每日一题||二叉树练习
Posted 一只小跃跃
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了每日一题||二叉树练习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
P1305:新二叉树
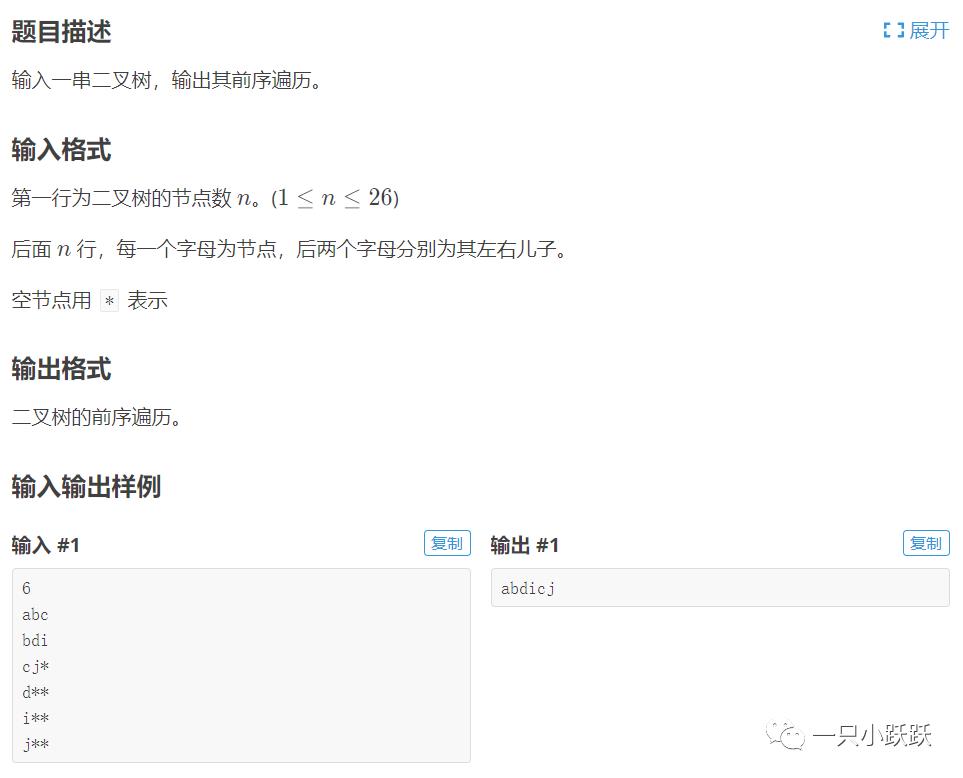
程序代码:
using namespace std;struct Node{char left;char right;}tree[1000];void dfs(char root){cout<<root;if(tree[root].left!='*'){dfs(tree[root].left);//左儿子做根继续}if(tree[root].right!='*'){dfs(tree[root].right);//右儿子做根继续}}int main(){int n;char temp,root;cin>>n;//第一步:构建树for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>temp;if(i==1){root=temp;}cin>>tree[temp].left>>tree[temp].right;}//第二步:遍历树dfs(root);return 0;}
P4913:二叉树深度
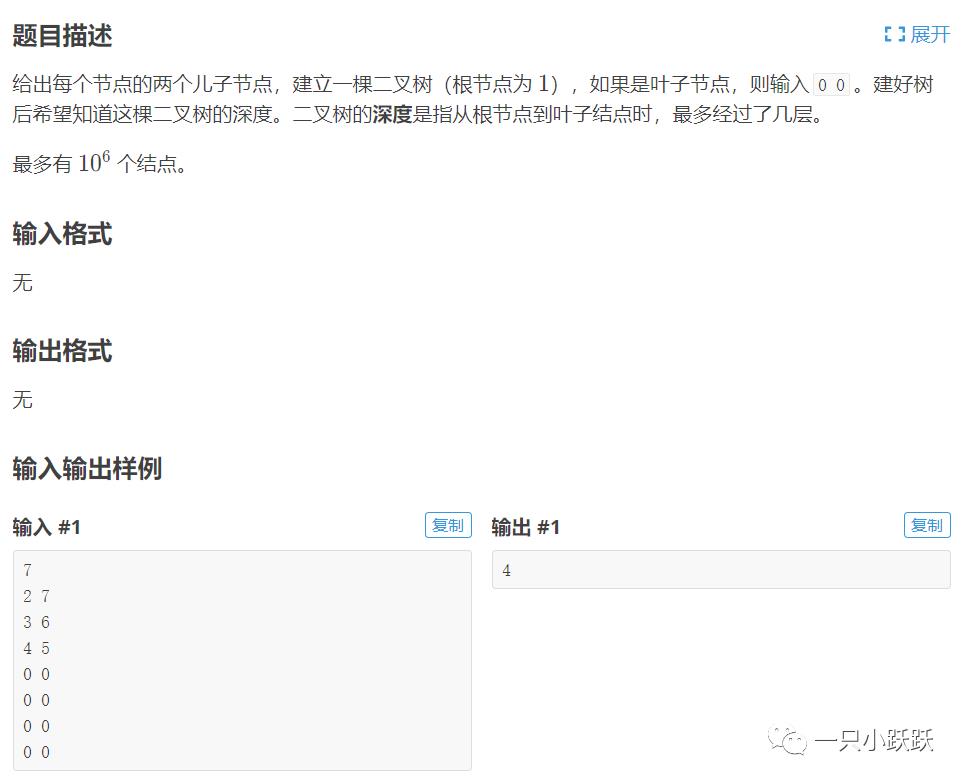
程序代码:
using namespace std;const int N=1e6+5;struct Node{int left;int right;}tree[N];int count;void dfs(int root,int step){//前序遍历向下搜索if(root==0){return ;}count=max(count,step);dfs(tree[root].left,step+1);dfs(tree[root].right,step+1);}int main(){int n;cin>>n;//第一步:构建树for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>tree[i].left>>tree[i].right;}//第二步:遍历树dfs(1,1);cout<<count;return 0;}
P1030:求先序排列
程序代码:方式一
using namespace std;//使用指针接收两个字符串char *in=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));//指向这个空间的地址char *post=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));struct Node{char data;Node *left,*right;};Node* build(int post_l,int post_r,int in_l,int in_r){if(post_l>post_r){return NULL;}Node *root=new Node;root->data=post[post_r];//后续遍历最后一个就是根int k;for( k=in_l;k<in_r;k++){if(in[k]==post[post_r]){break;}}//前序遍历:1 2 3 4 5 6 7//中序遍历:4 3 5 2 6 1 7//后续遍历:4 5 3 6 2 7 1int num=k-in_l;//中序遍历特点:根的左边是左子树,根的右边是右子树root->left=build(post_l,post_l+num-1,in_l,k);//后序遍历特点:root->right=build(post_l+num,post_r-1,k+1,in_r);return root;}//前序遍历函数void pre_order(Node *root){if(root==NULL){return ;}cout<<root->data;pre_order(root->left);pre_order(root->right);}int main(){cin>>in>>post;// scanf("%s",in);// scanf("%s",post);int len=strlen(in);//创造一棵树Node *root=build(0,len-1,0,len-1);pre_order(root);//前序遍历return 0;}
程序代码:方式二
using namespace std;struct Node{char data;Node *left,*right;};Node* build(char* in,char* post,int length){if(length==0){return NULL;}Node * root=new Node;root->data=*(post+length-1);int k=0;for(;k<length;k++){if(in[k]==root->data){break;}}cout<<root->data;root->left=build(in,post,k);root->right=build(in+k+1,post+k,length-(k+1));return root;}int main(){char *in=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));//动态开辟空间char *post=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));;cin>>in>>pre;int len=strlen(in);build(in,post,len);return 0;}
P1827:美国血统
程序代码:
using namespace std;struct Node{char data;Node *left,*right;};Node* build(char* in,char* pre,int length){if(length==0){return NULL;}Node * root=new Node;root->data=*pre;int k=0;for(;k<length;k++){if(in[k]==*pre){break;}}root->left=build(in,pre+1,k);root->right=build(in+k+1,pre+k+1,length-(k+1));cout<<root->data;return root;}int main(){char *in=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));//动态开辟空间char *pre=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));;cin>>in>>pre;int len=strlen(in);build(in,pre,len);return 0;}
以上是关于每日一题||二叉树练习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章