深度学习和目标检测系列教程 8-300:目标检测常见的标注工具LabelImg和将xml文件提取图像信息
Posted 刘润森!
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深度学习和目标检测系列教程 8-300:目标检测常见的标注工具LabelImg和将xml文件提取图像信息相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
@Author:Runsen
图像标注主要用于创建数据集进行图片的标注。本篇博客将推荐一款非常实用的图片标注工具LabelImg,重点介绍其安装使用过程。如果想简单点,请直接下载打包版(下载地址见结尾),无需编译,直接打开即可!
感谢原作者对Github的贡献,博主发现软件已经更新,可以关注最新版本。这个工具是一个用 Python 和 Qt 编写的完整的图形界面。最有意思的是,它的标注信息可以直接转换成XML文件,这和PASCAL VOC和ImageNet使用的XML是一样的。
附注。作者在5月份更新了代码,现在最新版本号是1.3.0,博主亲测,源码在Windows 10和Ubuntu 16.04上正常运行。
具体的安装查看Github教程:https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme/#installation
在原作者的github下载源码:https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg
。解压名为labelImg-master的文件夹,进入当前目录的命令行窗口,输入如下语句依次打开软件。
python labelImg.py

具体使用
-
修改默认的XML文件保存位置,使用快捷键“Ctrl+R”,更改为自定义位置,这里的路径一定不能包含中文,否则不会保存。
-
使用notepad++打开源文件夹中的data/predefined_classes.txt,修改默认分类,如person、car、motorcycle这三个分类。
-
“打开目录”打开图片文件夹,选择第一张图片开始标注,用“创建矩形框”或“Ctrl+N”启动框,点击结束框,双击选择类别。完成一张图片点击“保存”保存后,XML文件已经保存到本地了。单击“下一张图片”转到下一张图片。
-
贴标过程可以随时返回修改,保存的文件会覆盖上一个。
-
完成注解后,打开XML文件,发现和PASCAL VOC格式一样。
将xml文件提取图像信息
下面列举如何将xml文件提取图像信息,图片保存到image文件夹,xml保存标注内容。图片和标注的文件名字一样的。
下面是images图片中的一个。
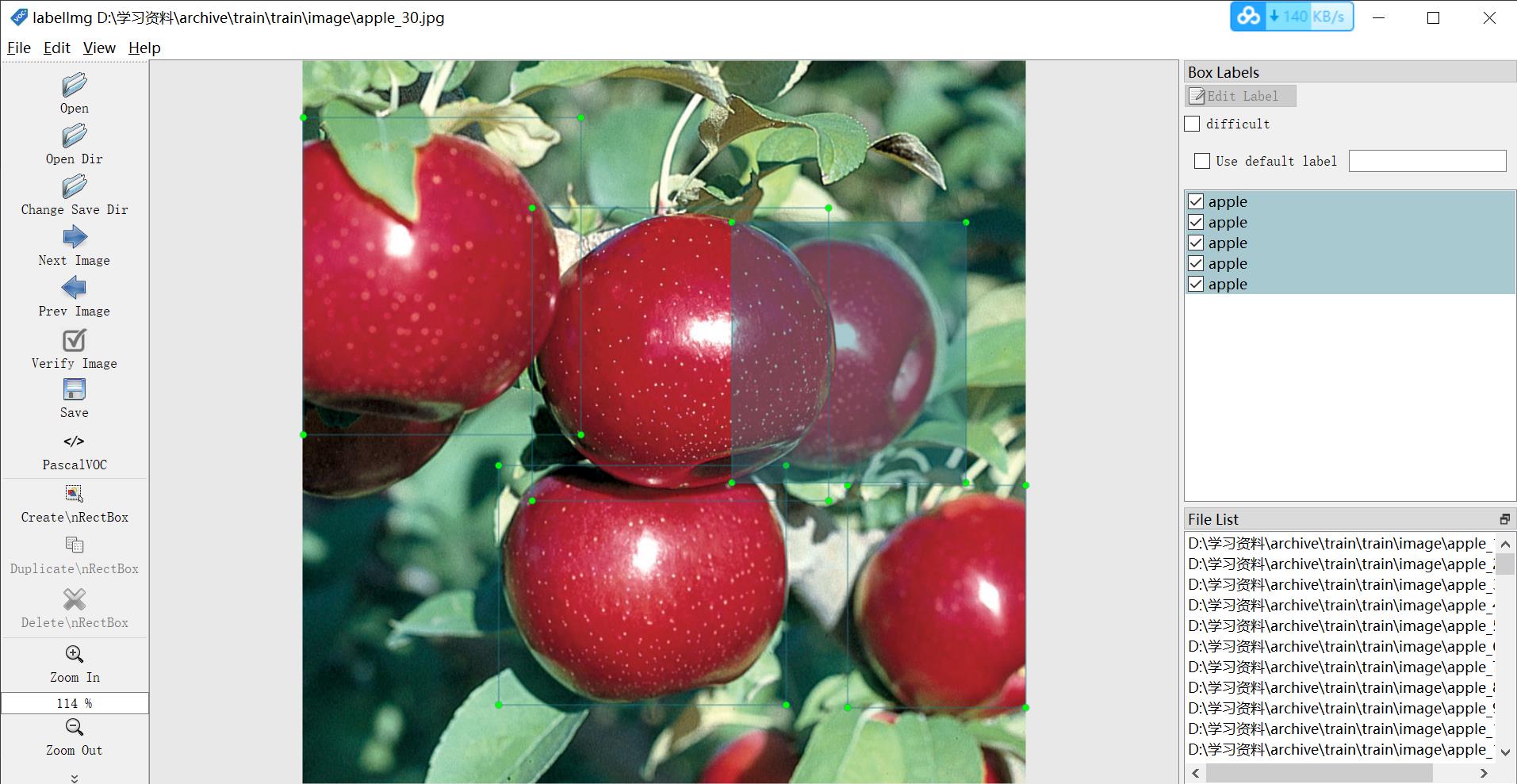
下面是对应的xml文件。
<annotation>
<folder>train</folder>
<filename>apple_30.jpg</filename>
<path>C:\\tensorflow1\\models\\research\\object_detection\\images\\train\\apple_30.jpg</path>
<source>
<database>Unknown</database>
</source>
<size>
<width>800</width>
<height>800</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented>
<object>
<name>apple</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>254</xmin>
<ymin>163</ymin>
<xmax>582</xmax>
<ymax>487</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>apple</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>217</xmin>
<ymin>448</ymin>
<xmax>535</xmax>
<ymax>713</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>apple</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>603</xmin>
<ymin>470</ymin>
<xmax>800</xmax>
<ymax>716</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>apple</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>468</xmin>
<ymin>179</ymin>
<xmax>727</xmax>
<ymax>467</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>apple</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>1</xmin>
<ymin>63</ymin>
<xmax>308</xmax>
<ymax>414</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
将xml文件提取图像信息,主要使用xml和opencv,基于torch提取,代码比较凌乱。
import os
import numpy as np
import cv2
import torch
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import albumentations as A
from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensorV2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from xml.etree import ElementTree as et
from torchvision import transforms as torchtrans
# defining the files directory and testing directory
train_image_dir = 'train/train/image'
train_xml_dir = 'train/train/xml'
# test_image_dir = 'test/test/image'
# test_xml_dir = 'test/test/xml'
class FruitImagesDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, image_dir, xml_dir, width, height, transforms=None):
self.transforms = transforms
self.image_dir = image_dir
self.xml_dir = xml_dir
self.height = height
self.width = width
# sorting the images for consistency
# To get images, the extension of the filename is checked to be jpg
self.imgs = [image for image in os.listdir(self.image_dir)
if image[-4:] == '.jpg']
self.xmls = [xml for xml in os.listdir(self.xml_dir)
if xml[-4:] == '.xml']
# classes: 0 index is reserved for background
self.classes = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_name = self.imgs[idx]
image_path = os.path.join(self.image_dir, img_name)
# reading the images and converting them to correct size and color
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB).astype(np.float32)
img_res = cv2.resize(img_rgb, (self.width, self.height), cv2.INTER_AREA)
# diving by 255
img_res /= 255.0
# annotation file
annot_filename = img_name[:-4] + '.xml'
annot_file_path = os.path.join(self.xml_dir, annot_filename)
boxes = []
labels = []
tree = et.parse(annot_file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# cv2 image gives size as height x width
wt = img.shape[1]
ht = img.shape[0]
# box coordinates for xml files are extracted and corrected for image size given
for member in root.findall('object'):
labels.append(self.classes.index(member.find('name').text))
# bounding box
xmin = int(member.find('bndbox').find('xmin').text)
xmax = int(member.find('bndbox').find('xmax').text)
ymin = int(member.find('bndbox').find('ymin').text)
ymax = int(member.find('bndbox').find('ymax').text)
xmin_corr = (xmin / wt) * self.width
xmax_corr = (xmax / wt) * self.width
ymin_corr = (ymin / ht) * self.height
ymax_corr = (ymax / ht) * self.height
boxes.append([xmin_corr, ymin_corr, xmax_corr, ymax_corr])
# convert boxes into a torch.Tensor
boxes = torch.as_tensor(boxes, dtype=torch.float32)
# getting the areas of the boxes
area = (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) * (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0])
# suppose all instances are not crowd
iscrowd = torch.zeros((boxes.shape[0],), dtype=torch.int64)
labels = torch.as_tensor(labels, dtype=torch.int64)
target = {}
target["boxes"] = boxes
target["labels"] = labels
target["area"] = area
target["iscrowd"] = iscrowd
# image_id
image_id = torch.tensor([idx])
target["image_id"] = image_id
if self.transforms:
sample = self.transforms(image=img_res,
bboxes=target['boxes'],
labels=labels)
img_res = sample['image']
target['boxes'] = torch.Tensor(sample['bboxes'])
return img_res, target
def __len__(self):
return len(self.imgs)
# function to convert a torchtensor back to PIL image
def torch_to_pil(img):
return torchtrans.ToPILImage()(img).convert('RGB')
def plot_img_bbox(img, target):
# plot the image and bboxes
fig, a = plt.subplots(1, 1)
fig.set_size_inches(5, 5)
a.imshow(img)
for box in (target['boxes']):
x, y, width, height = box[0], box[1], box[2] - box[0], box[3] - box[1]
rect = patches.Rectangle((x, y),
width, height,
linewidth=2,
edgecolor='r',
facecolor='none')
# Draw the bounding box on top of the image
a.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
def get_transform(train):
if train:
return A.Compose([
A.HorizontalFlip(0.5),
# ToTensorV2 converts image to pytorch tensor without div by 255
ToTensorV2(p=1.0)
], bbox_params={'format': 'pascal_voc', 'label_fields': ['labels']})
else:
return A.Compose([
ToTensorV2(p=1.0)
], bbox_params={'format': 'pascal_voc', 'label_fields': ['labels']})
dataset = FruitImagesDataset(train_image_dir,train_xml_dir, 480, 480, transforms= get_transform(train=True))
print(len(dataset))
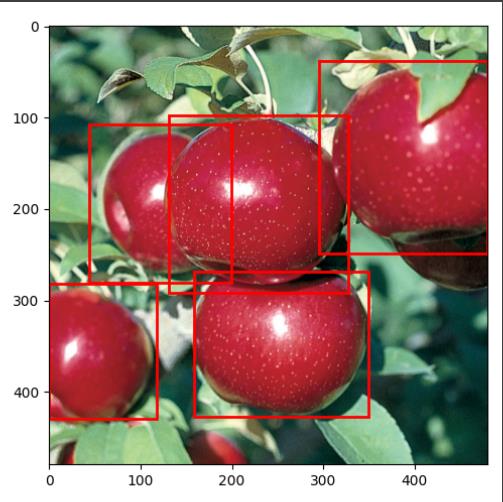
# getting the image and target for a test index. Feel free to change the index.
img, target = dataset[29]
print(img.shape, '\\n', target)
plot_img_bbox(torch_to_pil(img), target)
输出如下:
torch.Size([3, 480, 480])
{'boxes': tensor([[130.8000, 97.8000, 327.6000, 292.2000],
[159.0000, 268.8000, 349.8000, 427.8000],
[ 0.0000, 282.0000, 118.2000, 429.6000],
[ 43.8000, 107.4000, 199.2000, 280.2000],
[295.2000, 37.8000, 479.4000, 248.4000]]), 'labels': tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0]), 'area': tensor([38257.9258, 30337.2012, 17446.3223, 26853.1270, 38792.5195]), 'iscrowd': tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0]), 'image_id': tensor([29])}
下载地址
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1QZDgeYTHyAlD2xhtJqZ-Yw
提取码:srjn
以上是关于深度学习和目标检测系列教程 8-300:目标检测常见的标注工具LabelImg和将xml文件提取图像信息的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章