i = bottom,j = right-1 ; j > left ; j--){
ans[count++]=matrix[i][j];
}
for(int i = bottom , j = left ; i > top ; i--){
ans[count++]=matrix[i][j];
}
}
top++;
bottom--;
left++;
right--;
}
return ans;
}
}
值得注意的是,while中有4个循环,其中后两个需要判定一下,否则容易发生数组越界(最后只剩下一列的时候会出现越界)
包含min函数的栈30
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> A,B;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
A = new Stack<>();
B = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
A.push(x);
if(B.empty() || B.peek()>=x)
B.push(x);
}
public void pop() {
if(!B.empty() && A.peek().equals(B.peek()))
B.pop();
A.pop();
}
public int top() {
return A.peek();
}
public int min() {
return B.peek();
}
}
这道题中需要注意的是,Stack中存储的是Integer包装类,如果直接用==则会在[-128,-127]范围之外时比较错误,之内才会比较正确,equal重写过则不会出现该问题。
栈的压入,弹出序列31
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Deque<Integer> p1 = new LinkedList<>();
int len = pushed.length;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len ; i++){
while(p1.size()!=0 && p1.peek() == popped[j]){
p1.pop();
j++;
}
p1.push(pushed[i]);
while(p1.size()!=0 && p1.peek() == popped[j]){
p1.pop();
j++;
}
}
if(j != len)
return false;
return true;
}
}
本题中没有复杂思想,写了两个while进行判定。
参考答案之后精简算法:
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> p1 = new Stack<>();
int len = pushed.length;
int j = 0;
for(int obj : pushed){
p1.push(obj);
while(!p1.empty() && p1.peek()==popped[j]){
p1.pop();
j++;
}
}
return p1.empty();
}
}
从上到下打印二叉树32
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null)
return new int[0];
deque.add(root);
list.add(root.val);
while(deque.size()!=0){
TreeNode tr = deque.poll();
if(tr.left!=null){
deque.add(tr.left);
list.add(tr.left.val);
}
if(tr.right!=null){
deque.add(tr.right);
list.add(tr.right.val);
}
}
int[] ans = new int[list.size()];
int j = 0;
for(Integer i : list){
ans[j++] = i;
}
return ans;
}
}
思想:用队列进行BFS,遍历树的各个节点,存入一个数组。
这里可以注意一下,Deque既可以表示队列也可以表示栈,但是deque(LinkedList)中没有empty(),需要用size()或者提出元素判断。(JDK1.8)
从上到下打印二叉树32 -2
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return ans;
}
deque.add(root);
while((list = pollAll(deque)) != null){
ans.add(list);
}
return ans;
}
public List<Integer> pollAll(Deque<TreeNode> deque){
TreeNode tr;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int n = deque.size();
if(n==0)
return null;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
tr = deque.poll();
list.add(tr.val);
if(tr.left!=null){
deque.add(tr.left);
}
if(tr.right!=null){
deque.add(tr.right);
}
}
return list;
}
}
本题中需要注意的地方有:
deque作队列时,push和add一定要分清楚使用条件,不然会导致取元素顺序混乱。本题思想还是简单的,没有写最简形式。
复杂链表的复制35
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
Node temp = head;
Map<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
while(temp != null){
map.put(temp,new Node(temp.val));
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = head;
while(temp != null){
map.get(temp).next = map.get(temp.next);
map.get(temp).random = map.get(temp.random);
temp = temp.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
该题只是链表结构多了一个random指针,利用Map结构可以有效解决该问题。思路不难。
以上是关于LeetCode剑指Offer刷题总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章