数据结构&算法-图最短路径
Posted 彩色墨水
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构&算法-图最短路径相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
图最短路径介绍
对于网图来说,最短路径,是指两顶点之间经过的边上权值之和最少路径,并且我们称路径上的第一个顶点是源点,最后一个顶点终点。
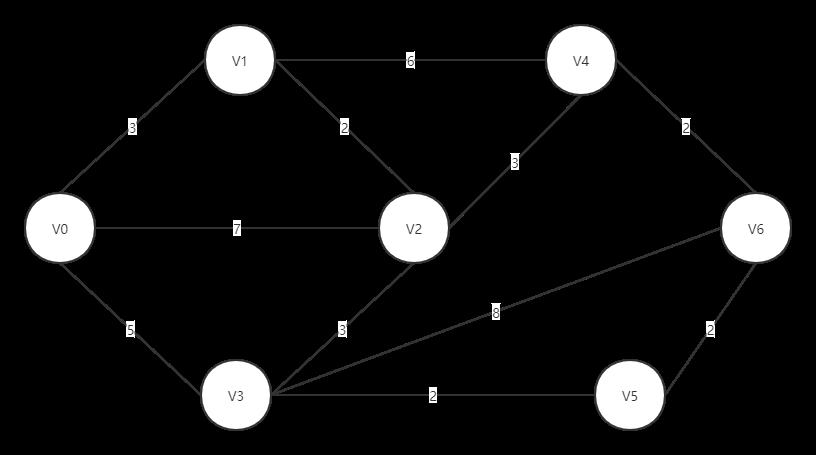
迪杰斯特拉算法运行结果
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// int[,] aaa = new int[4, 3];
LedByMatrix ledByMatrix = new LedByMatrix(7, new int[11, 3] { { 0, 1, 3 },{ 0, 2, 7 },{ 0, 3, 5 },
{ 1, 2, 2 },{ 2, 3, 3 },{ 1, 4, 6 },
{ 2, 4, 3 },{ 3, 6, 8 },{ 3, 5, 2 },
{ 5, 6, 2 },{ 4, 6, 2},});
Dijkstra dijkstra = new Dijkstra();
dijkstra.GetDijkstraPath(ledByMatrix.G);
//Floyd floyd = new Floyd();
//floyd.GetFloydPath(ledByMatrix.G);
}
/// <summary>
/// 邻接矩阵
/// </summary>
class LedByMatrix
{
int[,] _g;
int INFINITY = 65535;
public int[,] G { get => _g; }
/// <summary>
/// 初始化邻接矩阵
/// </summary>
/// <param name="vertexCount">顶点数</param>
/// <param name="arr">A-B及其权值,{1,3,7}表示V1到V3的权值是7</param>
public LedByMatrix(int vertexCount, int[,] arr)
{
_g = new int[vertexCount, vertexCount];
for (int i = 0; i < _g.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int J = 0; J < _g.GetLength(1); J++)
{
_g[i, J] = INFINITY;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++)
{
_g[arr[i, 0], arr[i, 1]] = arr[i, 2];
_g[arr[i, 1], arr[i, 0]] = arr[i, 2];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 打印邻接矩阵
/// </summary>
public void PrintLedByMatrix()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _g.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < _g.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(_g[i, j] + ",");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 迪杰斯特拉算法
/// </summary>
class Dijkstra
{
//初始化数据,到每个顶点的最短路径权值初始化
//求V0到某个顶点的最短路径
bool[] final;//V0到该点的最小路径已经求的
int[] pathMatirx;//到该点的最短路径前驱点
int[] shortPathTable;//到该点的最短路径权值
int INFINITY = 65535;
/// <summary>
/// 求最短路径
/// </summary>
/// <param name="G"></param>
public void GetDijkstraPath(int[,] G)
{
final = new bool[G.GetLength(0)];
pathMatirx = new int[G.GetLength(0)];
shortPathTable = new int[G.GetLength(0)];
for (int j = 0; j < G.GetLength(0); j++)
{
shortPathTable[j] = INFINITY;
final[j] = false;
pathMatirx[j] = 0;
shortPathTable[j] = G[0, j];
}
final[0] = true;
shortPathTable[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < G.GetLength(0); i++)
{
int min = INFINITY;
int k = 0;
for (int w = 0; w < G.GetLength(0); w++)
{
if (!final[w] && shortPathTable[w] < min)//还未确认的顶点中离V0最短的那个
{
min = shortPathTable[w];
k = w;
}
}
final[k] = true;
for (int w = 0; w < G.GetLength(0); w++)
{
if (!final[w] && min + G[k, w] < shortPathTable[w])//找凡是还没确认的顶点中,如果经过K顶点的路径比现在的路径短的话,更新
{
shortPathTable[w] = min + G[k, w];
pathMatirx[w] = k;//确认前驱点
}
}
}
PrintShortestPath();
}
/// <summary>
/// 打印最短路径
/// </summary>
public void PrintShortestPath()
{
for (int i = 0; i < shortPathTable.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(pathMatirx[i] + ",");
//Console.Write(shortPathTable[i] + ",");
}
}
}
弗洛伊德运行结果
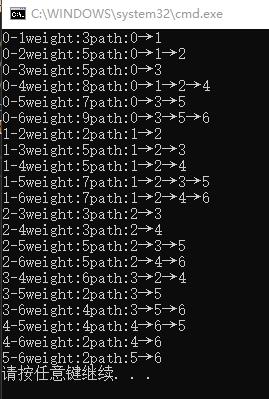
/// <summary>
/// 弗洛伊德算法
/// </summary>
class Floyd
{
int[,] pathmatirx;
int[,] shortPathTable;
int numV;
public void GetFloydPath(int[,] G)
{
numV = G.GetLength(0);
pathmatirx = new int[G.GetLength(0), G.GetLength(1)];
shortPathTable = new int[G.GetLength(0), G.GetLength(1)];
for (int i = 0; i < pathmatirx.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < pathmatirx.GetLength(1); j++)
{
pathmatirx[i, j] = j;
shortPathTable[i, j] = G[i, j];
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < numV; k++)
{
for (int v = 0; v < numV; v++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < numV; w++)
{
if (shortPathTable[v, w] > shortPathTable[v, k] + shortPathTable[k, w])
{
shortPathTable[v, w] = shortPathTable[v, k] + shortPathTable[k, w];
pathmatirx[v, w] = pathmatirx[v, k];
}
}
}
}
PrintPath();
}
void PrintPath()
{
for (int v = 0; v < numV; v++)
{
for (int w = v + 1; w < numV; w++)
{
Console.Write("{0}-{1}weight:{2}", v, w, shortPathTable[v, w]);
int k = pathmatirx[v, w];
Console.Write("path:{0}", v);
while (k != w)
{
Console.Write("→{0}", k);
k = pathmatirx[k, w];
}
Console.Write("→{0}", w);
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
以上是关于数据结构&算法-图最短路径的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章